6 editor-approved Amazon bestsellers for fall — from $10
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Concert Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
- TODAY Plaza

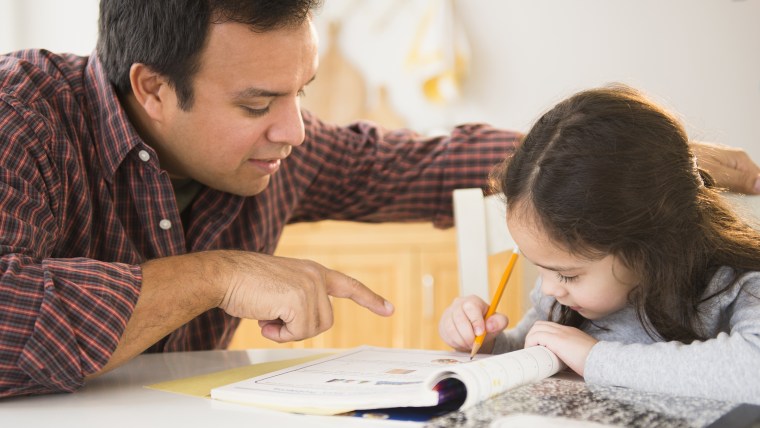
The end of homework? Why some schools are banning homework
Fed up with the tension over homework, some schools are opting out altogether.
No-homework policies are popping up all over, including schools in the U.S., where the shift to the Common Core curriculum is prompting educators to rethink how students spend their time.
“Homework really is a black hole,” said Etta Kralovec, an associate professor of teacher education at the University of Arizona South and co-author of “The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning.”
“I think teachers are going to be increasingly interested in having total control over student learning during the class day and not relying on homework as any kind of activity that’s going to support student learning.”
College de Saint-Ambroise, an elementary school in Quebec, is the latest school to ban homework, announcing this week that it would try the new policy for a year. The decision came after officials found that it was “becoming more and more difficult” for children to devote time to all the assignments they were bringing home, Marie-Ève Desrosiers, a spokeswoman with the Jonquière School Board, told the CBC .
Kralovec called the ban on homework a movement, though she estimated just a small handful of schools in the U.S. have such policies.
Gaithersburg Elementary School in Rockville, Maryland, is one of them, eliminating the traditional concept of homework in 2012. The policy is still in place and working fine, Principal Stephanie Brant told TODAY Parents. The school simply asks that students read 30 minutes each night.
“We felt like with the shift to the Common Core curriculum, and our knowledge of how our students need to think differently… we wanted their time to be spent in meaningful ways,” Brant said.
“We’re constantly asking parents for feedback… and everyone’s really happy with it so far. But it’s really a culture shift.”

It was a decision that was best for her community, Brant said, adding that she often gets phone calls from other principals inquiring how it’s working out.
The VanDamme Academy, a private K-8 school in Aliso Viejo, California, has a similar policy , calling homework “largely pointless.”
The Buffalo Academy of Scholars, a private school in Buffalo, New York, touts that it has called “a truce in the homework battle” and promises that families can “enjoy stress-free, homework-free evenings and more quality time together at home.”
Some schools have taken yet another approach. At Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Illinois, teachers do assign homework but it doesn’t count towards a student’s final grade.
Many schools in the U.S. have toyed with the idea of opting out of homework, but end up changing nothing because it is such a contentious issue among parents, Kralovec noted.
“There’s a huge philosophical divide between parents who want their kids to be very scheduled, very driven, and very ambitiously focused at school -- those parents want their kids to do homework,” she said.
“And then there are the parents who want a more child-centered life with their kids, who want their kids to be able to explore different aspects of themselves, who think their kids should have free time.”
So what’s the right amount of time to spend on homework?
National PTA spokeswoman Heidi May pointed to the organization’s “ 10 minute rule ,” which recommends kids spend about 10 minutes on homework per night for every year they’re in school. That would mean 10 minutes for a first-grader and an hour for a child in the sixth grade.
But many parents say their kids must spend much longer on their assignments. Last year, a New York dad tried to do his eight-grader’s homework for a week and it took him at least three hours on most nights.
More than 80 percent of respondents in a TODAY.com poll complained kids have too much homework. For homework critics like Kralovec, who said research shows homework has little value at the elementary and middle school level, the issue is simple.
“Kids are at school 7 or 8 hours a day, that’s a full working day and why should they have to take work home?” she asked.
Follow A. Pawlowski on Google+ and Twitter .

Empty nesters go straight from college dropoff to … Disney World!

30 do-it-yourself activities to cure kids’ boredom

How to talk to children about shootings: An age-by-age guide

Jenna Bush Hager shares how she helps her kids with first day of school nerves

Taylor Fritz's parents are famous in their own right: All about Guy and Kathy

See Hoda Kotb’s daughters hug it out in adorable video from first day of school post

Eugene Levy will host the Emmys with son Dan. What to know about his 2 kids

Tour Jennifer Garner's 'treehouse' home, which includes a Harry Potter-inspired office

'Fall' for these autumn-inspired baby names

Rory Feek and his older daughters battle publicly over care of youngest daughter Indiana
International
- U.S. Elections
- Left Opinions
- Mon David Pakman
- Tue Ruben Navarrette
- Wed Adrienne Lawrence
- Thu Jordan Reid
- Fri Dr. Rashad Richey
- Right Opinions
- Mon Larry Lindsey
- Tue Ben Weingarten
- Wed Newt Gingrich
- Timothy Carney
- John Fortier
- Matthew Continetti
- Robert Doar
- Fri Star Parker
- Peter Zeihan
- Dr. Frank Luntz
- Weapons and Warfare™
- America Speaks with Dr. Frank Luntz
- Editorial Mission

California set to approve groundbreaking law that cuts homework, alleviates stress
By Jack Aylmer (Energy Correspondent), Mathew Grisham (Digital Producer), Mirlie Larose (Producer), Jack Henry (Video Editor)
In California, a new law that could dramatically change the way homework is handled in state schools is nearing approval. The Healthy Homework Act is now awaiting the governor’s signature after passing both chambers of the state Legislature.
It aims to not only reduce homework, but also stress among students and parents. The author of the bill, Assemblywoman Pilar Schiavo, says she was inspired by a conversation with her young daughter, who asked if she could “ban homework.”

