Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base

Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples
Published on November 8, 2019 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics . It is most often used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses, that arise from theories.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o ) and (H a or H 1 ).
- Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test .
- Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
- Present the findings in your results and discussion section.
Though the specific details might vary, the procedure you will use when testing a hypothesis will always follow some version of these steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: state your null and alternate hypothesis, step 2: collect data, step 3: perform a statistical test, step 4: decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis, step 5: present your findings, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about hypothesis testing.
After developing your initial research hypothesis (the prediction that you want to investigate), it is important to restate it as a null (H o ) and alternate (H a ) hypothesis so that you can test it mathematically.
The alternate hypothesis is usually your initial hypothesis that predicts a relationship between variables. The null hypothesis is a prediction of no relationship between the variables you are interested in.
- H 0 : Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a : Men are, on average, taller than women.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
For a statistical test to be valid , it is important to perform sampling and collect data in a way that is designed to test your hypothesis. If your data are not representative, then you cannot make statistical inferences about the population you are interested in.
There are a variety of statistical tests available, but they are all based on the comparison of within-group variance (how spread out the data is within a category) versus between-group variance (how different the categories are from one another).
If the between-group variance is large enough that there is little or no overlap between groups, then your statistical test will reflect that by showing a low p -value . This means it is unlikely that the differences between these groups came about by chance.
Alternatively, if there is high within-group variance and low between-group variance, then your statistical test will reflect that with a high p -value. This means it is likely that any difference you measure between groups is due to chance.
Your choice of statistical test will be based on the type of variables and the level of measurement of your collected data .
- an estimate of the difference in average height between the two groups.
- a p -value showing how likely you are to see this difference if the null hypothesis of no difference is true.
Based on the outcome of your statistical test, you will have to decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
In most cases you will use the p -value generated by your statistical test to guide your decision. And in most cases, your predetermined level of significance for rejecting the null hypothesis will be 0.05 – that is, when there is a less than 5% chance that you would see these results if the null hypothesis were true.
In some cases, researchers choose a more conservative level of significance, such as 0.01 (1%). This minimizes the risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis ( Type I error ).
The results of hypothesis testing will be presented in the results and discussion sections of your research paper , dissertation or thesis .
In the results section you should give a brief summary of the data and a summary of the results of your statistical test (for example, the estimated difference between group means and associated p -value). In the discussion , you can discuss whether your initial hypothesis was supported by your results or not.
In the formal language of hypothesis testing, we talk about rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. You will probably be asked to do this in your statistics assignments.
However, when presenting research results in academic papers we rarely talk this way. Instead, we go back to our alternate hypothesis (in this case, the hypothesis that men are on average taller than women) and state whether the result of our test did or did not support the alternate hypothesis.
If your null hypothesis was rejected, this result is interpreted as “supported the alternate hypothesis.”
These are superficial differences; you can see that they mean the same thing.
You might notice that we don’t say that we reject or fail to reject the alternate hypothesis . This is because hypothesis testing is not designed to prove or disprove anything. It is only designed to test whether a pattern we measure could have arisen spuriously, or by chance.
If we reject the null hypothesis based on our research (i.e., we find that it is unlikely that the pattern arose by chance), then we can say our test lends support to our hypothesis . But if the pattern does not pass our decision rule, meaning that it could have arisen by chance, then we say the test is inconsistent with our hypothesis .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bevans, R. (2023, June 22). Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/hypothesis-testing/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, choosing the right statistical test | types & examples, understanding p values | definition and examples, what is your plagiarism score.
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 , the — null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
H a —, the alternative hypothesis: a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are reject H 0 if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or do not reject H 0 or decline to reject H 0 if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
| equal (=) | not equal (≠) greater than (>) less than (<) |
| greater than or equal to (≥) | less than (<) |
| less than or equal to (≤) | more than (>) |
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30 H a : More than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take fewer than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45
Example 9.4
An article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third of the students pass. The same article stated that 6.6 percent of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4 percent pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40 percent pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40 percent pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some internet articles. In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-statistics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Statistics
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Apr 16, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 13: Inferential Statistics
Understanding Null Hypothesis Testing
Learning Objectives
- Explain the purpose of null hypothesis testing, including the role of sampling error.
- Describe the basic logic of null hypothesis testing.
- Describe the role of relationship strength and sample size in determining statistical significance and make reasonable judgments about statistical significance based on these two factors.
The Purpose of Null Hypothesis Testing
As we have seen, psychological research typically involves measuring one or more variables for a sample and computing descriptive statistics for that sample. In general, however, the researcher’s goal is not to draw conclusions about that sample but to draw conclusions about the population that the sample was selected from. Thus researchers must use sample statistics to draw conclusions about the corresponding values in the population. These corresponding values in the population are called parameters . Imagine, for example, that a researcher measures the number of depressive symptoms exhibited by each of 50 clinically depressed adults and computes the mean number of symptoms. The researcher probably wants to use this sample statistic (the mean number of symptoms for the sample) to draw conclusions about the corresponding population parameter (the mean number of symptoms for clinically depressed adults).
Unfortunately, sample statistics are not perfect estimates of their corresponding population parameters. This is because there is a certain amount of random variability in any statistic from sample to sample. The mean number of depressive symptoms might be 8.73 in one sample of clinically depressed adults, 6.45 in a second sample, and 9.44 in a third—even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. Similarly, the correlation (Pearson’s r ) between two variables might be +.24 in one sample, −.04 in a second sample, and +.15 in a third—again, even though these samples are selected randomly from the same population. This random variability in a statistic from sample to sample is called sampling error . (Note that the term error here refers to random variability and does not imply that anyone has made a mistake. No one “commits a sampling error.”)
One implication of this is that when there is a statistical relationship in a sample, it is not always clear that there is a statistical relationship in the population. A small difference between two group means in a sample might indicate that there is a small difference between the two group means in the population. But it could also be that there is no difference between the means in the population and that the difference in the sample is just a matter of sampling error. Similarly, a Pearson’s r value of −.29 in a sample might mean that there is a negative relationship in the population. But it could also be that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample is just a matter of sampling error.
In fact, any statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in two ways:
- There is a relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects this.
- There is no relationship in the population, and the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The purpose of null hypothesis testing is simply to help researchers decide between these two interpretations.
The Logic of Null Hypothesis Testing
Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis (often symbolized H 0 and read as “H-naught”). This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error. Informally, the null hypothesis is that the sample relationship “occurred by chance.” The other interpretation is called the alternative hypothesis (often symbolized as H 1 ). This is the idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
Again, every statistical relationship in a sample can be interpreted in either of these two ways: It might have occurred by chance, or it might reflect a relationship in the population. So researchers need a way to decide between them. Although there are many specific null hypothesis testing techniques, they are all based on the same general logic. The steps are as follows:
- Assume for the moment that the null hypothesis is true. There is no relationship between the variables in the population.
- Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true.
- If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, then reject the null hypothesis in favour of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be extremely unlikely, then retain the null hypothesis .
Following this logic, we can begin to understand why Mehl and his colleagues concluded that there is no difference in talkativeness between women and men in the population. In essence, they asked the following question: “If there were no difference in the population, how likely is it that we would find a small difference of d = 0.06 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly likely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they retained the null hypothesis—concluding that there is no evidence of a sex difference in the population. We can also see why Kanner and his colleagues concluded that there is a correlation between hassles and symptoms in the population. They asked, “If the null hypothesis were true, how likely is it that we would find a strong correlation of +.60 in our sample?” Their answer to this question was that this sample relationship would be fairly unlikely if the null hypothesis were true. Therefore, they rejected the null hypothesis in favour of the alternative hypothesis—concluding that there is a positive correlation between these variables in the population.
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value . A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample result would be likely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the retention of the null hypothesis. But how low must the p value be before the sample result is considered unlikely enough to reject the null hypothesis? In null hypothesis testing, this criterion is called α (alpha) and is almost always set to .05. If there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true, then the null hypothesis is rejected. When this happens, the result is said to be statistically significant . If there is greater than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result when the null hypothesis is true, then the null hypothesis is retained. This does not necessarily mean that the researcher accepts the null hypothesis as true—only that there is not currently enough evidence to conclude that it is true. Researchers often use the expression “fail to reject the null hypothesis” rather than “retain the null hypothesis,” but they never use the expression “accept the null hypothesis.”
The Misunderstood p Value
The p value is one of the most misunderstood quantities in psychological research (Cohen, 1994) [1] . Even professional researchers misinterpret it, and it is not unusual for such misinterpretations to appear in statistics textbooks!
The most common misinterpretation is that the p value is the probability that the null hypothesis is true—that the sample result occurred by chance. For example, a misguided researcher might say that because the p value is .02, there is only a 2% chance that the result is due to chance and a 98% chance that it reflects a real relationship in the population. But this is incorrect . The p value is really the probability of a result at least as extreme as the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. So a p value of .02 means that if the null hypothesis were true, a sample result this extreme would occur only 2% of the time.
You can avoid this misunderstanding by remembering that the p value is not the probability that any particular hypothesis is true or false. Instead, it is the probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true.
Role of Sample Size and Relationship Strength
Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, “If the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as this one?” In other words, “What is the p value?” It can be helpful to see that the answer to this question depends on just two considerations: the strength of the relationship and the size of the sample. Specifically, the stronger the sample relationship and the larger the sample, the less likely the result would be if the null hypothesis were true. That is, the lower the p value. This should make sense. Imagine a study in which a sample of 500 women is compared with a sample of 500 men in terms of some psychological characteristic, and Cohen’s d is a strong 0.50. If there were really no sex difference in the population, then a result this strong based on such a large sample should seem highly unlikely. Now imagine a similar study in which a sample of three women is compared with a sample of three men, and Cohen’s d is a weak 0.10. If there were no sex difference in the population, then a relationship this weak based on such a small sample should seem likely. And this is precisely why the null hypothesis would be rejected in the first example and retained in the second.
Of course, sometimes the result can be weak and the sample large, or the result can be strong and the sample small. In these cases, the two considerations trade off against each other so that a weak result can be statistically significant if the sample is large enough and a strong relationship can be statistically significant even if the sample is small. Table 13.1 shows roughly how relationship strength and sample size combine to determine whether a sample result is statistically significant. The columns of the table represent the three levels of relationship strength: weak, medium, and strong. The rows represent four sample sizes that can be considered small, medium, large, and extra large in the context of psychological research. Thus each cell in the table represents a combination of relationship strength and sample size. If a cell contains the word Yes , then this combination would be statistically significant for both Cohen’s d and Pearson’s r . If it contains the word No , then it would not be statistically significant for either. There is one cell where the decision for d and r would be different and another where it might be different depending on some additional considerations, which are discussed in Section 13.2 “Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests”
| Sample Size | Weak relationship | Medium-strength relationship | Strong relationship |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small ( = 20) | No | No | = Maybe = Yes |
| Medium ( = 50) | No | Yes | Yes |
| Large ( = 100) | = Yes = No | Yes | Yes |
| Extra large ( = 500) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Although Table 13.1 provides only a rough guideline, it shows very clearly that weak relationships based on medium or small samples are never statistically significant and that strong relationships based on medium or larger samples are always statistically significant. If you keep this lesson in mind, you will often know whether a result is statistically significant based on the descriptive statistics alone. It is extremely useful to be able to develop this kind of intuitive judgment. One reason is that it allows you to develop expectations about how your formal null hypothesis tests are going to come out, which in turn allows you to detect problems in your analyses. For example, if your sample relationship is strong and your sample is medium, then you would expect to reject the null hypothesis. If for some reason your formal null hypothesis test indicates otherwise, then you need to double-check your computations and interpretations. A second reason is that the ability to make this kind of intuitive judgment is an indication that you understand the basic logic of this approach in addition to being able to do the computations.
Statistical Significance Versus Practical Significance
Table 13.1 illustrates another extremely important point. A statistically significant result is not necessarily a strong one. Even a very weak result can be statistically significant if it is based on a large enough sample. This is closely related to Janet Shibley Hyde’s argument about sex differences (Hyde, 2007) [2] . The differences between women and men in mathematical problem solving and leadership ability are statistically significant. But the word significant can cause people to interpret these differences as strong and important—perhaps even important enough to influence the college courses they take or even who they vote for. As we have seen, however, these statistically significant differences are actually quite weak—perhaps even “trivial.”
This is why it is important to distinguish between the statistical significance of a result and the practical significance of that result. Practical significance refers to the importance or usefulness of the result in some real-world context. Many sex differences are statistically significant—and may even be interesting for purely scientific reasons—but they are not practically significant. In clinical practice, this same concept is often referred to as “clinical significance.” For example, a study on a new treatment for social phobia might show that it produces a statistically significant positive effect. Yet this effect still might not be strong enough to justify the time, effort, and other costs of putting it into practice—especially if easier and cheaper treatments that work almost as well already exist. Although statistically significant, this result would be said to lack practical or clinical significance.
Key Takeaways
- Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding whether a statistical relationship in a sample reflects a real relationship in the population or is just due to chance.
- The logic of null hypothesis testing involves assuming that the null hypothesis is true, finding how likely the sample result would be if this assumption were correct, and then making a decision. If the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true, then it is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis. If it would not be unlikely, then the null hypothesis is retained.
