History of Computers
Cite this chapter.

- Bruce I. Blum 2
109 Accesses
We are in the midst of a revolution in technology and in the way we process information. The computer is at the heart of this revolution. Where it will take us is unknown, but we do know that events are moving rapidly. In fact, virtually everything related to digital computers took place in my generation’s adult lifetime. And I am not old.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Cited in Margaret Harmon, Stretching Man’s Mind: A History of Data Processing , Mason Charter, New York, 1975, p66, reprinted by permission. All rights reserved.
Google Scholar
Cited in Harmon, Op cit , p74.
Cited in Harmon, Op cit , p85.
Cited in Harmon, Op cit , p87.
Cited in Harmon, Op cit , pi03.
Adapted from S. Rosen, Digital Computers: History in Anthony Ralston, Edwin D. Reilly, Jr. (eds), Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Engineering , Second Edition, Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York, 1983, pp 538–9.
Conversation: Jay W. Forrester, Interviewed by Christopher Evans, Annals of the History of Computing (5,3) July 1983, pp 298–299.
John von Neumann, The Computer and the Brain , Yale University Press, 1958, Cited in J. Bernstein, The Analytical Engine , Random House, N.Y. 1966, p62, reprinted by permission.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Applied Physics Laboratory, The Johns Hopkins University, 20707, Laurel, Maryland, USA
Bruce I. Blum
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 1986 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Blum, B.I. (1986). History of Computers. In: Clinical Information Systems. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8593-6_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8593-6_1
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4613-8595-0
Online ISBN : 978-1-4613-8593-6
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Assignment ON" EVOLUTION AND HISTORY OF COMPUTER "