Download the SAN app today to stay up-to-date with Unbiased. Straight Facts™.
Point phone camera here
Schiavo said many parents support the idea, expressing frustration of the lack of quality time with their kids. Heavy homework and extracurricular activities topped the list of those potential distractions.
People supporting the current levels of homework argue that it sets up kids for future success. Supporters of the new bill argue that it can damage mental health and place an unnecessary burden on families.
The bill aims to address these concerns by encouraging teachers to carefully consider whether the homework they assign requires parental support or access to technology that not all students have. The Administrators Association of San Diego City Schools, a union representing management employees, is urging lawmakers to pass the legislation.
The union said it would help address the harmful effects of excessive or poorly designed homework , and mentioned that homework is linked to stress, headaches, exhaustion and even physical health problems like weight loss.
Mental and physical health aren’t the only concerns. The rise of artificial intelligence also raises new challenges in the classroom. Educators worry that students are using tools like ChatGPT to complete their assignments.
Related Stories
- LA school district joins growing number of schools considering cellphone bans
- 4-day school week gains popularity for teacher recruitment
- Utah schools spending $72M in upgrades amid rise in school shootings
Jack Aylmer
IN CALIFORNIA, A NEW LAW THAT COULD DRAMATICALLY CHANGE THE WAY HOMEWORK IS HANDLED IS NEARING APPROVAL.
THE HEALTHY HOMEWORK ACT, WHICH PASSED BOTH CHAMBERS OF THE STATE LEGISLATURE, IS NOW AWAITING THE GOVERNOR’S SIGNATURE. IF IT BECOMES LAW, IT COULD NOT ONLY REDUCE HOMEWORK BUT REDUCE STRESS FOR BOTH STUDENTS AND PARENTS.
THE AUTHOR OF THE BILL, ASSEMBLYWOMAN PILAR SCHIAVO, SAYS SHE WAS INSPIRED BY CONVERSATION WITH HER NINE-YEAR-OLD DAUGHTER, WHO ASKED IF SHE COULD “BAN HOMEWORK.”
SCHIAVO SAYS MANY PARENTS SUPPORT THE IDEA, EXPRESSING FRUSTRATION OVER THE LACK OF QUALITY TIME WITH THEIR KIDS DUE TO HEAVY HOMEWORK LOADS AND EXTRACURRICULAR ACTIVITIES.
SUPPORTERS OF HOMEWORK BELIEVE IT SETS KIDS UP FOR FUTURE SUCCESS, WHILE OPPONENTS ARGUE IT CAN DAMAGE MENTAL HEALTH AND PLACE AN UNNECESSARY BURDEN ON FAMILIES.
THE BILL AIMS TO ADDRESS THESE CONCERNS BY ENCOURAGING TEACHERS TO CAREFULLY CONSIDER WHETHER THE HOMEWORK THEY ASSIGN REQUIRES PARENTAL SUPPORT OR ACCESS TO TECHNOLOGY, THAT NOT ALL STUDENTS HAVE.
THE ADMINISTRATORS ASSOCIATION OF SAN DIEGO CITY SCHOOLS, A UNION REPRESENTING MANAGEMENT EMPLOYEES, IS URGING LAWMAKERS TO PASS THE HEALTHY HOMEWORK ACT, SAYING IT WOULD HELP ADDRESS THE HARMFUL EFFECTS OF EXCESSIVE OR POORLY DESIGNED HOMEWORK. THE UNION MENTIONED THAT HOMEWORK IS LINKED TO STRESS, HEADACHES, EXHAUSTION AND EVEN PHYSICAL HEALTH PROBLEMS LIKE WEIGHT LOSS.
MENTAL and PHYSICAL HEALTH AREN’T THE ONLY CONCERNS, THE RISE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ALSO RAISES NEW CHALLENGES IN THE CLASSROOM. EDUCATORS WORRY THAT STUDENT ARE USING TOOLS LIKE CHAT GPT TO COMPLETE THEIR ASSIGNMENTS.
AS CALIFORNIA INCHES CLOSER TO POTENTIALLY PASSING THE HEALTHY HOMEWORK LAW, THE CONVERSATION AROUND HOMEWORK, AND “HOW MUCH” CONTINUES TO EVOLVE.
WE’LL KEEP YOU UPDATED AS THIS STORY DEVELOPS.
MediaMiss™
Underreported stories from each side

26 states have blocked Title IX, nearly 700 schools won’t comply

RFK Jr. sues to remove himself from Wisconsin’s presidential ballot
Unbiased news.
MOST POPULAR