- The probability of obtaining the sample result if the null hypothesis were true (the p value) is based on two considerations: relationship strength and sample size. Reasonable judgments about whether a sample relationship is statistically significant can often be made by quickly considering these two factors.
- Statistical significance is not the same as relationship strength or importance. Even weak relationships can be statistically significant if the sample size is large enough. It is important to consider relationship strength and the practical significance of a result in addition to its statistical significance.
- Discussion: Imagine a study showing that people who eat more broccoli tend to be happier. Explain for someone who knows nothing about statistics why the researchers would conduct a null hypothesis test.
- The correlation between two variables is r = −.78 based on a sample size of 137.
- The mean score on a psychological characteristic for women is 25 ( SD = 5) and the mean score for men is 24 ( SD = 5). There were 12 women and 10 men in this study.
- In a memory experiment, the mean number of items recalled by the 40 participants in Condition A was 0.50 standard deviations greater than the mean number recalled by the 40 participants in Condition B.
- In another memory experiment, the mean scores for participants in Condition A and Condition B came out exactly the same!
- A student finds a correlation of r = .04 between the number of units the students in his research methods class are taking and the students’ level of stress.
Long Descriptions
“Null Hypothesis” long description: A comic depicting a man and a woman talking in the foreground. In the background is a child working at a desk. The man says to the woman, “I can’t believe schools are still teaching kids about the null hypothesis. I remember reading a big study that conclusively disproved it years ago.” [Return to “Null Hypothesis”]
“Conditional Risk” long description: A comic depicting two hikers beside a tree during a thunderstorm. A bolt of lightning goes “crack” in the dark sky as thunder booms. One of the hikers says, “Whoa! We should get inside!” The other hiker says, “It’s okay! Lightning only kills about 45 Americans a year, so the chances of dying are only one in 7,000,000. Let’s go on!” The comic’s caption says, “The annual death rate among people who know that statistic is one in six.” [Return to “Conditional Risk”]
Media Attributions
- Null Hypothesis by XKCD CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial)
- Conditional Risk by XKCD CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial)
- Cohen, J. (1994). The world is round: p < .05. American Psychologist, 49 , 997–1003. ↵
- Hyde, J. S. (2007). New directions in the study of gender similarities and differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 16 , 259–263. ↵
Values in a population that correspond to variables measured in a study.
The random variability in a statistic from sample to sample.
A formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample.
The idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only sampling error.
The idea that there is a relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects this relationship in the population.
When the relationship found in the sample would be extremely unlikely, the idea that the relationship occurred “by chance” is rejected.
When the relationship found in the sample is likely to have occurred by chance, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
The probability that, if the null hypothesis were true, the result found in the sample would occur.
How low the p value must be before the sample result is considered unlikely in null hypothesis testing.
When there is less than a 5% chance of a result as extreme as the sample result occurring and the null hypothesis is rejected.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5.6 Hypothesis Tests in Depth
Establishing the parameter of interest, type of distribution to use, the test statistic, and p -value can help you figure out how to go about a hypothesis test. However, there are several other factors you should consider when interpreting the results.
Rare Events
Suppose you make an assumption about a property of the population (this assumption is the null hypothesis). Then you gather sample data randomly. If the sample has properties that would be very unlikely to occur if the assumption is true, then you would conclude that your assumption about the population is probably incorrect. Remember that your assumption is just an assumption; it is not a fact, and it may or may not be true. But your sample data are real and are showing you a fact that seems to contradict your assumption.
Errors in Hypothesis Tests
When you perform a hypothesis test, there are four possible outcomes depending on the actual truth (or falseness) of the null hypothesis H 0 and the decision to reject or not. The outcomes are summarized in the following table:
| IS ACTUALLY | ||
|---|---|---|
| Action | ||
| Correct outcome | Type II error | |
| Type I error | Correct outcome | |
The four possible outcomes in the table are:
- The decision is not to reject H 0 when H 0 is true (correct decision).
- The decision is to reject H 0 when H 0 is true (incorrect decision known as a type I error ).
- The decision is not to reject H 0 when, in fact, H 0 is false (incorrect decision known as a type II error ).
- The decision is to reject H 0 when H 0 is false (correct decision whose probability is called the power of the test).
Each of the errors occurs with a particular probability. The Greek letters α and β represent the probabilities.
α = probability of a type I error = P (type I error) = probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. These are also known as false positives. We know that α is often determined in advance, and α = 0.05 is often widely accepted. In that case, you are saying, “We are OK making this type of error in 5% of samples.” In fact, the p -value is the exact probability of a type I error based on what you observed.
β = probability of a type II error = P (type II error) = probability of not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false. These are also known as false negatives.
The power of a test is 1 – β .
Ideally, α and β should be as small as possible because they are probabilities of errors but are rarely zero. We want a high power that is as close to one as well. Increasing the sample size can help us achieve these by reducing both α and β and therefore increasing the power of the test.
Suppose the null hypothesis, H 0 , is that Frank’s rock climbing equipment is safe.
Type I error: Frank thinks that his rock climbing equipment may not be safe when, in fact, it really is safe. Type II error: Frank thinks that his rock climbing equipment may be safe when, in fact, it is not safe.
α = probability that Frank thinks his rock climbing equipment may not be safe when, in fact, it really is safe. β = probability that Frank thinks his rock climbing equipment may be safe when, in fact, it is not safe.
Notice that, in this case, the error with the greater consequence is the type II error, in which Frank thinks his rock climbing equipment is safe, so he goes ahead and uses it.
Suppose the null hypothesis, H 0 , is that the blood cultures contain no traces of pathogen X . State the type I and type II errors.
Statistical Significance vs. Practical Significance
When the sample size becomes larger, point estimates become more precise and any real differences in the mean and null value become easier to detect and recognize. Even a very small difference would likely be detected if we took a large enough sample. Sometimes, researchers will take such large samples that even the slightest difference is detected, even differences where there is no practical value. In such cases, we still say the difference is statistically significant , but it is not practically significant.
For example, an online experiment might identify that placing additional ads on a movie review website statistically significantly increases viewership of a TV show by 0.001%, but this increase might not have any practical value.
One role of a data scientist in conducting a study often includes planning the size of the study. The data scientist might first consult experts or scientific literature to learn what would be the smallest meaningful difference from the null value. She also would obtain other information, such as a very rough estimate of the true proportion p , so that she could roughly estimate the standard error. From here, she could suggest a sample size that is sufficiently large enough to detect the real difference if it is meaningful. While larger sample sizes may still be used, these calculations are especially helpful when considering costs or potential risks, such as possible health impacts to volunteers in a medical study.
Click here for more multimedia resources, including podcasts, videos, lecture notes, and worked examples.
The decision is to reject the null hypothesis when, in fact, the null hypothesis is true
Erroneously rejecting a true null hypothesis or erroneously failing to reject a false null hypothesis
The probability of failing to reject a true hypothesis
Finding sufficient evidence that the observed effect is not just due to variability, often from rejecting the null hypothesis
Significant Statistics Copyright © 2024 by John Morgan Russell, OpenStaxCollege, OpenIntro is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
S.3 hypothesis testing.
In reviewing hypothesis tests, we start first with the general idea. Then, we keep returning to the basic procedures of hypothesis testing, each time adding a little more detail.
The general idea of hypothesis testing involves:
- Making an initial assumption.
- Collecting evidence (data).
- Based on the available evidence (data), deciding whether to reject or not reject the initial assumption.
Every hypothesis test — regardless of the population parameter involved — requires the above three steps.
Example S.3.1
Is normal body temperature really 98.6 degrees f section .
Consider the population of many, many adults. A researcher hypothesized that the average adult body temperature is lower than the often-advertised 98.6 degrees F. That is, the researcher wants an answer to the question: "Is the average adult body temperature 98.6 degrees? Or is it lower?" To answer his research question, the researcher starts by assuming that the average adult body temperature was 98.6 degrees F.
Then, the researcher went out and tried to find evidence that refutes his initial assumption. In doing so, he selects a random sample of 130 adults. The average body temperature of the 130 sampled adults is 98.25 degrees.
Then, the researcher uses the data he collected to make a decision about his initial assumption. It is either likely or unlikely that the researcher would collect the evidence he did given his initial assumption that the average adult body temperature is 98.6 degrees:
- If it is likely , then the researcher does not reject his initial assumption that the average adult body temperature is 98.6 degrees. There is not enough evidence to do otherwise.
- either the researcher's initial assumption is correct and he experienced a very unusual event;
- or the researcher's initial assumption is incorrect.
In statistics, we generally don't make claims that require us to believe that a very unusual event happened. That is, in the practice of statistics, if the evidence (data) we collected is unlikely in light of the initial assumption, then we reject our initial assumption.
Example S.3.2
Criminal trial analogy section .
One place where you can consistently see the general idea of hypothesis testing in action is in criminal trials held in the United States. Our criminal justice system assumes "the defendant is innocent until proven guilty." That is, our initial assumption is that the defendant is innocent.
In the practice of statistics, we make our initial assumption when we state our two competing hypotheses -- the null hypothesis ( H 0 ) and the alternative hypothesis ( H A ). Here, our hypotheses are:
- H 0 : Defendant is not guilty (innocent)
- H A : Defendant is guilty
In statistics, we always assume the null hypothesis is true . That is, the null hypothesis is always our initial assumption.
The prosecution team then collects evidence — such as finger prints, blood spots, hair samples, carpet fibers, shoe prints, ransom notes, and handwriting samples — with the hopes of finding "sufficient evidence" to make the assumption of innocence refutable.
In statistics, the data are the evidence.
The jury then makes a decision based on the available evidence:
- If the jury finds sufficient evidence — beyond a reasonable doubt — to make the assumption of innocence refutable, the jury rejects the null hypothesis and deems the defendant guilty. We behave as if the defendant is guilty.
- If there is insufficient evidence, then the jury does not reject the null hypothesis . We behave as if the defendant is innocent.
In statistics, we always make one of two decisions. We either "reject the null hypothesis" or we "fail to reject the null hypothesis."
Errors in Hypothesis Testing Section
Did you notice the use of the phrase "behave as if" in the previous discussion? We "behave as if" the defendant is guilty; we do not "prove" that the defendant is guilty. And, we "behave as if" the defendant is innocent; we do not "prove" that the defendant is innocent.
This is a very important distinction! We make our decision based on evidence not on 100% guaranteed proof. Again:
- If we reject the null hypothesis, we do not prove that the alternative hypothesis is true.
- If we do not reject the null hypothesis, we do not prove that the null hypothesis is true.
We merely state that there is enough evidence to behave one way or the other. This is always true in statistics! Because of this, whatever the decision, there is always a chance that we made an error .
Let's review the two types of errors that can be made in criminal trials:
| Jury Decision | Truth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Not Guilty | Guilty | ||
| Not Guilty | OK | ERROR | |
| Guilty | ERROR | OK | |
Table S.3.2 shows how this corresponds to the two types of errors in hypothesis testing.
| Decision | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Null Hypothesis | Alternative Hypothesis | ||
| Do not Reject Null | OK | Type II Error | |
| Reject Null | Type I Error | OK | |
Note that, in statistics, we call the two types of errors by two different names -- one is called a "Type I error," and the other is called a "Type II error." Here are the formal definitions of the two types of errors:
There is always a chance of making one of these errors. But, a good scientific study will minimize the chance of doing so!
Making the Decision Section
Recall that it is either likely or unlikely that we would observe the evidence we did given our initial assumption. If it is likely , we do not reject the null hypothesis. If it is unlikely , then we reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. Effectively, then, making the decision reduces to determining "likely" or "unlikely."
In statistics, there are two ways to determine whether the evidence is likely or unlikely given the initial assumption:
- We could take the " critical value approach " (favored in many of the older textbooks).
- Or, we could take the " P -value approach " (what is used most often in research, journal articles, and statistical software).
In the next two sections, we review the procedures behind each of these two approaches. To make our review concrete, let's imagine that μ is the average grade point average of all American students who major in mathematics. We first review the critical value approach for conducting each of the following three hypothesis tests about the population mean $\mu$:
| : = 3 | : > 3 | |
| : = 3 | : < 3 | |
| : = 3 | : ≠ 3 |
In Practice
- We would want to conduct the first hypothesis test if we were interested in concluding that the average grade point average of the group is more than 3.
- We would want to conduct the second hypothesis test if we were interested in concluding that the average grade point average of the group is less than 3.
- And, we would want to conduct the third hypothesis test if we were only interested in concluding that the average grade point average of the group differs from 3 (without caring whether it is more or less than 3).
Upon completing the review of the critical value approach, we review the P -value approach for conducting each of the above three hypothesis tests about the population mean \(\mu\). The procedures that we review here for both approaches easily extend to hypothesis tests about any other population parameter.
Module 9: Hypothesis Testing With One Sample
Null and alternative hypotheses, learning outcomes.
- Describe hypothesis testing in general and in practice
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 : The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.