Related Papers
Ndidi Opara
Edmund Miller
AJEET TELECOM
ELAIYA SENGUTTUVAN
Tahir Siddique
In this paper, emphasis has been given on the gradual and continuous advancement of computer from on and before 300BC to 2012 and beyond. During this very long period of time, a simple device like computer has witnessed many significant changes in its manufacturing and development. By and large, the changes are conceptual, manufacturing and in ever increasing applications. Abstract-In this paper, emphasis has been given on the gradual and continuous advancement of computer from on and before 300BC to 2012 and beyond. During this very long period of time, a simple device like computer has witnessed many significant changes in its manufacturing and development. By and large, the changes are conceptual, manufacturing and in ever increasing applications.
IEEE Potentials
Cresent Escriber
Fernando A G Alcoforado
This article aims to present how the computer, humanity's greatest invention, evolved and how its most likely future will be. The computer is humanity's greatest invention because the worldwide computer network made possible the use of the Internet as the technology that most changed the world with the advent of the information society. IBM developed the mainframe computer starting in 1952. In the 1970s, the dominance of mainframes began to be challenged by the emergence of microprocessors. The innovations greatly facilitated the task of developing and manufacturing smaller computers - then called minicomputers. In 1976, the first microcomputers appeared whose costs represented only a fraction of those practiced by manufacturers of mainframes and minicomputers. The existence of the computer provided the conditions for the advent of the Internet which is undoubtedly one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century, whose development took place in 1965. At the beginning of the 21st century, cloud computing emerged, which symbolizes the tendency to place all the infrastructure and information available digitally on the Internet. Current computers are electronic because they are made up of transistors used in electronic chips that have limitations given that there will be a time when it will no longer be possible to reduce the size of one of the components of the processors, the transistor. Quantum computers have been shown to be the newest answer in Physics and Computing to problems related to the limited capacity of electronic computers. Canadian company D-Wave claims to have produced the first commercial quantum computer. In addition to the quantum computer, Artificial Intelligence (AI) can reinvent computers.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
David Dennis
Daniel Ofoleta
Modou Mbodji, MMb
Bekka Billionea
Bayode Oluwatomilola
Proceedings of the IEEE
stanley mazor
arXiv (Cornell University)
Alexandre Benatti
Development of Mathematical Ideas of Mykhailo Kravchuk [Krawtchouk]
Ivan Katchanovski
Selin Oktan
IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology
Kuanysh Ospanov
Mallareddy Pindi
Obonyo Francis Alphonse
Interdisciplinary Science Reviews
Michael Mahoney
akhmad zaimi
GCAA Research Team
Gregoire Rousseau
Md Suzanul Islam Suzan
Ionescu Andreea
Genesis Chavez
Revista Dearq , Stephen Jones
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Generations of Computer 1st to 5th Explained with Pictures.
The history of computer technology is often used to refer to the origin of all the different generations of computers . From first to fifth each computer generation is characterized by significant technological development in their components, memory , and elements which essentially changed the way these devices work.
Several periods of generation from over the years advanced the technological evolution leads to the creation of today’s modern computer with more complex, more powerful, and increased capability and functionality.
Introduction to Computer Generations
This development period of electronic computing technology is called Computer Generation. There are five generations of computers identified, although the sixth generation could be in development now in the early 21st century.
During the evolutionary timeline, each generation of computers has improved a lot by undergoing considerable changes in their size, type, and functionality.
By analyzing them, one can trace the evolution of computer technology, to see how the computer industry has changed over the years and how great capabilities and software progress has been made by humankind in under a hundred years , as a result, the creation of different generations.
At present, the computer is playing a significant part in human existence because today’s digital computer is being used for every work in each field. If someday an issue occurs in the computer or the server is down, at that point all the work stops. This is how significant it is for technology development!
In this article, I will introduce you to all the generations of computers with pictures by explaining the complete information about their characteristics , names, components , and examples too.
Generations of Computer From 1st to 5th
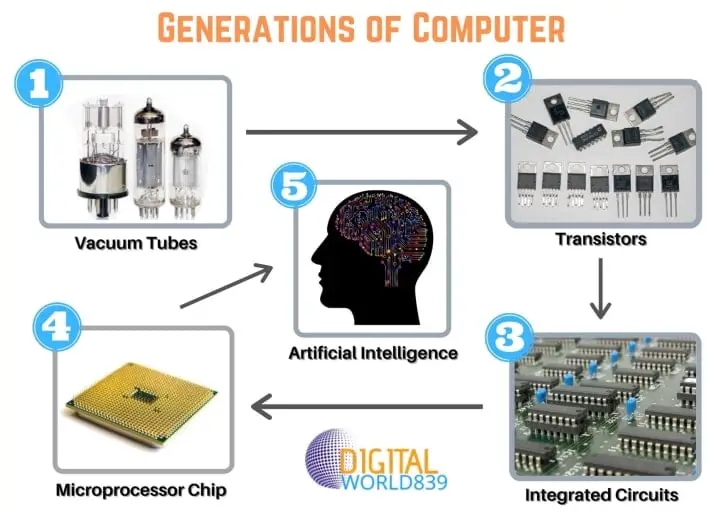
Let’s discover the series of computer generations in the following list:
1st Generation of Computer (1940-1956)
This first generation of computers was based on vacuum tube technology used for calculations, storage, and control, invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming. The vacuum tubes and diode valves were the chief components of the first generations of computers.

First-generation computers relied on the lowest-level machine language, in order to perform operations, and could only solve a single problem at a point of time.
Magnetic drums were used as the memory in these computers (were very slow in speed). The punched and magnetic tapes were used for the input and output function of the computer in order to display on prints even the results weren’t 100% accurate.