NASA deploys new solar sail system that could advance space exploration

California set to approve law that cuts homework, alleviates stress

Several dead, over two dozen injured in school shooting outside of Atlanta

Amazon says ‘error’ led Alexa to biased responses to Trump, Harris questions
Kamala harris pushes for 10x boost in new small business tax break, feds announce crackdown on russian disinformation in 2024 election, georgia school shooting suspect was questioned over online threats: fbi, livestock feed company admits fault in delivery that killed 70 horses, federal judge rules illinois’ concealed carry public transit ban unconstitutional, meta board says ‘from the river to the sea’ phrase is not hate speech, cartel leader’s arrest sparks fears of retaliation at us-mexico border, venezuela’s maduro orders christmas to start in october, wants opponent arrested, volvo improving electric trucks to make them a more viable long-hauling option, california passes landmark bill on ai replication of deceased performers, x expects brazil to shut down platform ‘soon’ as musk’s fight with judge heats up, new weapons and warfare episode, unbiased news. directly to your inbox. free.
Learn more about our emails. Unsubscribe anytime.
By entering your email, you agree to the Terms & Conditions and acknowledge the Privacy Policy .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Homework – Top 3 Pros and Cons
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- How Nayib Bukele’s ‘Iron Fist’ Has Transformed El Salvador
- What Makes a Friendship Last Forever?
- How to Read Political Polls Like a Pro
- Long COVID Looks Different in Kids
- What a $129 Frying Pan Says About America’s Eating Habits
- How ‘Friendshoring’ Made Southeast Asia Pivotal to the AI Revolution
- Column: Your Cynicism Isn’t Helping Anybody
- The 32 Most Anticipated Books of Fall 2024
Contact us at [email protected]
NY School District Mulls Getting Rid of Homework
By ida siegal • published may 30, 2018 • updated on may 31, 2018 at 5:06 am, what to know.
- A Rockland County school district is considering getting rid of homework for students at an elementary school
- Two fifth-grade boys had petitioned for a homework ban, citing stress from the work; but it turns out officials were already considering it
- A district administrator says it's not about banning homework, it's about "rethinking" it to help kids learn better
No homework: it's a mantra all kids want to hear. Now a New York school district is considering getting rid of it altogether.
The idea started as a petition from fifth-graders Christopher DeLeon and Niko Keelie at Farley Elementary School in Stony Point and grew from there, but it's also part of of a bigger nationwide trend.
"I got stressed by homework a lot, so I just -- it took me a minute of thinking -- I want to get rid of homework," said Keelie.
The two boys decided to write a petition and present it to the school district making their case. They said most of their classmates agreed with their proposal -- and it turned out the school district also agreed.
In fact, the district had already considered reimagining their homework policy.
"It's really not about banning homework or no homework -- it's about rethinking it, and how can we do it different to better the needs of our students," said assistant superintendent Kris Felicello.

Wrong-way mom charged with murder in Southern State Parkway crash that killed her son

What's that smell? Strange odor in southern NJ county explained
National school districts all over the country are experimenting with either eliminating homework or drastically reducing it, citing studies that have shown homework in elementary school doesn't actually help with learning and sometimes can hurt.
"If you go home and you do homework, you're just thinking about that, and then you stutter and stuff," said DeLeon. "But if you don't, then you're relaxed and calm, and if you take a test more calmly, you get a better grade 'cause you're not thinking about other stuff."
But not everyone agrees. Many parents have asked, if their children don't do homework, what will they do in the afternoon -- and how will they learn?
Felicello's response to that: "I hope that kids would go home and they would read and they would discover things that they're interested in doing, and go on YouTube and figure out how to play the ukulele, or go and research what's going on with Space X, or talk to their friends or get outside and play."
The district is considering different options: one would allow ask for homework for their kids. They hope to have the new homework policy ready to go for the next school year.
25 Reasons Homework Should Be Banned (Busywork Arguments)

As students across the globe plow through heaps of homework each night, one question lingers in the minds of educators, parents, and students alike: should homework be banned?
This question is not new, yet it continues to spark lively debate as research findings, anecdotal evidence, and personal experiences paint a complex picture of the pros and cons of homework.
On one hand, proponents of homework argue that it reinforces classroom learning, encourages a disciplined work ethic, and provides teachers with valuable insight into student comprehension. They see homework as an extension of classroom instruction that solidifies and enriches learning while fostering important skills like time management and self-discipline. It also offers an opportunity for parents to be involved in their children's education.
However, some people say there are a lot of downsides. They argue that excessive homework can lead to stress and burnout, reduce time for extracurricular activities and family interactions, exacerbate educational inequalities, and even negatively impact students' mental health.

This article presents 25 reasons why we might need to seriously consider this radical shift in our educational approach. But first, lets share some examples of what homework actually is.
Examples of Homework
These examples cover a wide range of subjects and complexity levels, reflecting the variety of homework assignments students might encounter throughout their educational journey.
- Spelling lists to memorize for a test
- Math worksheets for practicing basic arithmetic operations
- Reading assignments from children's books
- Simple science projects like growing a plant
- Basic geography assignments like labeling a map
- Art projects like drawing a family portrait
- Writing book reports or essays
- Advanced math problems
- Research projects on various topics
- Lab reports for science experiments
- Reading and responding to literature
- Preparing presentations on various topics
- Advanced math problems involving calculus or algebra
- Reading classic literature and writing analytical essays
- Research papers on historical events
- Lab reports for advanced science experiments
- Foreign language exercises
- Preparing for standardized tests
- College application essays
- Extensive research papers
- In-depth case studies
- Advanced problem-solving in subjects like physics, engineering, etc.
- Thesis or dissertation writing
- Extensive reading and literature reviews
- Internship or practicum experiences
Lack of proven benefits

Homework has long been a staple of traditional education, dating back centuries. However, the actual efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes remains disputed. A number of studies indicate that there's no conclusive evidence supporting the notion that homework improves academic performance, especially in primary education . In fact, research suggests that for younger students, the correlation between homework and academic achievement is weak or even negative .
Too much homework can often lead to increased stress and decreased enthusiasm for learning. This issue becomes particularly pressing when considering the common 'more is better' approach to homework, where the quantity of work given to students often outweighs the quality and effectiveness of the tasks. For instance, spending countless hours memorizing facts for a history test may not necessarily translate to better understanding or long-term retention of the subject matter.
However, it's worth noting that homework isn't completely devoid of benefits. It can help foster self-discipline, time management skills, and the ability to work independently. But, these positive outcomes are usually more pronounced in older students and when homework assignments are thoughtfully designed and not excessive in volume.
When discussing the merits and drawbacks of homework, it's critical to consider the nature of the assignments. Routine, repetitive tasks often associated with 'drill-and-practice' homework, such as completing rows of arithmetic problems or copying definitions from a textbook, rarely lead to meaningful learning. On the other hand, assignments that encourage students to apply what they've learned in class, solve problems, or engage creatively with the material can be more beneficial.
Increased stress