H a : The alternative hypothesis : It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make adecision. There are two options for a decision . They are “reject H 0 ” if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or “do not reject H 0 ” or “decline to reject H 0 ” if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
| equal (=) | not equal (≠) greater than (>) less than (<) |
| greater than or equal to (≥) | less than (<) |
| less than or equal to (≤) | more than (>) |
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
H 0 : No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30
H a : More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H 0 : The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. p = 0.25
H a : The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. p ≠ 0.25
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
H 0 : μ = 2.0
H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : μ __ 66 H a : μ __ 66
- H 0 : μ = 66
- H a : μ ≠ 66
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
H 0 : μ ≥ 5
H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : μ __ 45 H a : μ __ 45
- H 0 : μ ≥ 45
- H a : μ < 45
In an issue of U.S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H 0 : p ≤ 0.066
H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p __ 0.40 H a : p __ 0.40
- H 0 : p = 0.40
- H a : p > 0.40
Concept Review
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with H 0 . The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality (=, ≤ or ≥) Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with H a or H 1 , using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., (≠, >, or <). If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis. Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
H 0 and H a are contradictory.
- OpenStax, Statistics, Null and Alternative Hypotheses. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:58/Introductory_Statistics . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Introductory Statistics . Authored by : Barbara Illowski, Susan Dean. Provided by : Open Stax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
- Simple hypothesis testing | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy. Authored by : Khan Academy. Located at : https://youtu.be/5D1gV37bKXY . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Statistics By Jim
Making statistics intuitive
Statistical Hypothesis Testing Overview
By Jim Frost 59 Comments
In this blog post, I explain why you need to use statistical hypothesis testing and help you navigate the essential terminology. Hypothesis testing is a crucial procedure to perform when you want to make inferences about a population using a random sample. These inferences include estimating population properties such as the mean, differences between means, proportions, and the relationships between variables.
This post provides an overview of statistical hypothesis testing. If you need to perform hypothesis tests, consider getting my book, Hypothesis Testing: An Intuitive Guide .
Why You Should Perform Statistical Hypothesis Testing

Hypothesis testing is a form of inferential statistics that allows us to draw conclusions about an entire population based on a representative sample. You gain tremendous benefits by working with a sample. In most cases, it is simply impossible to observe the entire population to understand its properties. The only alternative is to collect a random sample and then use statistics to analyze it.
While samples are much more practical and less expensive to work with, there are trade-offs. When you estimate the properties of a population from a sample, the sample statistics are unlikely to equal the actual population value exactly. For instance, your sample mean is unlikely to equal the population mean. The difference between the sample statistic and the population value is the sample error.
Differences that researchers observe in samples might be due to sampling error rather than representing a true effect at the population level. If sampling error causes the observed difference, the next time someone performs the same experiment the results might be different. Hypothesis testing incorporates estimates of the sampling error to help you make the correct decision. Learn more about Sampling Error .
For example, if you are studying the proportion of defects produced by two manufacturing methods, any difference you observe between the two sample proportions might be sample error rather than a true difference. If the difference does not exist at the population level, you won’t obtain the benefits that you expect based on the sample statistics. That can be a costly mistake!
Let’s cover some basic hypothesis testing terms that you need to know.
Background information : Difference between Descriptive and Inferential Statistics and Populations, Parameters, and Samples in Inferential Statistics
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical analysis that uses sample data to assess two mutually exclusive theories about the properties of a population. Statisticians call these theories the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. A hypothesis test assesses your sample statistic and factors in an estimate of the sample error to determine which hypothesis the data support.
When you can reject the null hypothesis, the results are statistically significant, and your data support the theory that an effect exists at the population level.
The effect is the difference between the population value and the null hypothesis value. The effect is also known as population effect or the difference. For example, the mean difference between the health outcome for a treatment group and a control group is the effect.
Typically, you do not know the size of the actual effect. However, you can use a hypothesis test to help you determine whether an effect exists and to estimate its size. Hypothesis tests convert your sample effect into a test statistic, which it evaluates for statistical significance. Learn more about Test Statistics .
An effect can be statistically significant, but that doesn’t necessarily indicate that it is important in a real-world, practical sense. For more information, read my post about Statistical vs. Practical Significance .
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is one of two mutually exclusive theories about the properties of the population in hypothesis testing. Typically, the null hypothesis states that there is no effect (i.e., the effect size equals zero). The null is often signified by H 0 .
In all hypothesis testing, the researchers are testing an effect of some sort. The effect can be the effectiveness of a new vaccination, the durability of a new product, the proportion of defect in a manufacturing process, and so on. There is some benefit or difference that the researchers hope to identify.
However, it’s possible that there is no effect or no difference between the experimental groups. In statistics, we call this lack of an effect the null hypothesis. Therefore, if you can reject the null, you can favor the alternative hypothesis, which states that the effect exists (doesn’t equal zero) at the population level.
You can think of the null as the default theory that requires sufficiently strong evidence against in order to reject it.
For example, in a 2-sample t-test, the null often states that the difference between the two means equals zero.
When you can reject the null hypothesis, your results are statistically significant. Learn more about Statistical Significance: Definition & Meaning .
Related post : Understanding the Null Hypothesis in More Detail
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is the other theory about the properties of the population in hypothesis testing. Typically, the alternative hypothesis states that a population parameter does not equal the null hypothesis value. In other words, there is a non-zero effect. If your sample contains sufficient evidence, you can reject the null and favor the alternative hypothesis. The alternative is often identified with H 1 or H A .
For example, in a 2-sample t-test, the alternative often states that the difference between the two means does not equal zero.
You can specify either a one- or two-tailed alternative hypothesis:
If you perform a two-tailed hypothesis test, the alternative states that the population parameter does not equal the null value. For example, when the alternative hypothesis is H A : μ ≠ 0, the test can detect differences both greater than and less than the null value.
A one-tailed alternative has more power to detect an effect but it can test for a difference in only one direction. For example, H A : μ > 0 can only test for differences that are greater than zero.
Related posts : Understanding T-tests and One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Hypothesis Tests Explained

P-values are the probability that you would obtain the effect observed in your sample, or larger, if the null hypothesis is correct. In simpler terms, p-values tell you how strongly your sample data contradict the null. Lower p-values represent stronger evidence against the null. You use P-values in conjunction with the significance level to determine whether your data favor the null or alternative hypothesis.
Related post : Interpreting P-values Correctly
Significance Level (Alpha)
For instance, a significance level of 0.05 signifies a 5% risk of deciding that an effect exists when it does not exist.
Use p-values and significance levels together to help you determine which hypothesis the data support. If the p-value is less than your significance level, you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant. In other words, the evidence in your sample is strong enough to be able to reject the null hypothesis at the population level.
Related posts : Graphical Approach to Significance Levels and P-values and Conceptual Approach to Understanding Significance Levels
Types of Errors in Hypothesis Testing
Statistical hypothesis tests are not 100% accurate because they use a random sample to draw conclusions about entire populations. There are two types of errors related to drawing an incorrect conclusion.
- False positives: You reject a null that is true. Statisticians call this a Type I error . The Type I error rate equals your significance level or alpha (α).
- False negatives: You fail to reject a null that is false. Statisticians call this a Type II error. Generally, you do not know the Type II error rate. However, it is a larger risk when you have a small sample size , noisy data, or a small effect size. The type II error rate is also known as beta (β).
Statistical power is the probability that a hypothesis test correctly infers that a sample effect exists in the population. In other words, the test correctly rejects a false null hypothesis. Consequently, power is inversely related to a Type II error. Power = 1 – β. Learn more about Power in Statistics .
Related posts : Types of Errors in Hypothesis Testing and Estimating a Good Sample Size for Your Study Using Power Analysis
Which Type of Hypothesis Test is Right for You?
There are many different types of procedures you can use. The correct choice depends on your research goals and the data you collect. Do you need to understand the mean or the differences between means? Or, perhaps you need to assess proportions. You can even use hypothesis testing to determine whether the relationships between variables are statistically significant.
To choose the proper statistical procedure, you’ll need to assess your study objectives and collect the correct type of data . This background research is necessary before you begin a study.
Related Post : Hypothesis Tests for Continuous, Binary, and Count Data
Statistical tests are crucial when you want to use sample data to make conclusions about a population because these tests account for sample error. Using significance levels and p-values to determine when to reject the null hypothesis improves the probability that you will draw the correct conclusion.
To see an alternative approach to these traditional hypothesis testing methods, learn about bootstrapping in statistics !
If you want to see examples of hypothesis testing in action, I recommend the following posts that I have written:
- How Effective Are Flu Shots? This example shows how you can use statistics to test proportions.
- Fatality Rates in Star Trek . This example shows how to use hypothesis testing with categorical data.
- Busting Myths About the Battle of the Sexes . A fun example based on a Mythbusters episode that assess continuous data using several different tests.
- Are Yawns Contagious? Another fun example inspired by a Mythbusters episode.
Share this:

Reader Interactions
January 14, 2024 at 8:43 am
Hello professor Jim, how are you doing! Pls. What are the properties of a population and their examples? Thanks for your time and understanding.
January 14, 2024 at 12:57 pm
Please read my post about Populations vs. Samples for more information and examples.
Also, please note there is a search bar in the upper-right margin of my website. Use that to search for topics.
July 5, 2023 at 7:05 am
Hello, I have a question as I read your post. You say in p-values section
“P-values are the probability that you would obtain the effect observed in your sample, or larger, if the null hypothesis is correct. In simpler terms, p-values tell you how strongly your sample data contradict the null. Lower p-values represent stronger evidence against the null.”
But according to your definition of effect, the null states that an effect does not exist, correct? So what I assume you want to say is that “P-values are the probability that you would obtain the effect observed in your sample, or larger, if the null hypothesis is **incorrect**.”
July 6, 2023 at 5:18 am
Hi Shrinivas,
The correct definition of p-value is that it is a probability that exists in the context of a true null hypothesis. So, the quotation is correct in stating “if the null hypothesis is correct.”
Essentially, the p-value tells you the likelihood of your observed results (or more extreme) if the null hypothesis is true. It gives you an idea of whether your results are surprising or unusual if there is no effect.
Hence, with sufficiently low p-values, you reject the null hypothesis because it’s telling you that your sample results were unlikely to have occurred if there was no effect in the population.
I hope that helps make it more clear. If not, let me know I’ll attempt to clarify!
May 8, 2023 at 12:47 am
Thanks a lot Ny best regards
May 7, 2023 at 11:15 pm
Hi Jim Can you tell me something about size effect? Thanks
May 8, 2023 at 12:29 am
Here’s a post that I’ve written about Effect Sizes that will hopefully tell you what you need to know. Please read that. Then, if you have any more specific questions about effect sizes, please post them there. Thanks!
January 7, 2023 at 4:19 pm
Hi Jim, I have only read two pages so far but I am really amazed because in few paragraphs you made me clearly understand the concepts of months of courses I received in biostatistics! Thanks so much for this work you have done it helps a lot!
January 10, 2023 at 3:25 pm
Thanks so much!
June 17, 2021 at 1:45 pm
Can you help in the following question: Rocinante36 is priced at ₹7 lakh and has been designed to deliver a mileage of 22 km/litre and a top speed of 140 km/hr. Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses for mileage and top speed to check whether the new models are performing as per the desired design specifications.
April 19, 2021 at 1:51 pm
Its indeed great to read your work statistics.
I have a doubt regarding the one sample t-test. So as per your book on hypothesis testing with reference to page no 45, you have mentioned the difference between “the sample mean and the hypothesised mean is statistically significant”. So as per my understanding it should be quoted like “the difference between the population mean and the hypothesised mean is statistically significant”. The catch here is the hypothesised mean represents the sample mean.
Please help me understand this.
Regards Rajat
April 19, 2021 at 3:46 pm
Thanks for buying my book. I’m so glad it’s been helpful!
The test is performed on the sample but the results apply to the population. Hence, if the difference between the sample mean (observed in your study) and the hypothesized mean is statistically significant, that suggests that population does not equal the hypothesized mean.
For one sample tests, the hypothesized mean is not the sample mean. It is a mean that you want to use for the test value. It usually represents a value that is important to your research. In other words, it’s a value that you pick for some theoretical/practical reasons. You pick it because you want to determine whether the population mean is different from that particular value.
I hope that helps!
November 5, 2020 at 6:24 am
Jim, you are such a magnificent statistician/economist/econometrician/data scientist etc whatever profession. Your work inspires and simplifies the lives of so many researchers around the world. I truly admire you and your work. I will buy a copy of each book you have on statistics or econometrics. Keep doing the good work. Remain ever blessed
November 6, 2020 at 9:47 pm
Hi Renatus,
Thanks so much for you very kind comments. You made my day!! I’m so glad that my website has been helpful. And, thanks so much for supporting my books! 🙂
November 2, 2020 at 9:32 pm
Hi Jim, I hope you are aware of 2019 American Statistical Association’s official statement on Statistical Significance: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00031305.2019.1583913 In case you do not bother reading the full article, may I quote you the core message here: “We conclude, based on our review of the articles in this special issue and the broader literature, that it is time to stop using the term “statistically significant” entirely. Nor should variants such as “significantly different,” “p < 0.05,” and “nonsignificant” survive, whether expressed in words, by asterisks in a table, or in some other way."
With best wishes,
November 3, 2020 at 2:09 am
I’m definitely aware of the debate surrounding how to use p-values most effectively. However, I need to correct you on one point. The link you provide is NOT a statement by the American Statistical Association. It is an editorial by several authors.
There is considerable debate over this issue. There are problems with p-values. However, as the authors state themselves, much of the problem is over people’s mindsets about how to use p-values and their incorrect interpretations about what statistical significance does and does not mean.