Also, the first generation of computers available was based on the 8-bit microprocessor.
The disadvantages of 1st gen computers are that they were very enormous in size and heavy in weight (made of thousands of vacuum tubes ) , occupying large rooms. Also, once they were kept in one place it was difficult to transfer. Another con like using a decimal number system and many switches and cables.
In addition, they were also very expensive to operate with using a large amount of electricity, the vacuum tubes produced large amounts of heat, so an air conditioner was required for the proper functioning unless a lot of heat can cause a malfunction.
The advantage of the first generation of computers is that they could calculate in milliseconds (about five thousand sums per second.)
The computers of first-generation were managed to use in different fields like weather forecasting, solving mathematical problems, energy tasks, also in space research, military, and other scientific tasks.
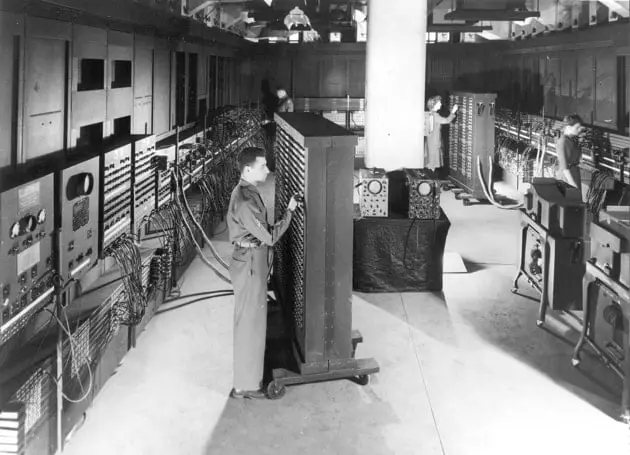
In the first generation of computers, the first computer of the world named “ENIAC” (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was discovered by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert in the year between 1943 to 1945.
ENIAC used panel-to-panel wiring and switches for programming, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, used about 18,000 vacuum tubes, and weighed 30 tons.
Characteristics of the 1st Generation of Computer:
- Vacuum tubes and diode valves were used as the main electronic component in the first generation computers.
- Punch cards, paper tape utilized for input and output operations.
- Magnetic drums used for storage.
- Huge in size and weight with a lot of power consumption.
- Very expensive in price also not reliable.
- Computers were programmed with low-level machine language also has low operating speed.
Examples of the first generation of computers are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) EDSEC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), (Electronic delay storage automatic calculator), IBM -701 and IBM 650.
ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer . This computer about 18,000 vacuum tubes used for the calculation result in huge in size, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, and weighed 30 tons. These were the harbingers of today’s digital computers. This first computing machine was designed by people J. P. Eckert, W. Mosley, J. W. Mauchly.
2nd Generation of Computer (1956-1964)
The second generation of computers replaced the vacuum tubes with a reliable component called transistors for manufacturing of computers was invented by William Shockley in 1947.

The transistors were the revolution in the computer field because this component advantaged the 2nd gen computer by increasing the performance, operating speed (hundreds of thousands of operations per second), as well as decreasing the electricity consumption of the computers.
Transistors were far superior to the vacuum tube, allowing computers to get faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient made and possible to reduce the size of computing equipment and ultimately heat reduced and reliability improved.
Computers of second-generation are characterized by the use of the first high-level programming languages, allowing programmers to specify instructions in words. At this time, early versions of COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL, and FORTRAN languages were developed .
These were the first computers to store their instructions in their memory, which went from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology. During this period, the first computer game name “ Spacewar ” was seen on a PDP-1 computer.

Do you know~ that the oldest abacus was a computing machine designed to calculate thousands of years ago, which is still used in schools today to do calculations.
Also, the concept of Central Processing Unit (CPU), multi-programming operating systems, programming language, memory, and input and output units (I / O units) were developed in the timeline of second-generation computers.
The major disadvantages of Second-generation computers were they still relied on punch cards for input and hard copies for output as well as still it was difficult to move the computers for the reason they were enough large and even some computers needed ACs.