Homework can often lead to a significant increase in stress levels among students. This is especially true when students are burdened with large volumes of homework, leaving them with little time to relax or pursue other activities. The feeling of constantly racing against the clock to meet deadlines can contribute to anxiety, frustration, and even burnout.
Contrary to popular belief, stress does not necessarily improve performance or productivity. In fact, high levels of stress can negatively impact memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. This counteracts the very purpose of homework, which is intended to reinforce learning and improve academic outcomes.
However, one might argue that homework can teach students about time management, organization, and how to handle pressure. These are important life skills that could potentially prepare them for future responsibilities. But it's essential to strike a balance. The pressure to complete homework should not come at the cost of a student's mental wellbeing.
Limited family time
Homework often infringes upon the time students can spend with their families. After spending the entire day in school, children come home to yet more academic work, leaving little room for quality family interactions. This limited family time can hinder the development of important interpersonal skills and familial bonds.
Moreover, family time isn't just about fun and relaxation. It also plays a crucial role in the social and emotional development of children. Opportunities for unstructured play, family conversations, and shared activities can contribute to children's well-being and character building.
Nonetheless, advocates of homework might argue that it can be a platform for parental involvement in a child's education. While this may be true, the involvement should not transform into parental control or cause friction due to differing expectations and pressures.
Reduced physical activity
Homework can often lead to reduced physical activity by eating into the time students have for sports, recreation, and simply being outdoors. Physical activity is essential for children's health, well-being, and even their academic performance. Research suggests that physical activity can enhance cognitive abilities, improve concentration, and reduce symptoms of ADHD .
Homework, especially when it's boring and repetitive, can deter students from engaging in physical activities, leading to a sedentary lifestyle. This lack of balance between work and play can contribute to physical health problems such as obesity, poor posture, and related health concerns.
Homework proponents might point out that disciplined time management could allow students to balance both work and play. However, given the demanding nature of many homework assignments, achieving this balance is often easier said than done.
Negative impact on sleep

A significant concern about homework is its impact on students' sleep patterns. Numerous studies have linked excessive homework to sleep deprivation in students. Children often stay up late to complete assignments, reducing the amount of sleep they get. Lack of sleep can result in a host of issues, from poor academic performance and difficulty concentrating to physical health problems like weakened immunity.
Even the quality of sleep can be affected. The stress and anxiety from a heavy workload can lead to difficulty falling asleep or restless nights. And let's not forget that students often need to wake up early for school, compounding the negative effects of late-night homework sessions.
On the other hand, some argue that homework can teach children time management skills, suggesting that effective organization could help prevent late-night work. However, when schools assign excessive amounts of homework, even the best time management might not prevent encroachment on sleep time.
Homework can exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Not all students have access to a conducive learning environment at home, necessary resources, or support from educated family members. For these students, homework can become a source of stress and disadvantage rather than an opportunity to reinforce learning.
Children from lower socio-economic backgrounds might need to contribute to household chores or part-time work, limiting the time they have for homework. This can create a gap in academic performance and grades, reflecting not on the students' abilities but their circumstances.
While homework is meant to level the playing field by providing additional learning time outside school, it often does the opposite. It's worth noting that students from privileged backgrounds can often access additional help like tutoring, further widening the gap.
Reduced creativity and independent thinking
Homework, particularly when it involves rote learning or repetitive tasks, can stifle creativity and independent thinking. Students often focus on getting the "right" answers to please teachers rather than exploring different ideas and solutions. This can hinder their ability to think creatively and solve problems independently, skills that are increasingly in demand in the modern world.
Homework defenders might claim that it can also promote independent learning. True, when thoughtfully designed, homework can encourage this. But, voluminous or repetitive tasks tend to promote compliance over creativity.
Diminished interest in learning
Overburdening students with homework can diminish their interest in learning. After long hours in school followed by more academic tasks at home, learning can begin to feel like a chore. This can lead to a decline in intrinsic motivation and an unhealthy association of learning with stress and exhaustion.
In theory, homework can deepen interest in a subject, especially when it involves projects or research. Yet, an excess of homework, particularly routine tasks, might achieve the opposite, turning learning into a source of stress rather than enjoyment.
Inability to pursue personal interests
Homework can limit students' ability to pursue personal interests. Hobbies, personal projects, and leisure activities are crucial for personal development and well-being. With heavy homework loads, students may struggle to find time for these activities, missing out on opportunities to discover new interests and talents.
Supporters of homework might argue that it teaches students to manage their time effectively. However, even with good time management, an overload of homework can crowd out time for personal interests.
Excessive workload
The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
While homework can help consolidate classroom learning, too much can be counterproductive. It's important to consider the overall workload of students, including school, extracurricular activities, and personal time, when assigning homework.
Limited time for reflection
Homework can limit the time students have for reflection. Reflection is a critical part of learning, allowing students to digest and integrate new information. With the constant flow of assignments, there's often little time left for this crucial process. Consequently, the learning becomes superficial, and the true understanding of subjects can be compromised.
Although homework is meant to reinforce what's taught in class, the lack of downtime for reflection might hinder deep learning. It's important to remember that learning is not just about doing, but also about thinking.
Increased pressure on young children
Young children are particularly vulnerable to the pressures of homework. At an age where play and exploration are vital for cognitive and emotional development, too much homework can create undue pressure and stress. This pressure can instigate a negative relationship with learning from an early age, potentially impacting their future attitude towards education.
Advocates of homework often argue that it prepares children for the rigors of their future academic journey. However, placing too much academic pressure on young children might overshadow the importance of learning through play and exploration.
Lack of alignment with real-world skills
Traditional homework often lacks alignment with real-world skills. Assignments typically focus on academic abilities at the expense of skills like creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. These are crucial for success in the modern workplace and are often under-emphasized in homework tasks.
Homework can be an opportunity to develop these skills when properly structured. However, tasks often focus on memorization and repetition, rather than cultivating skills relevant to the real world.
Loss of motivation
Excessive homework can lead to a loss of motivation. The constant pressure to complete assignments and meet deadlines can diminish a student's intrinsic motivation to learn. This loss of motivation might not only affect their academic performance but also their love of learning, potentially having long-term effects on their educational journey.
Some believe homework instills discipline and responsibility. But, it's important to balance these benefits against the potential for homework to undermine motivation and engagement.
Disruption of work-life balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is as important for students as it is for adults. Overloading students with homework can disrupt this balance, leaving little time for relaxation, socializing, and extracurricular activities. All of these are vital for a student's overall development and well-being.
Homework supporters might argue that it prepares students for the workloads they'll face in college and beyond. But it's also crucial to ensure students have time to relax, recharge, and engage in non-academic activities for a well-rounded development.
Impact on mental health
There's a growing body of evidence showing the negative impact of excessive homework on students' mental health. The stress and anxiety from heavy homework loads can contribute to issues like depression, anxiety, and even thoughts of suicide. Student well-being should be a top priority in education, and the impact of homework on mental health cannot be ignored.
While some might argue that homework helps students develop resilience and coping skills, it's important to ensure these potential benefits don't come at the expense of students' mental health.
Limited time for self-care
With excessive homework, students often find little time for essential self-care activities. These can include physical exercise, proper rest, healthy eating, mindfulness, or even simple leisure activities. These activities are critical for maintaining physical health, emotional well-being, and cognitive function.
Some might argue that managing homework alongside self-care responsibilities teaches students valuable life skills. However, it's important that these skills don't come at the cost of students' health and well-being.
Decreased family involvement
Homework can inadvertently lead to decreased family involvement in a child's learning. Parents often feel unqualified or too busy to help with homework, leading to missed opportunities for family learning interactions. This can also create stress and conflict within the family, especially when parents have high expectations or are unable to assist.
Some believe homework can facilitate parental involvement in education. But, when it becomes a source of stress or conflict, it can discourage parents from engaging in their child's learning.
Reinforcement of inequalities
Homework can unintentionally reinforce inequalities. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds might lack access to resources like private tutors or a quiet study space, placing them at a disadvantage compared to their more privileged peers. Additionally, these students might have additional responsibilities at home, further limiting their time to complete homework.
While the purpose of homework is often to provide additional learning opportunities, it can inadvertently reinforce existing disparities. Therefore, it's essential to ensure that homework doesn't favor students who have more resources at home.