If you were to read my website more thoroughly, you’d be aware that I share many of their concerns and I address them in multiple posts. One of the authors’ key points is the need to be thoughtful and conduct thoughtful research and analysis. I emphasize this aspect in multiple posts on this topic. I’ll ask you to read the following three because they all address some of the authors’ concerns and suggestions. But you might run across others to read as well.
Five Tips for Using P-values to Avoid Being Misled How to Interpret P-values Correctly P-values and the Reproducibility of Experimental Results
September 24, 2020 at 11:52 pm
HI Jim, i just want you to know that you made explanation for Statistics so simple! I should say lesser and fewer words that reduce the complexity. All the best! 🙂
September 25, 2020 at 1:03 am
Thanks, Rene! Your kind words mean a lot to me! I’m so glad it has been helpful!
September 23, 2020 at 2:21 am
Honestly, I never understood stats during my entire M.Ed course and was another nightmare for me. But how easily you have explained each concept, I have understood stats way beyond my imagination. Thank you so much for helping ignorant research scholars like us. Looking forward to get hardcopy of your book. Kindly tell is it available through flipkart?
September 24, 2020 at 11:14 pm
I’m so happy to hear that my website has been helpful!
I checked on flipkart and it appears like my books are not available there. I’m never exactly sure where they’re available due to the vagaries of different distribution channels. They are available on Amazon in India.
Introduction to Statistics: An Intuitive Guide (Amazon IN) Hypothesis Testing: An Intuitive Guide (Amazon IN)
July 26, 2020 at 11:57 am
Dear Jim I am a teacher from India . I don’t have any background in statistics, and still I should tell that in a single read I can follow your explanations . I take my entire biostatistics class for botany graduates with your explanations. Thanks a lot. May I know how I can avail your books in India
July 28, 2020 at 12:31 am
Right now my books are only available as ebooks from my website. However, soon I’ll have some exciting news about other ways to obtain it. Stay tuned! I’ll announce it on my email list. If you’re not already on it, you can sign up using the form that is in the right margin of my website.
June 22, 2020 at 2:02 pm
Also can you please let me if this book covers topics like EDA and principal component analysis?
June 22, 2020 at 2:07 pm
This book doesn’t cover principal components analysis. Although, I wouldn’t really classify that as a hypothesis test. In the future, I might write a multivariate analysis book that would cover this and others. But, that’s well down the road.
My Introduction to Statistics covers EDA. That’s the largely graphical look at your data that you often do prior to hypothesis testing. The Introduction book perfectly leads right into the Hypothesis Testing book.
June 22, 2020 at 1:45 pm
Thanks for the detailed explanation. It does clear my doubts. I saw that your book related to hypothesis testing has the topics that I am studying currently. I am looking forward to purchasing it.
Regards, Take Care
June 19, 2020 at 1:03 pm
For this particular article I did not understand a couple of statements and it would great if you could help: 1)”If sample error causes the observed difference, the next time someone performs the same experiment the results might be different.” 2)”If the difference does not exist at the population level, you won’t obtain the benefits that you expect based on the sample statistics.”
I discovered your articles by chance and now I keep coming back to read & understand statistical concepts. These articles are very informative & easy to digest. Thanks for the simplifying things.
June 20, 2020 at 9:53 pm
I’m so happy to hear that you’ve found my website to be helpful!
To answer your questions, keep in mind that a central tenant of inferential statistics is that the random sample that a study drew was only one of an infinite number of possible it could’ve drawn. Each random sample produces different results. Most results will cluster around the population value assuming they used good methodology. However, random sampling error always exists and makes it so that population estimates from a sample almost never exactly equal the correct population value.
So, imagine that we’re studying a medication and comparing the treatment and control groups. Suppose that the medicine is truly not effect and that the population difference between the treatment and control group is zero (i.e., no difference.) Despite the true difference being zero, most sample estimates will show some degree of either a positive or negative effect thanks to random sampling error. So, just because a study has an observed difference does not mean that a difference exists at the population level. So, on to your questions:
1. If the observed difference is just random error, then it makes sense that if you collected another random sample, the difference could change. It could change from negative to positive, positive to negative, more extreme, less extreme, etc. However, if the difference exists at the population level, most random samples drawn from the population will reflect that difference. If the medicine has an effect, most random samples will reflect that fact and not bounce around on both sides of zero as much.
2. This is closely related to the previous answer. If there is no difference at the population level, but say you approve the medicine because of the observed effects in a sample. Even though your random sample showed an effect (which was really random error), that effect doesn’t exist. So, when you start using it on a larger scale, people won’t benefit from the medicine. That’s why it’s important to separate out what is easily explained by random error versus what is not easily explained by it.
I think reading my post about how hypothesis tests work will help clarify this process. Also, in about 24 hours (as I write this), I’ll be releasing my new ebook about Hypothesis Testing!
May 29, 2020 at 5:23 am
Hi Jim, I really enjoy your blog. Can you please link me on your blog where you discuss about Subgroup analysis and how it is done? I need to use non parametric and parametric statistical methods for my work and also do subgroup analysis in order to identify potential groups of patients that may benefit more from using a treatment than other groups.
May 29, 2020 at 2:12 pm
Hi, I don’t have a specific article about subgroup analysis. However, subgroup analysis is just the dividing up of a larger sample into subgroups and then analyzing those subgroups separately. You can use the various analyses I write about on the subgroups.
Alternatively, you can include the subgroups in regression analysis as an indicator variable and include that variable as a main effect and an interaction effect to see how the relationships vary by subgroup without needing to subdivide your data. I write about that approach in my article about comparing regression lines . This approach is my preferred approach when possible.
April 19, 2020 at 7:58 am
sir is confidence interval is a part of estimation?
April 17, 2020 at 3:36 pm
Sir can u plz briefly explain alternatives of hypothesis testing? I m unable to find the answer
April 18, 2020 at 1:22 am
Assuming you want to draw conclusions about populations by using samples (i.e., inferential statistics ), you can use confidence intervals and bootstrap methods as alternatives to the traditional hypothesis testing methods.
March 9, 2020 at 10:01 pm
Hi JIm, could you please help with activities that can best teach concepts of hypothesis testing through simulation, Also, do you have any question set that would enhance students intuition why learning hypothesis testing as a topic in introductory statistics. Thanks.
March 5, 2020 at 3:48 pm
Hi Jim, I’m studying multiple hypothesis testing & was wondering if you had any material that would be relevant. I’m more trying to understand how testing multiple samples simultaneously affects your results & more on the Bonferroni Correction
March 5, 2020 at 4:05 pm
I write about multiple comparisons (aka post hoc tests) in the ANOVA context . I don’t talk about Bonferroni Corrections specifically but I cover related types of corrections. I’m not sure if that exactly addresses what you want to know but is probably the closest I have already written. I hope it helps!
January 14, 2020 at 9:03 pm
Thank you! Have a great day/evening.
January 13, 2020 at 7:10 pm
Any help would be greatly appreciated. What is the difference between The Hypothesis Test and The Statistical Test of Hypothesis?
January 14, 2020 at 11:02 am
They sound like the same thing to me. Unless this is specialized terminology for a particular field or the author was intending something specific, I’d guess they’re one and the same.
April 1, 2019 at 10:00 am
so these are the only two forms of Hypothesis used in statistical testing?
April 1, 2019 at 10:02 am
Are you referring to the null and alternative hypothesis? If so, yes, that’s those are the standard hypotheses in a statistical hypothesis test.
April 1, 2019 at 9:57 am
year very insightful post, thanks for the write up
October 27, 2018 at 11:09 pm
hi there, am upcoming statistician, out of all blogs that i have read, i have found this one more useful as long as my problem is concerned. thanks so much
October 27, 2018 at 11:14 pm
Hi Stano, you’re very welcome! Thanks for your kind words. They mean a lot! I’m happy to hear that my posts were able to help you. I’m sure you will be a fantastic statistician. Best of luck with your studies!
October 26, 2018 at 11:39 am
Dear Jim, thank you very much for your explanations! I have a question. Can I use t-test to compare two samples in case each of them have right bias?
October 26, 2018 at 12:00 pm
Hi Tetyana,
You’re very welcome!
The term “right bias” is not a standard term. Do you by chance mean right skewed distributions? In other words, if you plot the distribution for each group on a histogram they have longer right tails? These are not the symmetrical bell-shape curves of the normal distribution.
If that’s the case, yes you can as long as you exceed a specific sample size within each group. I include a table that contains these sample size requirements in my post about nonparametric vs parametric analyses .
Bias in statistics refers to cases where an estimate of a value is systematically higher or lower than the true value. If this is the case, you might be able to use t-tests, but you’d need to be sure to understand the nature of the bias so you would understand what the results are really indicating.
I hope this helps!
April 2, 2018 at 7:28 am
Simple and upto the point 👍 Thank you so much.
April 2, 2018 at 11:11 am
Hi Kalpana, thanks! And I’m glad it was helpful!
March 26, 2018 at 8:41 am
Am I correct if I say: Alpha – Probability of wrongly rejection of null hypothesis P-value – Probability of wrongly acceptance of null hypothesis
March 28, 2018 at 3:14 pm
You’re correct about alpha. Alpha is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null is true.
Unfortunately, your definition of the p-value is a bit off. The p-value has a fairly convoluted definition. It is the probability of obtaining the effect observed in a sample, or more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true. The p-value does NOT indicate the probability that either the null or alternative is true or false. Although, those are very common misinterpretations. To learn more, read my post about how to interpret p-values correctly .
March 2, 2018 at 6:10 pm
I recently started reading your blog and it is very helpful to understand each concept of statistical tests in easy way with some good examples. Also, I recommend to other people go through all these blogs which you posted. Specially for those people who have not statistical background and they are facing to many problems while studying statistical analysis.
Thank you for your such good blogs.
March 3, 2018 at 10:12 pm
Hi Amit, I’m so glad that my blog posts have been helpful for you! It means a lot to me that you took the time to write such a nice comment! Also, thanks for recommending by blog to others! I try really hard to write posts about statistics that are easy to understand.
January 17, 2018 at 7:03 am
I recently started reading your blog and I find it very interesting. I am learning statistics by my own, and I generally do many google search to understand the concepts. So this blog is quite helpful for me, as it have most of the content which I am looking for.
January 17, 2018 at 3:56 pm
Hi Shashank, thank you! And, I’m very glad to hear that my blog is helpful!
January 2, 2018 at 2:28 pm
thank u very much sir.
January 2, 2018 at 2:36 pm
You’re very welcome, Hiral!
November 21, 2017 at 12:43 pm
Thank u so much sir….your posts always helps me to be a #statistician
November 21, 2017 at 2:40 pm
Hi Sachin, you’re very welcome! I’m happy that you find my posts to be helpful!
November 19, 2017 at 8:22 pm
great post as usual, but it would be nice to see an example.
November 19, 2017 at 8:27 pm
Thank you! At the end of this post, I have links to four other posts that show examples of hypothesis tests in action. You’ll find what you’re looking for in those posts!
Comments and Questions Cancel reply
Hypothesis Testing (cont...)
Hypothesis testing, the null and alternative hypothesis.
In order to undertake hypothesis testing you need to express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. The null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis are statements regarding the differences or effects that occur in the population. You will use your sample to test which statement (i.e., the null hypothesis or alternative hypothesis) is most likely (although technically, you test the evidence against the null hypothesis). So, with respect to our teaching example, the null and alternative hypothesis will reflect statements about all statistics students on graduate management courses.
The null hypothesis is essentially the "devil's advocate" position. That is, it assumes that whatever you are trying to prove did not happen ( hint: it usually states that something equals zero). For example, the two different teaching methods did not result in different exam performances (i.e., zero difference). Another example might be that there is no relationship between anxiety and athletic performance (i.e., the slope is zero). The alternative hypothesis states the opposite and is usually the hypothesis you are trying to prove (e.g., the two different teaching methods did result in different exam performances). Initially, you can state these hypotheses in more general terms (e.g., using terms like "effect", "relationship", etc.), as shown below for the teaching methods example:
| Null Hypotheses (H ): | Undertaking seminar classes has no effect on students' performance. |
| Alternative Hypothesis (H ): | Undertaking seminar class has a positive effect on students' performance. |
Depending on how you want to "summarize" the exam performances will determine how you might want to write a more specific null and alternative hypothesis. For example, you could compare the mean exam performance of each group (i.e., the "seminar" group and the "lectures-only" group). This is what we will demonstrate here, but other options include comparing the distributions , medians , amongst other things. As such, we can state:
| Null Hypotheses (H ): | The mean exam mark for the "seminar" and "lecture-only" teaching methods is the same in the population. |
| Alternative Hypothesis (H ): | The mean exam mark for the "seminar" and "lecture-only" teaching methods is not the same in the population. |
Now that you have identified the null and alternative hypotheses, you need to find evidence and develop a strategy for declaring your "support" for either the null or alternative hypothesis. We can do this using some statistical theory and some arbitrary cut-off points. Both these issues are dealt with next.
Significance levels
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as the so-called p -value . Depending on the statistical test you have chosen, you will calculate a probability (i.e., the p -value) of observing your sample results (or more extreme) given that the null hypothesis is true . Another way of phrasing this is to consider the probability that a difference in a mean score (or other statistic) could have arisen based on the assumption that there really is no difference. Let us consider this statement with respect to our example where we are interested in the difference in mean exam performance between two different teaching methods. If there really is no difference between the two teaching methods in the population (i.e., given that the null hypothesis is true), how likely would it be to see a difference in the mean exam performance between the two teaching methods as large as (or larger than) that which has been observed in your sample?