This second generation of computers was first used in the fields like the atomic energy industry and nuclear power plants and other commercial fields.
Characteristics of the 2nd Generation of Computer:
- Computers based on transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- Magnetic Tape was used to store data.
- Relatively small in size and reduced weight with low energy consumption than 1st gen computers.
- Faster, reliable, and less expensive than the first generation.
- Use of storage devices, printers, and operating systems, etc.
- Higher-level languages like COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL, and FORTRAN were developed and used.
Examples of the second generation of computers include IBM 1620, CDC 1604, IBM 7094, UNIVAC 1108, IBM 620, CDC 3600, IBM 4044, Honeywell 400, IBM 1401 Mainframe, and PDP-1 minicomputer. IBM was actively working, producing transistor versions of its computers.
3rd Generation of Computer (1964-1971)
The third generation appeared in the form of integrated circuits (invented by Jack Kilby from 1958 to 1964). An IC (integrated circuit) is consists of many small transistors mounted on chips , which are called semiconductors.
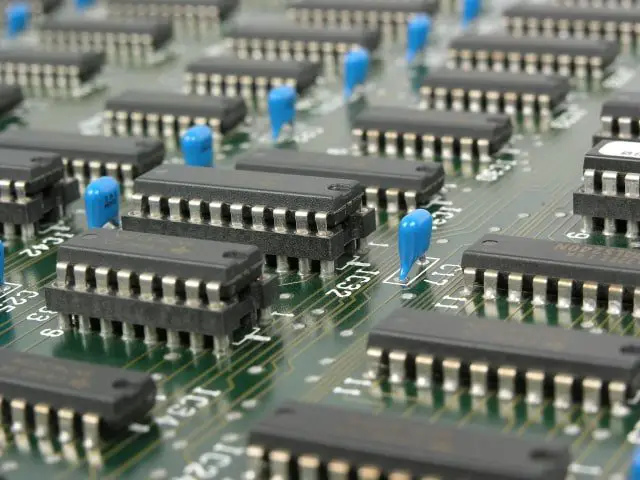
This synchronized chip became an important foundation for the third generation computers when scientists combined hundreds of transistors fit in this circuit result in a more powerful electronic segment called an integrated circuit.
Multiprogramming was implemented (this is when there are several executable programs in memory) at the same time that it diminished their manufacturing costs. In the mid-60s. IBM improved the term “computer architecture”. By the end of the 60s. mini-computers appeared.
This revolutionary innovation allowed to expansion of the processing capacity and memory of the machines.
Instead of punch cards and prints, users interacted via keyboards and monitors , and interacted with an operating system, allowing the device to run various applications at once with a central program that monitored the memory.

As you can see, the first appearance of computer monitors fell on the second generation of computers. The invention belongs to the company IBM, which in 1964 released the commercial display station IBM-2250.
it was used in the system/360 series. The model had a vector monochrome display measuring 12×12 inches, with a resolution of 1024×1024 pixels and a refresh rate of 40 Hz. This invention revolutionized today’s different types of monitors including LCD, LED, OLED monitors.
The invention of IC incredibly decreased the size of computers and made it easy for transportation from one place to another. The working speed and efficiency of this generation of computers were much faster than the previous generation and even cheaper.
High-end languages such as PASCAL, BASIC, FORTRAN – II TO IV, COBOL, ALGOL developed in this generation.
For the first time, they got access to a mass audience allowed computers to penetrate into different spheres of human activity since they were smaller and cheaper. Along these, they turned out to be more specialized (i.e., there were different computers for different tasks).
The 3rd generation of computers was the initial move towards the miniaturization of computers and quickly expanded their scope: control, automation of scientific experiments, data transmission, etc. In addition to being used in the manufacture of radios, TVs, and other similar devices .
Characteristics of the 3rd Generation of Computer:
- In this generation, computers based on Integrated Circuit was more powerful than the transistor.
- The size of the computers was likewise little because the size of the IC being more modest than the circuit size of the transistors.
- More reliable, inexpensive, faster, energy-efficient, as well as very light in weight than 2nd gen computers.
- The first Computer Mouse and Keyboard were appeared and used in the 3rd generation of computers
- Use of new versions of high-level languages like BASIC, COBOL, FORTRAN, PASCAL, and ALGOL
- Available for a mass audience and made it possible for general purpose usage.
Some of the most popular models of the 3rd generation of computers were the ICL 2903, ICL 1900, TDC-B16, IBM 360 and 370, Honeywell 6000, UNIVAC 1108, PDP-8, and PDP-11, which were ideal in their handling multiprocessing capabilities, reliability, and flexibility than previous generations.
4th Generation of Computer (1971-2010)
The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits equivalent to about millions of transistors were assembled and brought the whole central processing unit and other fundamental elements of the machine into a small chip called a microprocessor fitted on the CPU socket.
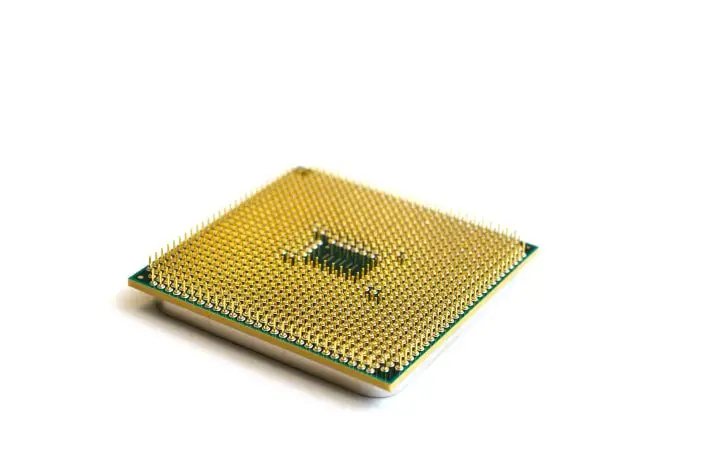
These computers used Very Large Scale Integrated circuits technology also called VLSI technology. After the invention, the microprocessor began to used in computing machines in the fourth and fifth generations of computers.
Within the framework of the considered generation in 1971, the first microprocessor appeared as an unexpected result of Intel’s work on calculator circuits and further development of minicomputers ( PDP-11 ).
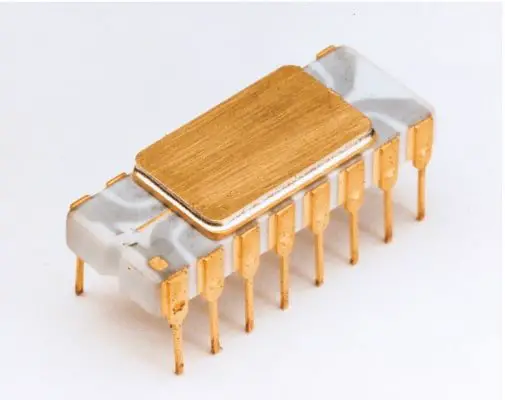
The first personal computer and a microcomputer was “ ALTAIR ” developed by the company MITS in 1974. Also, the first microprocessor was the Intel 4004, manufactured in 1971, initially for an electronic calculator. Whereas the computers of the first generation filled an entire room, while now the 4th generation ‘microprocessors’ fit in the palm of the hand.
This generation of computers used an operating system based on the graphical user interface (GUI), which means these numbers were very easy to perform mathematical and logical tasks.
The computers started to utilize high-speed memory systems on integrated circuits with a capacity of several megabytes. Computer performance has increased significantly (hundreds of millions of operations per second).
The high-level language like C, C ++, Java, PHP, Python, Visual Basic, was utilized to compose programs in the computers of the fourth generation.