Reduced time for play and creativity
Homework can take away from time for play and creative activities. These activities are not only enjoyable but also crucial for the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children. Play allows children to explore, imagine, and create, fostering innovative thinking and problem-solving skills.
Some may argue that homework teaches discipline and responsibility. Yet, it's vital to remember that play also has significant learning benefits and should be a part of every child's daily routine.
Increased cheating and academic dishonesty
The pressure to complete homework can sometimes lead to increased cheating and academic dishonesty. When faced with a large volume of homework, students might resort to copying from friends or searching for answers online. This undermines the educational value of homework and fosters unhealthy academic practices.
While homework is intended to consolidate learning, the risk of promoting dishonest behaviors is a concern that needs to be addressed.
Strained teacher-student relationships
Excessive homework can strain teacher-student relationships. If students begin to associate teachers with stress or anxiety from homework, it can hinder the development of a positive learning relationship. Furthermore, if teachers are perceived as being unfair or insensitive with their homework demands, it can impact the overall classroom dynamic.
While homework can provide an opportunity for teachers to monitor student progress, it's important to ensure that it doesn't negatively affect the teacher-student relationship.
Negative impact on family dynamics
Homework can impact family dynamics. Parents might feel compelled to enforce homework completion, leading to potential conflict, stress, and tension within the family. These situations can disrupt the harmony in the household and strain relationships.
Homework is sometimes seen as a tool to engage parents in their child's education. However, it's crucial to ensure that this involvement doesn't turn into a source of conflict or pressure.
Cultural and individual differences
Homework might not take into account cultural and individual differences. Education is not a one-size-fits-all process, and what works for one student might not work for another. Some students might thrive on hands-on learning, while others prefer auditory or visual learning methods. By standardizing homework, we might ignore these individual learning styles and preferences.
Homework can also overlook cultural differences. For students from diverse cultural backgrounds, certain types of homework might seem irrelevant or difficult to relate to, leading to disengagement or confusion.
Encouragement of surface-level learning
Homework often encourages surface-level learning instead of deep understanding. When students are swamped with homework, they're likely to rush through assignments to get them done, rather than taking the time to understand the concepts. This can result in superficial learning where students memorize information to regurgitate it on assignments and tests, instead of truly understanding and internalizing the knowledge.
While homework is meant to reinforce classroom learning, the quality of learning is more important than the quantity. It's important to design homework in a way that encourages deep, meaningful learning instead of mere rote memorization.
Related posts:
- Diathesis-Stress Model (Definition + Examples)
- HPA Axis (Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis)
- General Adaptation Syndrome Theory
- Careers in Psychology
- The Stress Response (General Adaptation Syndome)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
Stop Homework in Government Schools
- Signatures 13
- Privacy Policy
H omework is wrecking our kids: The research is clear, let’s ban elementary homework
“There is no evidence that any amount of homework improves the academic performance of elementary students.”
This statement, by homework research guru Harris Cooper, of Duke University, is startling to hear, no matter which side of the homework debate you’re on. Can it be true that the hours of lost playtime, power struggles and tears are all for naught? That millions of families go through a nightly ritual that doesn’t help? Homework is such an accepted practice, it’s hard for most adults to even question its value.
When you look at the facts, however, here’s what you find: Homework has benefits, but its benefits are age dependent.
For elementary-aged children, research suggests that studying in class gets superior learning results, while extra schoolwork at home is just . . . extra work. Even in middle school, the relationship between homework and academic success is minimal at best. By the time kids reach high school, homework provides academic benefit, but only in moderation. More than two hours per night is the limit. After that amount, the benefits taper off. “The research is very clear,” agrees Etta Kralovec, education professor at the University of Arizona. “There’s no benefit at the elementary school level.”