So, you might get a p -value such as 0.03 (i.e., p = .03). This means that there is a 3% chance of finding a difference as large as (or larger than) the one in your study given that the null hypothesis is true. However, you want to know whether this is "statistically significant". Typically, if there was a 5% or less chance (5 times in 100 or less) that the difference in the mean exam performance between the two teaching methods (or whatever statistic you are using) is as different as observed given the null hypothesis is true, you would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. Alternately, if the chance was greater than 5% (5 times in 100 or more), you would fail to reject the null hypothesis and would not accept the alternative hypothesis. As such, in this example where p = .03, we would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. We reject it because at a significance level of 0.03 (i.e., less than a 5% chance), the result we obtained could happen too frequently for us to be confident that it was the two teaching methods that had an effect on exam performance.
Whilst there is relatively little justification why a significance level of 0.05 is used rather than 0.01 or 0.10, for example, it is widely used in academic research. However, if you want to be particularly confident in your results, you can set a more stringent level of 0.01 (a 1% chance or less; 1 in 100 chance or less).

One- and two-tailed predictions
When considering whether we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis, we need to consider the direction of the alternative hypothesis statement. For example, the alternative hypothesis that was stated earlier is:
| Alternative Hypothesis (H ): | Undertaking seminar classes has a positive effect on students' performance. |
The alternative hypothesis tells us two things. First, what predictions did we make about the effect of the independent variable(s) on the dependent variable(s)? Second, what was the predicted direction of this effect? Let's use our example to highlight these two points.
Sarah predicted that her teaching method (independent variable: teaching method), whereby she not only required her students to attend lectures, but also seminars, would have a positive effect (that is, increased) students' performance (dependent variable: exam marks). If an alternative hypothesis has a direction (and this is how you want to test it), the hypothesis is one-tailed. That is, it predicts direction of the effect. If the alternative hypothesis has stated that the effect was expected to be negative, this is also a one-tailed hypothesis.
Alternatively, a two-tailed prediction means that we do not make a choice over the direction that the effect of the experiment takes. Rather, it simply implies that the effect could be negative or positive. If Sarah had made a two-tailed prediction, the alternative hypothesis might have been:
| Alternative Hypothesis (H ): | Undertaking seminar classes has an effect on students' performance. |
In other words, we simply take out the word "positive", which implies the direction of our effect. In our example, making a two-tailed prediction may seem strange. After all, it would be logical to expect that "extra" tuition (going to seminar classes as well as lectures) would either have a positive effect on students' performance or no effect at all, but certainly not a negative effect. However, this is just our opinion (and hope) and certainly does not mean that we will get the effect we expect. Generally speaking, making a one-tail prediction (i.e., and testing for it this way) is frowned upon as it usually reflects the hope of a researcher rather than any certainty that it will happen. Notable exceptions to this rule are when there is only one possible way in which a change could occur. This can happen, for example, when biological activity/presence in measured. That is, a protein might be "dormant" and the stimulus you are using can only possibly "wake it up" (i.e., it cannot possibly reduce the activity of a "dormant" protein). In addition, for some statistical tests, one-tailed tests are not possible.
Rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis
Let's return finally to the question of whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
If our statistical analysis shows that the significance level is below the cut-off value we have set (e.g., either 0.05 or 0.01), we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. Alternatively, if the significance level is above the cut-off value, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and cannot accept the alternative hypothesis. You should note that you cannot accept the null hypothesis, but only find evidence against it.
Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples, How to State
What is the null hypothesis, how to state the null hypothesis, null hypothesis overview.

Why is it Called the “Null”?
The word “null” in this context means that it’s a commonly accepted fact that researchers work to nullify . It doesn’t mean that the statement is null (i.e. amounts to nothing) itself! (Perhaps the term should be called the “nullifiable hypothesis” as that might cause less confusion).
Why Do I need to Test it? Why not just prove an alternate one?
The short answer is, as a scientist, you are required to ; It’s part of the scientific process. Science uses a battery of processes to prove or disprove theories, making sure than any new hypothesis has no flaws. Including both a null and an alternate hypothesis is one safeguard to ensure your research isn’t flawed. Not including the null hypothesis in your research is considered very bad practice by the scientific community. If you set out to prove an alternate hypothesis without considering it, you are likely setting yourself up for failure. At a minimum, your experiment will likely not be taken seriously.

- Null hypothesis : H 0 : The world is flat.
- Alternate hypothesis: The world is round.
Several scientists, including Copernicus , set out to disprove the null hypothesis. This eventually led to the rejection of the null and the acceptance of the alternate. Most people accepted it — the ones that didn’t created the Flat Earth Society !. What would have happened if Copernicus had not disproved the it and merely proved the alternate? No one would have listened to him. In order to change people’s thinking, he first had to prove that their thinking was wrong .
How to State the Null Hypothesis from a Word Problem
You’ll be asked to convert a word problem into a hypothesis statement in statistics that will include a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis . Breaking your problem into a few small steps makes these problems much easier to handle.
Step 2: Convert the hypothesis to math . Remember that the average is sometimes written as μ.
H 1 : μ > 8.2
Broken down into (somewhat) English, that’s H 1 (The hypothesis): μ (the average) > (is greater than) 8.2
Step 3: State what will happen if the hypothesis doesn’t come true. If the recovery time isn’t greater than 8.2 weeks, there are only two possibilities, that the recovery time is equal to 8.2 weeks or less than 8.2 weeks.
H 0 : μ ≤ 8.2
Broken down again into English, that’s H 0 (The null hypothesis): μ (the average) ≤ (is less than or equal to) 8.2
How to State the Null Hypothesis: Part Two
But what if the researcher doesn’t have any idea what will happen.
Example Problem: A researcher is studying the effects of radical exercise program on knee surgery patients. There is a good chance the therapy will improve recovery time, but there’s also the possibility it will make it worse. Average recovery times for knee surgery patients is 8.2 weeks.
Step 1: State what will happen if the experiment doesn’t make any difference. That’s the null hypothesis–that nothing will happen. In this experiment, if nothing happens, then the recovery time will stay at 8.2 weeks.
H 0 : μ = 8.2
Broken down into English, that’s H 0 (The null hypothesis): μ (the average) = (is equal to) 8.2
Step 2: Figure out the alternate hypothesis . The alternate hypothesis is the opposite of the null hypothesis. In other words, what happens if our experiment makes a difference?
H 1 : μ ≠ 8.2
In English again, that’s H 1 (The alternate hypothesis): μ (the average) ≠ (is not equal to) 8.2
That’s How to State the Null Hypothesis!
Check out our Youtube channel for more stats tips!
Gonick, L. (1993). The Cartoon Guide to Statistics . HarperPerennial. Kotz, S.; et al., eds. (2006), Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences , Wiley.
- Null hypothesis
by Marco Taboga , PhD
In a test of hypothesis , a sample of data is used to decide whether to reject or not to reject a hypothesis about the probability distribution from which the sample was extracted.
The hypothesis is called the null hypothesis, or simply "the null".
Table of contents

The null is like the defendant in a criminal trial
How is the null hypothesis tested, example 1 - proportion of defective items, measurement, test statistic, critical region, interpretation, example 2 - reliability of a production plant, rejection and failure to reject, not rejecting and accepting are not the same thing, failure to reject can be due to lack of power, rejections are easier to interpret, but be careful, takeaways - how to (and not to) formulate a null hypothesis, more examples, more details, best practices in science, keep reading the glossary.
Formulating null hypotheses and subjecting them to statistical testing is one of the workhorses of the scientific method.
Scientists in all fields make conjectures about the phenomena they study, translate them into null hypotheses and gather data to test them.
This process resembles a trial:
the defendant (the null hypothesis) is accused of being guilty (wrong);
evidence (data) is gathered in order to prove the defendant guilty (reject the null);
if there is evidence beyond any reasonable doubt, the defendant is found guilty (the null is rejected);
otherwise, the defendant is found not guilty (the null is not rejected).
Keep this analogy in mind because it helps to better understand statistical tests, their limitations, use and misuse, and frequent misinterpretation.
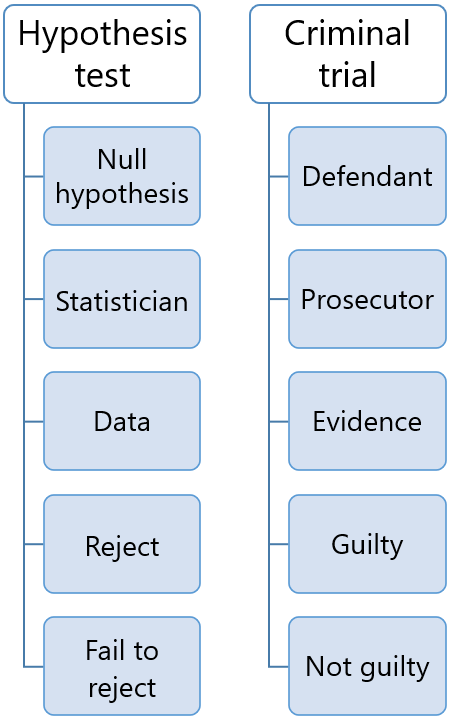
Before collecting the data:
we decide how to summarize the relevant characteristics of the sample data in a single number, the so-called test statistic ;
we derive the probability distribution of the test statistic under the hypothesis that the null is true (the data is regarded as random; therefore, the test statistic is a random variable);
we decide what probability of incorrectly rejecting the null we are willing to tolerate (the level of significance , or size of the test ); the level of significance is typically a small number, such as 5% or 1%.
we choose one or more intervals of values (collectively called rejection region) such that the probability that the test statistic falls within these intervals is equal to the desired level of significance; the rejection region is often a tail of the distribution of the test statistic (one-tailed test) or the union of the left and right tails (two-tailed test).

Then, the data is collected and used to compute the value of the test statistic.
A decision is taken as follows:
if the test statistic falls within the rejection region, then the null hypothesis is rejected;
otherwise, it is not rejected.
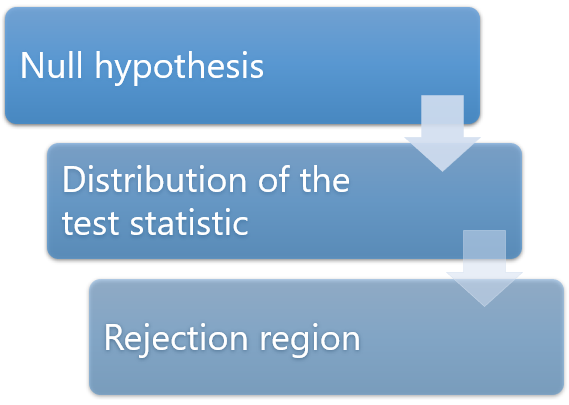
We now make two examples of practical problems that lead to formulate and test a null hypothesis.
A new method is proposed to produce light bulbs.
The proponents claim that it produces less defective bulbs than the method currently in use.
To check the claim, we can set up a statistical test as follows.
We keep the light bulbs on for 10 consecutive days, and then we record whether they are still working at the end of the test period.
The probability that a light bulb produced with the new method is still working at the end of the test period is the same as that of a light bulb produced with the old method.
100 light bulbs are tested:
50 of them are produced with the new method (group A)
the remaining 50 are produced with the old method (group B).
The final data comprises 100 observations of:
an indicator variable which is equal to 1 if the light bulb is still working at the end of the test period and 0 otherwise;
a categorical variable that records the group (A or B) to which each light bulb belongs.
We use the data to compute the proportions of working light bulbs in groups A and B.
The proportions are estimates of the probabilities of not being defective, which are equal for the two groups under the null hypothesis.
We then compute a z-statistic (see here for details) by:
taking the difference between the proportion in group A and the proportion in group B;
standardizing the difference:
we subtract the expected value (which is zero under the null hypothesis);
we divide by the standard deviation (it can be derived analytically).
The distribution of the z-statistic can be approximated by a standard normal distribution .
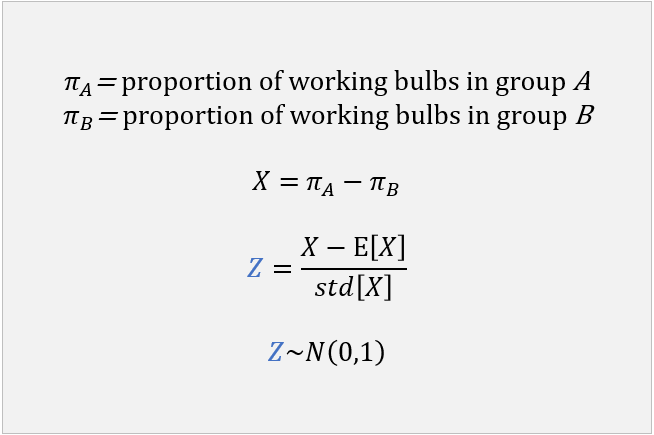
We decide that the level of confidence must be 5%. In other words, we are going to tolerate a 5% probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis.