The advent of the first personal computers in the mid-70s gave every common user the same computing resources that enormous computers had during the 60s. These computers were made more modest, faster, and less expensive can undoubtedly be put on a table or desk. Which marked the so-called era of personal computers .
Peripheral devices examples , such as mice, joysticks, handheld devices, etc., were developed during this 4th generation. Computers could be connected together in a network to share information with each other, this has played an important role in the birth and development of LAN, Ethernet, and the Internet .

The most popular companies in the world like Intel and AMD were rising. Then again, companies like Microsoft and Apple introduced their operating systems ‘Windows’ and ‘Macintosh’ in the generation of this computer. Because of which the act of multimedia started.
This is the era where personal computers were born, an idea that actually persists today. Also, these were the generation of DEC’s (Digital Equipment Corporation) minicomputers.
Characteristics of the 4th Generation of Computer:
- Computers based on microprocessors and VLSI technology .
- The computers of 4th gen were small in size, lightweight, and almost portable computers.
- The integrating of multi cores in processors like Dual core , Octa core, etc has began.
- The processing speed of this computer generation was much faster and reliable than the previous three generations.
- The size and cost of power supply units has reduced.
- Use of languages like C, C ++, .Net, Java, PHP, Python , Visual Basic.
- Use of GUI Based OS with more memory capacity.
- Accessible to the Internet .
- Due to the low cost of these computers, they were available to every common man.
Desktops, Laptops, Workstations, Tablets, Chromebooks , and Smartphones, are examples of the fourth generation of computers.
Good to Know~ Alan Turing is the father of modern computers born in England in 1912.
5th Generation of Computer (2010-At Present)
Artificial intelligence is the name of the fifth as well as the latest generation of computers based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology is the process of integrating or embedding millions of transistors on a single silicon microchip.