Before going further, let’s dispel the myth that these research results are due to a handful of poorly constructed studies. In fact, it’s the opposite. Cooper compiled 120 studies in 1989 and another 60 studies in 2006. This comprehensive analysis of multiple research studies found no evidence of academic benefit at the elementary level. It did, however, find a negative impact on children’s attitudes toward school.
This is what’s worrying. Homework does have an impact on young students, but it’s not a good one. A child just beginning school deserves the chance to develop a love of learning. Instead, homework at a young age causes many kids to turn against school, future homework and academic learning. And it’s a long road. A child in kindergarten is facing 13 years of homework ahead of her.
Then there’s the damage to personal relationships. In thousands of homes across the country, families battle over homework nightly. Parents nag and cajole. Overtired children protest and cry. Instead of connecting and supporting each other at the end of the day, too many families find themselves locked in the “did you do your homework?” cycle.
When homework comes prematurely, it’s hard for children to cope with assignments independently—they need adult help to remember assignments and figure out how to do the work. Kids slide into the habit of relying on adults to help with homework or, in many cases, do their homework. Parents often assume the role of Homework Patrol Cop. Being chief nag is a nasty, unwanted job, but this role frequently lingers through the high school years. Besides the constant conflict, having a Homework Patrol Cop in the house undermines one of the purported purposes of homework: responsibility.
What works better than traditional homework at the elementary level is simply reading at home. This can mean parents reading aloud to children as well as children reading. The key is to make sure it’s joyous. If a child doesn’t want to practice her reading skills after a long school day, let her listen instead. Any other projects that come home should be optional and occasional. If the assignment does not promote greater love of school and interest in learning, then it has no place in an elementary school-aged child’s day.
Elementary school kids deserve a ban on homework. This can be achieved at the family, classroom or school level. Families can opt out, teachers can set a culture of no homework (or rare, optional homework), and schools can take time to read the research and rekindle joy in learning.
Homework has no place in a young child’s life. With no academic benefit, there are simply better uses for after-school hours.
Carri-Anne Parker Contact the author of the petition
| We have closed this petition and we have removed signatories' personal information. European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires a legitimate reason for storing personal information and that the information be stored for the shortest time possible. |
| to manage your petition. |
Is there something you want to change?
Change doesn't happen by staying silent. The author of this petition stood up and took action. Will you do the same? Start a social movement by creating a petition.
Other petitions you might be interested in
Petition concerning academic staff quality, classroom facilities, sports coaching &fee increases. [අධ්යයන කාර්ය මණ්ඩලයේ ගුණාත්මකභාවය, පන්ති කාමර පහසුකම්, ක්රීඩා පුහුණු කිරීම් සහ ගාස්තු වැඩිකිරීම].
319 Created: 2024-08-30
Please help us Save Oakfield C of E Primary School in Ryde
218 Created: 2024-09-04
Urgent Help Needed – Orphaned, Autistic Young Man at Risk of Deportation to Inhumane Conditions in Albania
2920 Created: 2024-08-13
Correcting Oak Harbor’s Mayor Salary Change
189 Created: 2024-08-31
Stop North Yorkshire council banning overnight campervan stopovers on Royal Albert Drive Scarborough
1741 Created: 2024-08-03
24hr Clinics in ward 100 City of Tshwane
159 Created: 2024-09-03
Unfair debit hold on Tymebank without communication with account holder
154 Created: 2024-08-30
Change the NVSS class bell
115 Created: 2024-09-03
Save Godshill Primary school
106 Created: 2024-09-04
Noordhoek Garden Emporium Equestrian Padel Court Petition
85 Created: 2024-08-30
Create a solution for BYD Atto 3 to charge at Tesla Superchargers
217 Created: 2024-07-15
Return to the UK's Christian Constitution
338 Created: 2024-08-14
Request Management Office of Tuan 2 under CPI land to allow installation of Washing Machine at Balcony
58 Created: 2024-09-03
Save wroxall primary school
57 Created: 2024-09-04
For the future of Wilenius' traditional shipyard and Porvoo's centuries-old wooden boat culture
2418 Created: 2023-01-13
Petition against the shooting and killing of Vervet Monkeys and wildlife
423 Created: 2024-07-02
Justice for Chantel Pasqualle
4076 Created: 2024-08-12
A Six-Year Setback: Demanding Action on First Nations Life Expectancy in BC
73 Created: 2024-08-29
RECOGNITION OF THE IMPEDED SEE OF BENEDICT XVI AND CONVOCATION OF THE CONCLAVE
15884 Created: 2023-10-23
Permanent operating license for the Roll FM radio channel
4333 Created: 2024-07-04
Petitions.net
- Start a Petition
- How to write a petition?