The critical region is the right 5%-tail of the normal distribution, that is, the set of all values greater than 1.645 (see the glossary entry on critical values if you are wondering how this value was obtained).
If the test statistic is greater than 1.645, then the null hypothesis is rejected; otherwise, it is not rejected.
A rejection is interpreted as significant evidence that the new production method produces less defective items; failure to reject is interpreted as insufficient evidence that the new method is better.
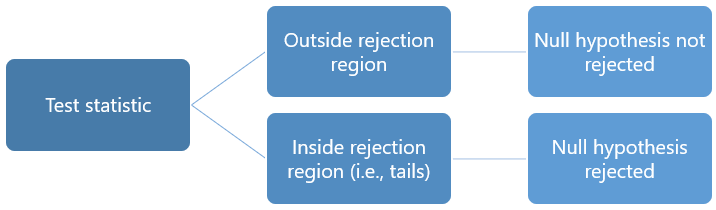
A production plant incurs high costs when production needs to be halted because some machinery fails.
The plant manager has decided that he is not willing to tolerate more than one halt per year on average.
If the expected number of halts per year is greater than 1, he will make new investments in order to improve the reliability of the plant.
A statistical test is set up as follows.
The reliability of the plant is measured by the number of halts.
The number of halts in a year is assumed to have a Poisson distribution with expected value equal to 1 (using the Poisson distribution is common in reliability testing).
The manager cannot wait more than one year before taking a decision.
There will be a single datum at his disposal: the number of halts observed during one year.
The number of halts is used as a test statistic. By assumption, it has a Poisson distribution under the null hypothesis.
The manager decides that the probability of incorrectly rejecting the null can be at most 10%.
A Poisson random variable with expected value equal to 1 takes values:
larger than 1 with probability 26.42%;
larger than 2 with probability 8.03%.
Therefore, it is decided that the critical region will be the set of all values greater than or equal to 3.
If the test statistic is strictly greater than or equal to 3, then the null is rejected; otherwise, it is not rejected.
A rejection is interpreted as significant evidence that the production plant is not reliable enough (the average number of halts per year is significantly larger than tolerated).
Failure to reject is interpreted as insufficient evidence that the plant is unreliable.
This section discusses the main problems that arise in the interpretation of the outcome of a statistical test (reject / not reject).
When the test statistic does not fall within the critical region, then we do not reject the null hypothesis.
Does this mean that we accept the null? Not really.
In general, failure to reject does not constitute, per se, strong evidence that the null hypothesis is true .
Remember the analogy between hypothesis testing and a criminal trial. In a trial, when the defendant is declared not guilty, this does not mean that the defendant is innocent. It only means that there was not enough evidence (not beyond any reasonable doubt) against the defendant.
In turn, lack of evidence can be due:
either to the fact that the defendant is innocent ;
or to the fact that the prosecution has not been able to provide enough evidence against the defendant, even if the latter is guilty .
This is the very reason why courts do not declare defendants innocent, but they use the locution "not guilty".
In a similar fashion, statisticians do not say that the null hypothesis has been accepted, but they say that it has not been rejected.

To better understand why failure to reject does not in general constitute strong evidence that the null hypothesis is true, we need to use the concept of statistical power .
The power of a test is the probability (calculated ex-ante, i.e., before observing the data) that the null will be rejected when another hypothesis (called the alternative hypothesis ) is true.
Let's consider the first of the two examples above (the production of light bulbs).
In that example, the null hypothesis is: the probability that a light bulb is defective does not decrease after introducing a new production method.
Let's make the alternative hypothesis that the probability of being defective is 1% smaller after changing the production process (assume that a 1% decrease is considered a meaningful improvement by engineers).
How much is the ex-ante probability of rejecting the null if the alternative hypothesis is true?
If this probability (the power of the test) is small, then it is very likely that we will not reject the null even if it is wrong.
If we use the analogy with criminal trials, low power means that most likely the prosecution will not be able to provide sufficient evidence, even if the defendant is guilty.
Thus, in the case of lack of power, failure to reject is almost meaningless (it was anyway highly likely).
This is why, before performing a test, it is good statistical practice to compute its power against a relevant alternative .
If the power is found to be too small, there are usually remedies. In particular, statistical power can usually be increased by increasing the sample size (see, e.g., the lecture on hypothesis tests about the mean ).
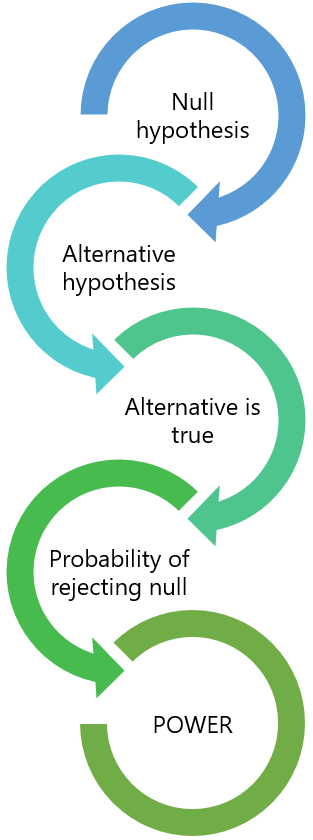
As we have explained above, interpreting a failure to reject the null hypothesis is not always straightforward. Instead, interpreting a rejection is somewhat easier.
When we reject the null, we know that the data has provided a lot of evidence against the null. In other words, it is unlikely (how unlikely depends on the size of the test) that the null is true given the data we have observed.
There is an important caveat though. The null hypothesis is often made up of several assumptions, including:
the main assumption (the one we are testing);
other assumptions (e.g., technical assumptions) that we need to make in order to set up the hypothesis test.
For instance, in Example 2 above (reliability of a production plant), the main assumption is that the expected number of production halts per year is equal to 1. But there is also a technical assumption: the number of production halts has a Poisson distribution.
It must be kept in mind that a rejection is always a joint rejection of the main assumption and all the other assumptions .
Therefore, we should always ask ourselves whether the null has been rejected because the main assumption is wrong or because the other assumptions are violated.
In the case of Example 2 above, is a rejection of the null due to the fact that the expected number of halts is greater than 1 or is it due to the fact that the distribution of the number of halts is very different from a Poisson distribution?
When we suspect that a rejection is due to the inappropriateness of some technical assumption (e.g., assuming a Poisson distribution in the example), we say that the rejection could be due to misspecification of the model .
The right thing to do when these kind of suspicions arise is to conduct so-called robustness checks , that is, to change the technical assumptions and carry out the test again.
In our example, we could re-run the test by assuming a different probability distribution for the number of halts (e.g., a negative binomial or a compound Poisson - do not worry if you have never heard about these distributions).
If we keep obtaining a rejection of the null even after changing the technical assumptions several times, the we say that our rejection is robust to several different specifications of the model .

What are the main practical implications of everything we have said thus far? How does the theory above help us to set up and test a null hypothesis?
What we said can be summarized in the following guiding principles:
A test of hypothesis is like a criminal trial and you are the prosecutor . You want to find evidence that the defendant (the null hypothesis) is guilty. Your job is not to prove that the defendant is innocent. If you find yourself hoping that the defendant is found not guilty (i.e., the null is not rejected) then something is wrong with the way you set up the test. Remember: you are the prosecutor.
Compute the power of your test against one or more relevant alternative hypotheses. Do not run a test if you know ex-ante that it is unlikely to reject the null when the alternative hypothesis is true.
Beware of technical assumptions that you add to the main assumption you want to test. Make robustness checks in order to verify that the outcome of the test is not biased by model misspecification.
More examples of null hypotheses and how to test them can be found in the following lectures.
| Where the example is found | Null hypothesis |
|---|---|
| The mean of a normal distribution is equal to a certain value | |
| The variance of a normal distribution is equal to a certain value | |
| A vector of parameters estimated by MLE satisfies a set of linear or non-linear restrictions | |
| A regression coefficient is equal to a certain value |
The lecture on Hypothesis testing provides a more detailed mathematical treatment of null hypotheses and how they are tested.
This lecture on the null hypothesis was featured in Stanford University's Best practices in science .

Previous entry: Normal equations
Next entry: Parameter
How to cite
Please cite as:
Taboga, Marco (2021). "Null hypothesis", Lectures on probability theory and mathematical statistics. Kindle Direct Publishing. Online appendix. https://www.statlect.com/glossary/null-hypothesis.
Most of the learning materials found on this website are now available in a traditional textbook format.
- Permutations
- Characteristic function
- Almost sure convergence
- Likelihood ratio test
- Uniform distribution
- Bernoulli distribution
- Multivariate normal distribution
- Chi-square distribution
- Maximum likelihood
- Mathematical tools
- Fundamentals of probability
- Probability distributions
- Asymptotic theory
- Fundamentals of statistics
- About Statlect
- Cookies, privacy and terms of use
- Precision matrix
- Distribution function
- Mean squared error
- IID sequence
- To enhance your privacy,
- we removed the social buttons,
- but don't forget to share .
What is The Null Hypothesis & When Do You Reject The Null Hypothesis
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A null hypothesis is a statistical concept suggesting no significant difference or relationship between measured variables. It’s the default assumption unless empirical evidence proves otherwise.
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (i.e., one variable does not affect the other).
The null hypothesis is the statement that a researcher or an investigator wants to disprove.
Testing the null hypothesis can tell you whether your results are due to the effects of manipulating the dependent variable or due to random chance.
How to Write a Null Hypothesis
Null hypotheses (H0) start as research questions that the investigator rephrases as statements indicating no effect or relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
It is a default position that your research aims to challenge or confirm.
For example, if studying the impact of exercise on weight loss, your null hypothesis might be:
There is no significant difference in weight loss between individuals who exercise daily and those who do not.
Examples of Null Hypotheses
| Research Question | Null Hypothesis |
|---|---|
| Do teenagers use cell phones more than adults? | Teenagers and adults use cell phones the same amount. |
| Do tomato plants exhibit a higher rate of growth when planted in compost rather than in soil? | Tomato plants show no difference in growth rates when planted in compost rather than soil. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation does not decrease the incidence of depression. |
| Does daily exercise increase test performance? | There is no relationship between daily exercise time and test performance. |
| Does the new vaccine prevent infections? | The vaccine does not affect the infection rate. |
| Does flossing your teeth affect the number of cavities? | Flossing your teeth has no effect on the number of cavities. |
When Do We Reject The Null Hypothesis?
We reject the null hypothesis when the data provide strong enough evidence to conclude that it is likely incorrect. This often occurs when the p-value (probability of observing the data given the null hypothesis is true) is below a predetermined significance level.
If the collected data does not meet the expectation of the null hypothesis, a researcher can conclude that the data lacks sufficient evidence to back up the null hypothesis, and thus the null hypothesis is rejected.
Rejecting the null hypothesis means that a relationship does exist between a set of variables and the effect is statistically significant ( p > 0.05).
If the data collected from the random sample is not statistically significance , then the null hypothesis will be accepted, and the researchers can conclude that there is no relationship between the variables.
You need to perform a statistical test on your data in order to evaluate how consistent it is with the null hypothesis. A p-value is one statistical measurement used to validate a hypothesis against observed data.
Calculating the p-value is a critical part of null-hypothesis significance testing because it quantifies how strongly the sample data contradicts the null hypothesis.
The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p -value between 0 and 1. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis.
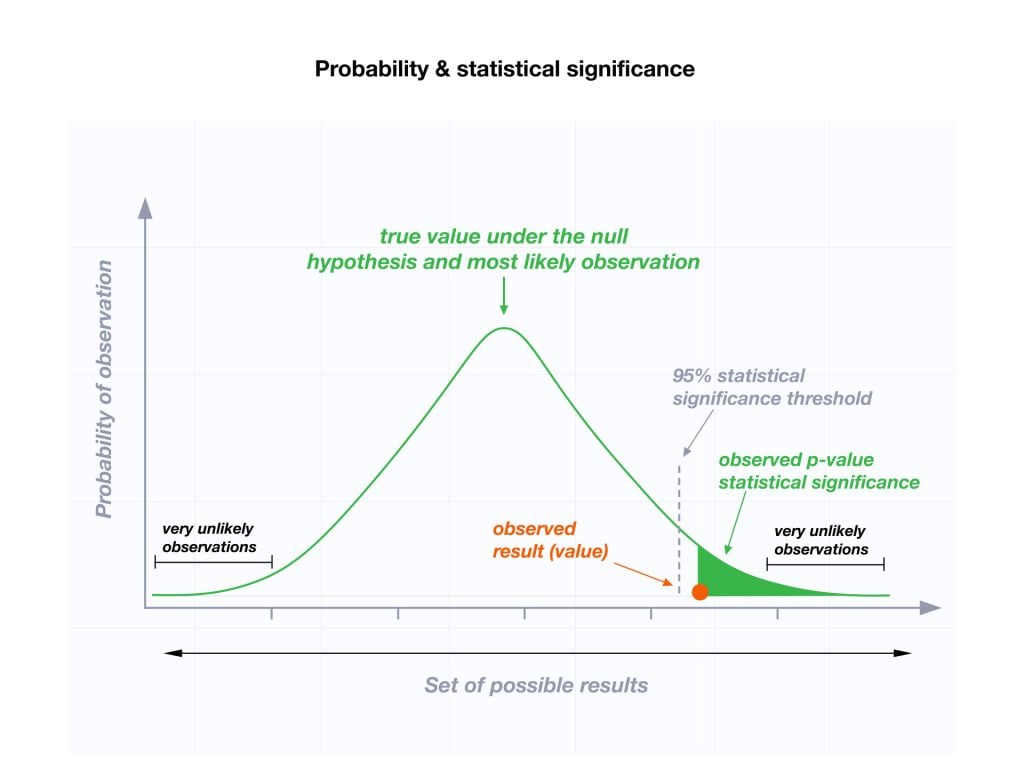
Usually, a researcher uses a confidence level of 95% or 99% (p-value of 0.05 or 0.01) as general guidelines to decide if you should reject or keep the null.