Computing in the 5th computer generation is versatile made portable, powerful, lightweight, innovative, comfortable with low electricity consumption . Because of the Internet’s advantages , it extended its limits of use to limits never before suspected.
The main objective of the latest fifth-generation computing and effort made by computer researchers is to make them smart by incorporating Artificial Intelligence so as to develop devices that respond to the input of natural language and are capable of learning and self-organizing even in 2022 it is under development.
This new information technology has greatly increased the size and working ability of the microprocessor, which has prompted the use of computers in the various fields of Entertainment, Accounting, Educational institutes , Film-making, Traffic-control, Business applications , and Hospitals, Engineering, Researches, Defense, etc.
That’s why a computer of the 5th generation is also known as the AI (Artificial Intelligence) generation of computers.
Some computers are being intended to do all the work themselves as a human act, behave, and communicate. The best example of this is an Artificial Intelligence (AI) based computing machine in the 5th generation of computers “ Sophia ” a robot.
Characteristics of the 5th Generation of Computer:
- The main focus on AI-based computers.
- Computers made of microprocessors based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology.
- The processing speed is quite high can perform billions of calculations in a second.
- Computers are portable, cheap, reliable, fast, and available in various forms and sizes like a Desktop, Laptop, Smartphone, Smartwatches, etc.
- Invention of the operating system such as Windows, Macintosh and ChromeOS of Chromebooks .
- Multimedia has evolved in this generation by combining Sound, Graphics, or Picture and Text.
- Development of Internet of Things.
Computers of the fifth generation are being made to think like us. For which continuous advancement of technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Robotics, etc. Although the examples of AI computing software such as Chatbots, Windows Cortana, Google Assistant, Apple Siri, Speech recognition, that are being used today.
Classification of the computer by generations
| ) | . | |||
| ) | ||||
| ) | ||||
| ) | ||||
| ) |
Factors/Reasons for the development of computer generations:
There below are the general factors associated with the development and change in the generations of electronic computers:
- Improvement of the element base,
- Downsizing,
- Technological progress (increased performance, speed, and memory)
- Reduced cost,
- Development of software ,
- Changes in architecture, expansion of the range of tasks solved by computers,
- Simplification and standardization of hardware.
- Changing the way of interaction between the user and the computer.
How many generations of computers have there been?
There are 5 computer generations till now i.e. vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, microprocessors, and the last one is artificial intelligence. 6th generation yet to come may be either in the form of quantum computers or developing the existing artificial intelligence technology to a greater extent.
What is the 6th generation of computers?
Electronic computers are usually divided into five generations now and the 6th generation is still in development but has the potential to give birth to the sixth generation of computers may be in the form of quantum computing.
Which is the current modern generation of computers today?
The technologies based on artificial intelligence are the current and the latest generation of computers(5th GEN) today.
What is the historical development of computers according to generation?
In accordance with the methodology for assessing the development of computer technology, the first generation was considered to be vacuum tube computers, the second – transistor computers, the third – computers on integrated circuits, the fourth – using microprocessors, and the fifth generation computers is based on the artificial intelligence.
What is the generation of a colossus computer?
Colossus computer was the first generation of the computer developed and designed by Tommy Flowers at Bletchley Park in the year 1944 with the purpose of cracking Hitler’s codes.
The sixth will also discover in the future since there are some flaws of technology in this generation that will be revived or resolved in the upcoming generation.
It takes much time and research to publish such an article ” Generation of Computer 1st to 5th “ If you liked the insights of the article you can support us by sharing this post on social networks.
Share this Post !
Similar Posts

Writing speed on the SSD has dropped: Reasons & Fixes?

Analog Computer: Features, Examples and its Comparison with Digital Computer.