- Campaign tips
- Start a Petition
To: Congress
Ban homework.

Why is this important?
100 signatures reached
50 signatures reached
25 signatures reached
10 signatures reached
- Sign Up for Emails
- Privacy Policy
- Sign Up For SMS
- Petition Inquiries
- Terms of Use
- Partner With Us
- Press Inquiries
- Sign Up For Emails
MoveOn Civic Action does not necessarily endorse the contents of petitions posted on this site. MoveOn Petitions is an open tool that anyone can use to post a petition advocating any point of view, so long as the petition does not violate our terms of service .
Opinion Columnists | Opinion: Vote “yes” in November to save…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
Digital Replica Edition
- Endorsements
Opinion Columnists
Opinion columnists | opinion: vote “yes” in november to save colorado’s mountain lions, lynx and bobcats from trophy hunters, cats aren’t trophies ballot measure would ban trophy hunting and trapping of wild cats in colorado.

Our coalition held a press conference Friday at The Wild Animal Sanctuary, the perfect venue, given that founder Pat Craig is renowned for saving big cats from horrific cruelty at the hands of mankind.
On this cool August morning, we saw a mountain lion, her sweet butterfly-patterned face hiding in the grass before she walked away, which is quintessential lion behavior when humans are present. We saw two lynx and a bobcat, making up all three of the wild cats that will be spared from trophy hunting and fur trapping with a “yes” vote.
Among the cats were CATs supporters: A powerful display of serious-minded voices for true wildlife conservation.
The room was silent, however, when shown raw footage of packs of dogs chasing lions and bobcats into trees, where they were shot as trophies.
Our campaign follows the journalistic virtue of “show, don’t tell” and this film shows the lion trophy hunting outfitters, who sell our wild cat as “your trophy” for upwards of $8,000 (the exact price for a lesser-maned African lion). In their own words, Colorado lion trophy hunters and fur trappers told the crowd that they were after their personal big trophy lion, a bucket list item, a thrill-kill.
Watch the video, “This is NOT Conservation,” on YouTube.
Veterinarian, Dr. Valerie Johnson, who holds a PhD from Colorado State University, connected the dots. “Mountain lion trophy hunters of Colorado are in the same vein as the people who pay big money to go to Africa and cut the tusks off elephants, or heads off lions,” she told the crowd.
Erik Molvar spoke as a hunter, although he’s a well-published biologist in wildlife conservation.
“Hunters are like me, they subscribe to hunting ethics … Hunting for big cats is trophy hunting, pure and simple. It’s not to fill the freezer, it’s to bring home a trophy … to brag about and impress your friends,” Molvar said. “That doesn’t respect the quarry, so it doesn’t deserve any particular respect from the general public, either.”
Perhaps the most well-received voice was that of J Dallas Gudgell, an experienced environmental scientist and member of the Fort Peck Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes.
“As an Indigenous person concerned with and raised in a framework of right relationship with the natural world, I find trophy hunting and egocentric activity upends nature’s natural balance,” explained Gudgell, who is Wildlife and Tribal Policy Director for the International Wildlife Coexistence Network, one of the 100 groups endorsing CATs. “I support the people’s right to participate in the Democratic process to protect wild cats from senseless use.”
Dr. Christine Capaldo, a specialist in feline medicine, spoke of the bobcat in her southwestern Colorado community who was fur-trapped and strangled to death just to sell its fur on the lucrative Chinese fur market.
“Allowing unlimited numbers of bobcats to be killed isn’t about wildlife biology or management, it’s about greed, trophies, the despicable fur trade to China, and a complete disregard for the welfare of wildlife …Colorado’s native wild cats should not ever be for sale.”
Dr. Mickey Pardo, PhD, a wildlife biologist in Fort Collins, recently featured in the New York Times and National Geographic for his work, explained,
“As a biologist, I support the CATs ballot measure to ban trophy hunting and trapping of wild cats in Colorado. The scientific evidence is clear that hunting these animals is completely unnecessary and the methods used to hunt them are exceptionally cruel.”
Deanna Meyer, born and raised in Colorado, runs a rural family farm in lion country, abutting National Forest Lands, and she will vote “yes” to CATs based on her personal experience.
“One Christmas Day two years ago, I followed the sounds, finding six dogs who treed a terrified bobcat on my land,” Meyer said. “I was infuriated when I found out that there was nothing I could do. When this initiative passes, it will end this harassment and protect lions and bobcats who aren’t causing conflicts with humans.”
Delia Malone closed the event, speaking as a West Slope field ecologist, and Wildlife Chair for the Colorado Sierra Club, which endorses CATs. She’s vice chair of Roaring Fork Audubon, which is one of six Audubon Societies of Colorado that endorses CATs as well.
“At my home in Redstone which borders roadless area, we’re lucky enough to have a cougar family that has lived in the forest above us for generations — we’ve never had a negative encounter with the cougar family,” Malone said. “Trophy killing of lions contradicts the science, it is ethically wrong and should be outlawed.”
Every speaker at this event shows Colorado voters who we are: A vast coalition of wildlife experts, conservationists and diverse citizens, statewide including the most rural citizens living with lions, who all agree that this kind of fringe hunting for heads and fur has no place in the great state of Colorado, where we respect ethical outdoor activities, including ethical hunting of deer and elk for food.
As Pat Craig said so well: “Let’s be clear: Mountain lions and bobcats are not a food source as many callous individuals like to suggest. Instead, they are hunted solely for their heads and beautiful coats.”
Julie Marshall is the director of communications for Cats Aren’t Trophies.
Sign up for Sound Off to get a weekly roundup of our columns, editorials and more.
To send a letter to the editor about this article, submit online or check out our guidelines for how to submit by email or mail.
- Report an Error
- Submit a News Tip
More in Opinion Columnists

Opinion Columnists | Opinion: Leverage the Ride for Magnus to swiftly turn the tide of pedestrian traffic deaths

Opinion Columnists | Opinion: As wildfire risk rises in the West, the backcountry becomes more dangerous for hikers and backpackers

Opinion Columnists | Opinion: Labor Day is an opportunity to reflect on Colorado’s long fight for workers’ rights

Opinion Columnists | Opinion: America survived Watergate and it’ll survive the November election, too