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level, you reject the null hypothesis.
In other words, smaller p-values are taken as stronger evidence against the null hypothesis. Conversely, when the p-value is greater than your significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
In this case, the sample data provides insufficient data to conclude that the effect exists in the population.
Because you can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population, your inferences about a population will sometimes be incorrect.
When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error. When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s called a type II error.
Why Do We Never Accept The Null Hypothesis?
The reason we do not say “accept the null” is because we are always assuming the null hypothesis is true and then conducting a study to see if there is evidence against it. And, even if we don’t find evidence against it, a null hypothesis is not accepted.
A lack of evidence only means that you haven’t proven that something exists. It does not prove that something doesn’t exist.
It is risky to conclude that the null hypothesis is true merely because we did not find evidence to reject it. It is always possible that researchers elsewhere have disproved the null hypothesis, so we cannot accept it as true, but instead, we state that we failed to reject the null.
One can either reject the null hypothesis, or fail to reject it, but can never accept it.
Why Do We Use The Null Hypothesis?
We can never prove with 100% certainty that a hypothesis is true; We can only collect evidence that supports a theory. However, testing a hypothesis can set the stage for rejecting or accepting this hypothesis within a certain confidence level.
The null hypothesis is useful because it can tell us whether the results of our study are due to random chance or the manipulation of a variable (with a certain level of confidence).
A null hypothesis is rejected if the measured data is significantly unlikely to have occurred and a null hypothesis is accepted if the observed outcome is consistent with the position held by the null hypothesis.
Rejecting the null hypothesis sets the stage for further experimentation to see if a relationship between two variables exists.
Hypothesis testing is a critical part of the scientific method as it helps decide whether the results of a research study support a particular theory about a given population. Hypothesis testing is a systematic way of backing up researchers’ predictions with statistical analysis.
It helps provide sufficient statistical evidence that either favors or rejects a certain hypothesis about the population parameter.
Purpose of a Null Hypothesis
- The primary purpose of the null hypothesis is to disprove an assumption.
- Whether rejected or accepted, the null hypothesis can help further progress a theory in many scientific cases.
- A null hypothesis can be used to ascertain how consistent the outcomes of multiple studies are.
Do you always need both a Null Hypothesis and an Alternative Hypothesis?
The null (H0) and alternative (Ha or H1) hypotheses are two competing claims that describe the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. They are mutually exclusive, which means that only one of the two hypotheses can be true.
While the null hypothesis states that there is no effect in the population, an alternative hypothesis states that there is statistical significance between two variables.
The goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample. In order to undertake hypothesis testing, you must express your research hypothesis as a null and alternative hypothesis. Both hypotheses are required to cover every possible outcome of the study.
What is the difference between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis claims that there is an effect or relationship in the population.
It is the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are always mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
What are some problems with the null hypothesis?
One major problem with the null hypothesis is that researchers typically will assume that accepting the null is a failure of the experiment. However, accepting or rejecting any hypothesis is a positive result. Even if the null is not refuted, the researchers will still learn something new.
Why can a null hypothesis not be accepted?
We can either reject or fail to reject a null hypothesis, but never accept it. If your test fails to detect an effect, this is not proof that the effect doesn’t exist. It just means that your sample did not have enough evidence to conclude that it exists.
We can’t accept a null hypothesis because a lack of evidence does not prove something that does not exist. Instead, we fail to reject it.
Failing to reject the null indicates that the sample did not provide sufficient enough evidence to conclude that an effect exists.
If the p-value is greater than the significance level, then you fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Is a null hypothesis directional or non-directional?
A hypothesis test can either contain an alternative directional hypothesis or a non-directional alternative hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is one that contains the less than (“<“) or greater than (“>”) sign.
A nondirectional hypothesis contains the not equal sign (“≠”). However, a null hypothesis is neither directional nor non-directional.
A null hypothesis is a prediction that there will be no change, relationship, or difference between two variables.
The directional hypothesis or nondirectional hypothesis would then be considered alternative hypotheses to the null hypothesis.
Gill, J. (1999). The insignificance of null hypothesis significance testing. Political research quarterly , 52 (3), 647-674.
Krueger, J. (2001). Null hypothesis significance testing: On the survival of a flawed method. American Psychologist , 56 (1), 16.
Masson, M. E. (2011). A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior research methods , 43 , 679-690.
Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods , 5 (2), 241.
Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test. Psychological bulletin , 57 (5), 416.
- Data Science
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Computer Vision
- Artificial Intelligence
- AI ML DS Interview Series
- AI ML DS Projects series
- Data Engineering
- Web Scrapping
Understanding Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing involves formulating assumptions about population parameters based on sample statistics and rigorously evaluating these assumptions against empirical evidence. This article sheds light on the significance of hypothesis testing and the critical steps involved in the process.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
A hypothesis is an assumption or idea, specifically a statistical claim about an unknown population parameter. For example, a judge assumes a person is innocent and verifies this by reviewing evidence and hearing testimony before reaching a verdict.
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
To test the validity of the claim or assumption about the population parameter:
- A sample is drawn from the population and analyzed.
- The results of the analysis are used to decide whether the claim is true or not.
Example: You say an average height in the class is 30 or a boy is taller than a girl. All of these is an assumption that we are assuming, and we need some statistical way to prove these. We need some mathematical conclusion whatever we are assuming is true.
Defining Hypotheses
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): In statistics, the null hypothesis is a general statement or default position that there is no relationship between two measured cases or no relationship among groups. In other words, it is a basic assumption or made based on the problem knowledge. Example : A company’s mean production is 50 units/per da H 0 : [Tex]\mu [/Tex] = 50.
- Alternative hypothesis (H 1 ): The alternative hypothesis is the hypothesis used in hypothesis testing that is contrary to the null hypothesis. Example: A company’s production is not equal to 50 units/per day i.e. H 1 : [Tex]\mu [/Tex] [Tex]\ne [/Tex] 50.
Key Terms of Hypothesis Testing
- Level of significance : It refers to the degree of significance in which we accept or reject the null hypothesis. 100% accuracy is not possible for accepting a hypothesis, so we, therefore, select a level of significance that is usually 5%. This is normally denoted with [Tex]\alpha[/Tex] and generally, it is 0.05 or 5%, which means your output should be 95% confident to give a similar kind of result in each sample.
- P-value: The P value , or calculated probability, is the probability of finding the observed/extreme results when the null hypothesis(H0) of a study-given problem is true. If your P-value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample claims to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
- Critical value : The critical value in statistics is a threshold or cutoff point used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test.
- Degrees of freedom: Degrees of freedom are associated with the variability or freedom one has in estimating a parameter. The degrees of freedom are related to the sample size and determine the shape.
Why do we use Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is an important procedure in statistics. Hypothesis testing evaluates two mutually exclusive population statements to determine which statement is most supported by sample data. When we say that the findings are statistically significant, thanks to hypothesis testing.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Test
One tailed test focuses on one direction, either greater than or less than a specified value. We use a one-tailed test when there is a clear directional expectation based on prior knowledge or theory. The critical region is located on only one side of the distribution curve. If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
One-Tailed Test
There are two types of one-tailed test:
- Left-Tailed (Left-Sided) Test: The alternative hypothesis asserts that the true parameter value is less than the null hypothesis. Example: H 0 : [Tex]\mu \geq 50 [/Tex] and H 1 : [Tex]\mu < 50 [/Tex]
- Right-Tailed (Right-Sided) Test : The alternative hypothesis asserts that the true parameter value is greater than the null hypothesis. Example: H 0 : [Tex]\mu \leq50 [/Tex] and H 1 : [Tex]\mu > 50 [/Tex]
Two-Tailed Test
A two-tailed test considers both directions, greater than and less than a specified value.We use a two-tailed test when there is no specific directional expectation, and want to detect any significant difference.
Example: H 0 : [Tex]\mu = [/Tex] 50 and H 1 : [Tex]\mu \neq 50 [/Tex]
To delve deeper into differences into both types of test: Refer to link
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in Hypothesis Testing?
In hypothesis testing, Type I and Type II errors are two possible errors that researchers can make when drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. These errors are associated with the decisions made regarding the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
- Type I error: When we reject the null hypothesis, although that hypothesis was true. Type I error is denoted by alpha( [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ).
- Type II errors : When we accept the null hypothesis, but it is false. Type II errors are denoted by beta( [Tex]\beta [/Tex] ).
Null Hypothesis is True | Null Hypothesis is False | |
|---|---|---|
Null Hypothesis is True (Accept) | Correct Decision | Type II Error (False Negative) |
Alternative Hypothesis is True (Reject) | Type I Error (False Positive) | Correct Decision |
How does Hypothesis Testing work?
Step 1: define null and alternative hypothesis.
State the null hypothesis ( [Tex]H_0 [/Tex] ), representing no effect, and the alternative hypothesis ( [Tex]H_1 [/Tex] ), suggesting an effect or difference.
We first identify the problem about which we want to make an assumption keeping in mind that our assumption should be contradictory to one another, assuming Normally distributed data.
Step 2 – Choose significance level
Select a significance level ( [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ), typically 0.05, to determine the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis. It provides validity to our hypothesis test, ensuring that we have sufficient data to back up our claims. Usually, we determine our significance level beforehand of the test. The p-value is the criterion used to calculate our significance value.
Step 3 – Collect and Analyze data.
Gather relevant data through observation or experimentation. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to obtain a test statistic.
Step 4-Calculate Test Statistic
The data for the tests are evaluated in this step we look for various scores based on the characteristics of data. The choice of the test statistic depends on the type of hypothesis test being conducted.
There are various hypothesis tests, each appropriate for various goal to calculate our test. This could be a Z-test , Chi-square , T-test , and so on.
- Z-test : If population means and standard deviations are known. Z-statistic is commonly used.
- t-test : If population standard deviations are unknown. and sample size is small than t-test statistic is more appropriate.
- Chi-square test : Chi-square test is used for categorical data or for testing independence in contingency tables
- F-test : F-test is often used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare variances or test the equality of means across multiple groups.
We have a smaller dataset, So, T-test is more appropriate to test our hypothesis.
T-statistic is a measure of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the variability within each group. It is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the standard error of the difference. It is also known as the t-value or t-score.
Step 5 – Comparing Test Statistic:
In this stage, we decide where we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis. There are two ways to decide where we should accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Method A: Using Crtical values
Comparing the test statistic and tabulated critical value we have,
- If Test Statistic>Critical Value: Reject the null hypothesis.
- If Test Statistic≤Critical Value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Note: Critical values are predetermined threshold values that are used to make a decision in hypothesis testing. To determine critical values for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Method B: Using P-values
We can also come to an conclusion using the p-value,
- If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level i.e. ( [Tex]p\leq\alpha [/Tex] ), you reject the null hypothesis. This indicates that the observed results are unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, providing evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than the significance level i.e. ( [Tex]p\geq \alpha[/Tex] ), you fail to reject the null hypothesis. This suggests that the observed results are consistent with what would be expected under the null hypothesis.
Note : The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Step 7- Interpret the Results
At last, we can conclude our experiment using method A or B.
Calculating test statistic
To validate our hypothesis about a population parameter we use statistical functions . We use the z-score, p-value, and level of significance(alpha) to make evidence for our hypothesis for normally distributed data .
1. Z-statistics:
When population means and standard deviations are known.
[Tex]z = \frac{\bar{x} – \mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}[/Tex]
- [Tex]\bar{x} [/Tex] is the sample mean,
- μ represents the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation
- and n is the size of the sample.
2. T-Statistics
T test is used when n<30,
t-statistic calculation is given by:
[Tex]t=\frac{x̄-μ}{s/\sqrt{n}} [/Tex]
- t = t-score,
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean,
- s = standard deviation of the sample,
- n = sample size
3. Chi-Square Test
Chi-Square Test for Independence categorical Data (Non-normally distributed) using:
[Tex]\chi^2 = \sum \frac{(O_{ij} – E_{ij})^2}{E_{ij}}[/Tex]
- [Tex]O_{ij}[/Tex] is the observed frequency in cell [Tex]{ij} [/Tex]
- i,j are the rows and columns index respectively.
- [Tex]E_{ij}[/Tex] is the expected frequency in cell [Tex]{ij}[/Tex] , calculated as : [Tex]\frac{{\text{{Row total}} \times \text{{Column total}}}}{{\text{{Total observations}}}}[/Tex]
Real life Examples of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s examine hypothesis testing using two real life situations,
Case A: D oes a New Drug Affect Blood Pressure?
Imagine a pharmaceutical company has developed a new drug that they believe can effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Before bringing the drug to market, they need to conduct a study to assess its impact on blood pressure.
- Before Treatment: 120, 122, 118, 130, 125, 128, 115, 121, 123, 119
- After Treatment: 115, 120, 112, 128, 122, 125, 110, 117, 119, 114
Step 1 : Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis : (H 0 )The new drug has no effect on blood pressure.
- Alternate Hypothesis : (H 1 )The new drug has an effect on blood pressure.
Step 2: Define the Significance level
Let’s consider the Significance level at 0.05, indicating rejection of the null hypothesis.
If the evidence suggests less than a 5% chance of observing the results due to random variation.
Step 3 : Compute the test statistic
Using paired T-test analyze the data to obtain a test statistic and a p-value.
The test statistic (e.g., T-statistic) is calculated based on the differences between blood pressure measurements before and after treatment.
t = m/(s/√n)
- m = mean of the difference i.e X after, X before
- s = standard deviation of the difference (d) i.e d i = X after, i − X before,
- n = sample size,
then, m= -3.9, s= 1.8 and n= 10
we, calculate the , T-statistic = -9 based on the formula for paired t test
Step 4: Find the p-value
The calculated t-statistic is -9 and degrees of freedom df = 9, you can find the p-value using statistical software or a t-distribution table.
thus, p-value = 8.538051223166285e-06
Step 5: Result
- If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the researchers reject the null hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than 0.05, they fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Since the p-value (8.538051223166285e-06) is less than the significance level (0.05), the researchers reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
Python Implementation of Case A
Let’s create hypothesis testing with python, where we are testing whether a new drug affects blood pressure. For this example, we will use a paired T-test. We’ll use the scipy.stats library for the T-test.
Scipy is a mathematical library in Python that is mostly used for mathematical equations and computations.
We will implement our first real life problem via python,
import numpy as np from scipy import stats # Data before_treatment = np . array ([ 120 , 122 , 118 , 130 , 125 , 128 , 115 , 121 , 123 , 119 ]) after_treatment = np . array ([ 115 , 120 , 112 , 128 , 122 , 125 , 110 , 117 , 119 , 114 ]) # Step 1: Null and Alternate Hypotheses # Null Hypothesis: The new drug has no effect on blood pressure. # Alternate Hypothesis: The new drug has an effect on blood pressure. null_hypothesis = "The new drug has no effect on blood pressure." alternate_hypothesis = "The new drug has an effect on blood pressure." # Step 2: Significance Level alpha = 0.05 # Step 3: Paired T-test t_statistic , p_value = stats . ttest_rel ( after_treatment , before_treatment ) # Step 4: Calculate T-statistic manually m = np . mean ( after_treatment - before_treatment ) s = np . std ( after_treatment - before_treatment , ddof = 1 ) # using ddof=1 for sample standard deviation n = len ( before_treatment ) t_statistic_manual = m / ( s / np . sqrt ( n )) # Step 5: Decision if p_value <= alpha : decision = "Reject" else : decision = "Fail to reject" # Conclusion if decision == "Reject" : conclusion = "There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different." else : conclusion = "There is insufficient evidence to claim a significant difference in average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug." # Display results print ( "T-statistic (from scipy):" , t_statistic ) print ( "P-value (from scipy):" , p_value ) print ( "T-statistic (calculated manually):" , t_statistic_manual ) print ( f "Decision: { decision } the null hypothesis at alpha= { alpha } ." ) print ( "Conclusion:" , conclusion )
T-statistic (from scipy): -9.0 P-value (from scipy): 8.538051223166285e-06 T-statistic (calculated manually): -9.0 Decision: Reject the null hypothesis at alpha=0.05. Conclusion: There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
In the above example, given the T-statistic of approximately -9 and an extremely small p-value, the results indicate a strong case to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of 0.05.
- The results suggest that the new drug, treatment, or intervention has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure.
- The negative T-statistic indicates that the mean blood pressure after treatment is significantly lower than the assumed population mean before treatment.
Case B : Cholesterol level in a population
Data: A sample of 25 individuals is taken, and their cholesterol levels are measured.
Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL): 205, 198, 210, 190, 215, 205, 200, 192, 198, 205, 198, 202, 208, 200, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205.
Populations Mean = 200
Population Standard Deviation (σ): 5 mg/dL(given for this problem)
Step 1: Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H 1 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL.
As the direction of deviation is not given , we assume a two-tailed test, and based on a normal distribution table, the critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) can be calculated through the z-table and are approximately -1.96 and 1.96.
The test statistic is calculated by using the z formula Z = [Tex](203.8 – 200) / (5 \div \sqrt{25}) [/Tex] and we get accordingly , Z =2.039999999999992.
Step 4: Result
Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis. And conclude that, there is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL
Python Implementation of Case B
import scipy.stats as stats import math import numpy as np # Given data sample_data = np . array ( [ 205 , 198 , 210 , 190 , 215 , 205 , 200 , 192 , 198 , 205 , 198 , 202 , 208 , 200 , 205 , 198 , 205 , 210 , 192 , 205 , 198 , 205 , 210 , 192 , 205 ]) population_std_dev = 5 population_mean = 200 sample_size = len ( sample_data ) # Step 1: Define the Hypotheses # Null Hypothesis (H0): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL. # Alternate Hypothesis (H1): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL. # Step 2: Define the Significance Level alpha = 0.05 # Two-tailed test # Critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) critical_value_left = stats . norm . ppf ( alpha / 2 ) critical_value_right = - critical_value_left # Step 3: Compute the test statistic sample_mean = sample_data . mean () z_score = ( sample_mean - population_mean ) / \ ( population_std_dev / math . sqrt ( sample_size )) # Step 4: Result # Check if the absolute value of the test statistic is greater than the critical values if abs ( z_score ) > max ( abs ( critical_value_left ), abs ( critical_value_right )): print ( "Reject the null hypothesis." ) print ( "There is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL." ) else : print ( "Fail to reject the null hypothesis." ) print ( "There is not enough evidence to conclude that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL." )
Reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL.
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
- Although a useful technique, hypothesis testing does not offer a comprehensive grasp of the topic being studied. Without fully reflecting the intricacy or whole context of the phenomena, it concentrates on certain hypotheses and statistical significance.
- The accuracy of hypothesis testing results is contingent on the quality of available data and the appropriateness of statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or poorly formulated hypotheses can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying solely on hypothesis testing may cause analysts to overlook significant patterns or relationships in the data that are not captured by the specific hypotheses being tested. This limitation underscores the importance of complimenting hypothesis testing with other analytical approaches.
Hypothesis testing stands as a cornerstone in statistical analysis, enabling data scientists to navigate uncertainties and draw credible inferences from sample data. By systematically defining null and alternative hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and leveraging statistical tests, researchers can assess the validity of their assumptions. The article also elucidates the critical distinction between Type I and Type II errors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced decision-making process inherent in hypothesis testing. The real-life example of testing a new drug’s effect on blood pressure using a paired T-test showcases the practical application of these principles, underscoring the importance of statistical rigor in data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what are the 3 types of hypothesis test.
There are three types of hypothesis tests: right-tailed, left-tailed, and two-tailed. Right-tailed tests assess if a parameter is greater, left-tailed if lesser. Two-tailed tests check for non-directional differences, greater or lesser.
2.What are the 4 components of hypothesis testing?
Null Hypothesis ( [Tex]H_o [/Tex] ): No effect or difference exists. Alternative Hypothesis ( [Tex]H_1 [/Tex] ): An effect or difference exists. Significance Level ( [Tex]\alpha [/Tex] ): Risk of rejecting null hypothesis when it’s true (Type I error). Test Statistic: Numerical value representing observed evidence against null hypothesis.
3.What is hypothesis testing in ML?
Statistical method to evaluate the performance and validity of machine learning models. Tests specific hypotheses about model behavior, like whether features influence predictions or if a model generalizes well to unseen data.
4.What is the difference between Pytest and hypothesis in Python?
Pytest purposes general testing framework for Python code while Hypothesis is a Property-based testing framework for Python, focusing on generating test cases based on specified properties of the code.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- data-science
- Top Android Apps for 2024
- Top Cell Phone Signal Boosters in 2024
- Best Travel Apps (Paid & Free) in 2024
- The Best Smart Home Devices for 2024
- 15 Most Important Aptitude Topics For Placements [2024]
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

COMMENTS
Null Hypothesis H 0: The correlation in the population is zero: ρ = 0. Alternative Hypothesis H A: The correlation in the population is not zero: ρ ≠ 0. For all these cases, the analysts define the hypotheses before the study. After collecting the data, they perform a hypothesis test to determine whether they can reject the null hypothesis.
When using the p-value to evaluate a hypothesis test, the following rhymes can come in handy:. If the p-value is low, the null must go.. If the p-value is high, the null must fly.. This memory aid relates a p-value less than the established alpha ("the p-value is low") as rejecting the null hypothesis and, likewise, relates a p-value higher than the established alpha ("the p-value is ...
The null hypothesis (H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis (Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the population.". The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That's because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. \(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy ...
The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis are types of conjectures used in statistical tests to make statistical inferences, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions and separating scientific claims from statistical noise.. The statement being tested in a test of statistical significance is called the null hypothesis. The test of significance is designed to assess the strength ...
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
In hypothesis testing, the goal is to see if there is sufficient statistical evidence to reject a presumed null hypothesis in favor of a conjectured alternative hypothesis.The null hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_0\) while the alternative hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_1\). An hypothesis test is a statistical decision; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor ...
The Null hypothesis \(\left(H_{O}\right)\) is a statement about the comparisons, e.g., between a sample statistic and the population, or between two treatment groups. The former is referred to as a one-tailed test whereas the latter is called a two-tailed test. The null hypothesis is typically "no statistical difference" between the ...
A crucial step in null hypothesis testing is finding the likelihood of the sample result if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. A low p value means that the sample result would be unlikely if the null hypothesis were true and leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis. A high p value means that the sample ...
When you perform a hypothesis test, there are four possible outcomes depending on the actual truth (or falseness) of the null hypothesis H 0 and the decision to reject or not. The outcomes are summarized in the following table: Figure 5.14: Type I and type II errors; H 0 IS ACTUALLY; Action: True:
S.3 Hypothesis Testing. In reviewing hypothesis tests, we start first with the general idea. Then, we keep returning to the basic procedures of hypothesis testing, each time adding a little more detail. The general idea of hypothesis testing involves: Making an initial assumption. Collecting evidence (data).
An example of Neyman-Pearson hypothesis testing (or null hypothesis statistical significance testing) can be made by a change to the radioactive suitcase example. If the "suitcase" is actually a shielded container for the transportation of radioactive material, then a test might be used to select among three hypotheses: no radioactive source ...
A hypothesis test uses sample data to determine whether or not some claim about a population parameter is true. Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, which take the following forms: H 0 (Null Hypothesis): Population parameter =, ≤, ≥ some value
Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Introduction to Statistics
The null hypothesis is one of two mutually exclusive theories about the properties of the population in hypothesis testing. Typically, the null hypothesis states that there is no effect (i.e., the effect size equals zero). The null is often signified by H 0.
Let's return finally to the question of whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. If our statistical analysis shows that the significance level is below the cut-off value we have set (e.g., either 0.05 or 0.01), we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. Alternatively, if the significance level is above ...
A hypothesis test consists of five steps: 1. State the hypotheses. State the null and alternative hypotheses. These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true then the other must be false. 2. Determine a significance level to use for the hypothesis. Decide on a significance level.
In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with H0.
Step 1: Figure out the hypothesis from the problem. The hypothesis is usually hidden in a word problem, and is sometimes a statement of what you expect to happen in the experiment. The hypothesis in the above question is "I expect the average recovery period to be greater than 8.2 weeks.". Step 2: Convert the hypothesis to math.
Null hypothesis. by Marco Taboga, PhD. In a test of hypothesis, a sample of data is used to decide whether to reject or not to reject a hypothesis about the probability distribution from which the sample was extracted.. The hypothesis is called the null hypothesis, or simply "the null".
A tutorial on a practical Bayesian alternative to null-hypothesis significance testing. Behavior research methods, 43, 679-690. Nickerson, R. S. (2000). Null hypothesis significance testing: a review of an old and continuing controversy. Psychological methods, 5(2), 241. Rozeboom, W. W. (1960). The fallacy of the null-hypothesis significance test.
Aug 5, 2022. 6. Photo by Andrew George on Unsplash. Student's t-tests are commonly used in inferential statistics for testing a hypothesis on the basis of a difference between sample means. However, people often misinterpret the results of t-tests, which leads to false research findings and a lack of reproducibility of studies.
Null hypothesis, often denoted as H0, is a foundational concept in statistical hypothesis testing. It represents an assumption that no significant difference, effect, or relationship exists between variables within a population. Learn more about Null Hypothesis, its formula, symbol and example in this article
16.3.5 Step 5: Determine the probability of the data under the null hypothesis. This is the step where NHST starts to violate our intuition - rather than determining the likelihood that the null hypothesis is true given the data, we instead determine the likelihood of the data under the null hypothesis - because we started out by assuming that the null hypothesis is true!
Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
Statistics document from University of Cincinnati, Main Campus, 1 page, CHAPTER 8 Hypothesis test- inferential procedure; uses data from sample to draw conclusion about population Critical region- sample outcomes that are very UNLIKELY to occur if null is true. Enough to reject hypothesis Alpha level- probability of type 1 er