Sorry, our services aren't available at this time in your country.
Thanks for your understanding. We hope to come back soon!
We use cookies to make this service simpler. Find out more about cookies
UK Government and Parliament
We’re waiting for a new Petitions Committee
Petitions had to stop because of the recent general election. Once a new Petitions Committee is set up by the House of Commons, petitions will start again.
Find out more on the Petitions Committee website
Rejected petition ban homework for all UK students
homework is putting more stress on our students. there is no need for homework after they have been at school all day, and it is very damaging to their mental health.
issue a ban on homework
This petition was rejected
Why was this petition rejected?
There’s already a petition about this issue. We cannot accept a new petition when we already have one about a very similar issue.
You are more likely to get action on this issue if you sign and share a single petition.
You may wish to sign this petition which calls for the same action: https://petition.parliament.uk/petitions/584262
We only reject petitions that don’t meet the petition standards .
- Date submitted 10 May 2021
The data shows the number of people who have signed the petition by country as well as in the constituency of each Member of Parliament. This data is available for all petitions on the site. It is not a list of people who have signed the petition. The only name that is shared on the site is that of the petition creator.
BAN Homework in all secondary and Primary’s schools!


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Homework has always been a stress creator for students across America. It certainly has more me. Sign this petition for not only for a change, but for a benefit for students. After school is for relaxing, hanging out with your friends, and many other good things for you. It is not meant for doing something that does not make you happy, its not meant for causing stress.
Homework should be banned all around the USA, the reason is because home isn't the extra place for work, and is a waste of every kids time. Another reason it should be banned is that homework prevents other homework from getting done; Because you've spent a certain amount of time on this Essay for one of your classes , you forgot that there's math homework sitting in your binder, which ...
We are calling on lawmakers across the country: Ban excessive homework nationwide in the U.S.! Let us learn effectively during school hours so that we can live fully outside them too! Please sign this petition if you believe in creating an education system that values quality over quantity and promotes student well-being above all else.
College de Saint-Ambroise, an elementary school in Quebec, is the latest school to ban homework, announcing this week that it would try the new policy for a year. The decision came after officials ...
But Sofia may well now be laughing, with California poised to introduce a Bill that would allow schools to ban "excessive", and perhaps in some cases all, homework. The state, a Democratic ...
the author of the bill, assemblywoman pilar schiavo, says she was inspired by conversation with her nine-year-old daughter, who asked if she could "ban homework." schiavo says many parents support the idea, expressing frustration over the lack of quality time with their kids due to heavy homework loads and extracurricular activities.
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students.
Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We've known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that "homework had no association with achievement gains" when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [7]
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
No homework: it's a mantra all kids want to hear. Now a New York school district is considering getting rid of it altogether. The idea started as a petition from fifth-graders Christopher DeLeon ...
Excessive workload. The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
As most of you probably said, homework is in their daily routine. However, if they were to not do their homework, no matter what excuse they might come up with, even most legitimate ones, you'd still be viewed the same. An irresponsible, incompetent, slacker. Because common belief is: "Well if you don't do your homework, it sh.
By the time kids reach high school, homework provides academic benefit, but only in moderation. More than two hours per night is the limit. After that amount, the benefits taper off. "The research is very clear," agrees Etta Kralovec, education professor at the University of Arizona. "There's no benefit at the elementary school level.".
To start off, I'd like to explain to you why we should not have homework. First, homework obviously has negative effects on students. Some effects are that the students get frustrated if they can't or don't know how to do their homework, there will be no time for the students to do extracurricular activities, and the students might just not want to learn anymore because they don't understand ...
Sep. 4—MORGANTOWN — Lest anyone think all the intensity surrounding the citywide camping ban adopted early Wednesday morning by Morgantown City Council was on the audience side of the podium ...
Rejected petition PETITION TO BAN ALL HOMEWORK. I want to ban all homework. We already have to do 6-7 hours of work at school and we are supposed to relax when we get home, but no the schools just want to make our lives miserable. And all the schools are on about mental health when doing homework actually just destroys our mental health.
We want the Government to stop schools from being able to set homework. Children have personal lives and families, and should not have to sacrifice their personal time to do homework. ... Closed petition Ban schools from being able to set homework ... This petition is closed All petitions run for 6 months. 600 signatures. Show on a map. 10,000 ...
Cats Aren't Trophies ballot measure would ban hunting Colorado mountain lions, lynx, bobcats and other wild cats, says Julie Marshall, director of communications for Cats Aren't Trophies.
Make your petition known to President of the United States. Send them an email. U.S. Senate. State Governors. Change.org. Health. Ban homework from schools except for as a punishment. I would like to state my opinion about homework and why it should be banned for the health and safety of America to an extent.
Ban Homework! 36 people have signed this petition. Add your name now! Georgia Bower 22 Comments. Many teenagers these days are losing sleep because of homework. It is causing a great deal of stress and does not allow some teens to have a fun social experience outside of school because they are stuck at home completing homework for every subject.
Get petition data (json format) About petition data The data shows the number of people who have signed the petition by country as well as in the constituency of each Member of Parliament. This data is available for all petitions on the site.
Many students are suffering under pressure about homework, and barely have any time at home. Let's change that by switching to Finland's school system, which only has 5 hour school days, and no homework! Sign this petition so that we can leverage the government to change the school system! 45% of high schoolers are stressed about school, and 61% of all teenagers ages 13-17 are stressed ...
Rejected petition ban homework for all UK students homework is putting more stress on our students. there is no need for homework after they have been at school all day, and it is very damaging to their mental health. ... This data is available for all petitions on the site. It is not a list of people who have signed the petition.
They should ban homework in England in secondary schools because it is the most important years to be studying at school to get GCSE but if you have homework all the time you are missing out on learning. Plus you can spend hours doing the pieces of homeworks and the teachers might not mark them in which you don't know whether you are improving.