5 Different Types of Monitors For Computer or TV.
How to Tell if a Motherboard has WiFi? (in 5 Easy Steps).
26 thoughts on “generations of computer 1st to 5th explained with pictures.”.
yes that awesome
You’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you enjoyed this information!
This the best platform for student to learn from very gradual, this information is really helpful
It was so wonderful and interesting thank you so much
Hi Rachel, you’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you enjoyed this information!
You have explained the generation of computers very well, by reading this article anyone will understand about the generation of computers.
You’re welcome. Glad you learned some new & informative stuff.
Yes you right sir
Thanks for DIGITALWORLD839.COM for publication of the topics on computers
Wow it helped a lot
Hi Angel, you’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you found this information helpful!
You’re welcome, Asif.
Thank you so much
You’re welcome, Zamzam.
thank you! you help me a lot
Very informative and really precise on the subjects. Thanks.
This’s really helped me with my school project. Thanks so much!
It’s outstanding To much details given by the writer
Well understood!
well understood! thank you
That sounds nice It’ll boost the academic performance of computer student?
Thanks i found this platform very interesting
Thanks for the information it’s really useful
That’s great
thank so much for the help much appreciated.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 7. Evolution of computers
Topic A: Computer generations
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Basic Terms

Vacuum tube – an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.

Transistor – an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
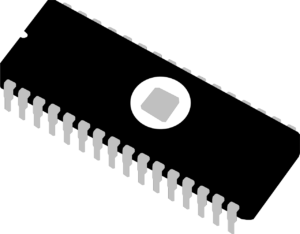
Integrated circuit (IC) – a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes , resistors, etc.).

Microprocessor – an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.

CPU (central processing unit) – It is often referred to as the brain or engine of a computer where most of the processing and operations take place (CPU is part of a microprocessor).

Magnetic drum – a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
Magnetic core – uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.

Machine language – a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
Assembly language is like the machine language that a computer can understand, except that assembly language uses abbreviated words (e.g. ADD, SUB, DIV…) in place of numbers (0s and 1s).

Artificial intelligence (AI) – an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
First Generation of Computers
Classification of generations of computers.
The evolution of computer technology is often divided into five generations.
| Generations of computers | Generations timeline | Evolving hardware |
|---|---|---|
| First generation | 1940s-1950s | Vacuum tube based |
| Second generation | 1950s-1960s | Transistor based |
| Third generation | 1960s-1970s | Integrated circuit based |
| Fourth generation | 1970s-present | Microprocessor based |
| Fifth generation | The present and the future | Artificial intelligence based |
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s)

- Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
- Programming language – machine language

- Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
- Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701, etc.
- Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942 and1963.
Second Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of second generation of computers (1950s-1960s).
- Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk

- Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
- Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, etc.
Third Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of third generation of computers (1960s-1970s).
- Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk

- Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called minicomputers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation computers).

- Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108, etc.
Fourth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fourth generation of computers (1970s-present).

- VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
- RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost when the computer is turned off).

- A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
- Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
- Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third generation computers).

- Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
- Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.

Fifth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fifth generation of computers (the present and the future).

- ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
- Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously.
- Language – understand natural language (human language).
- Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
- Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the fourth generation computers).
- Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.

- Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.

The computer – this amazing technology went from a government/business-only technology to being everywhere from people’s homes, work places, to people’s pockets in less than 100 years.

an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.
an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes, resistors, etc.).
an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer's central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.
The brain or engine of a computer, where most of the processing and operations take place.
a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.
a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
a physical device that is used to store data, information, and programs in a computer.
an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
Key Concepts of Computer Studies Copyright © 2020 by Meizhong Wang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Generations of Computers – Computer Fundamentals
Generations of Computer : The modern computer took its shape with the arrival of your time. It had been around the 16th century when the evolution of the computer started. The initial computer faced many changes, obviously for the betterment. It continuously improved itself in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and price to urge the form of the fashionable day computer.
Basic Terms Related to Computers
The basic terms related to generations of computers are listed below.
- Vacuum Tube: Vacuum tubes have the functionality of controlling the flow of electronics in a vacuum. Generally, it is used in switches, amplifiers, radios, televisions, etc.
- Transistor: A transistor helps in controlling the flow of electricity in devices, it works as an amplifier or a switch.
- Integrated Circuit (IC): Integrated circuits are silicon chips that contain their circuit elements like transistors, resistors, etc.
- Microprocessors: Microprocessors are the components that contain the CPU and its circuits and are present in the Integrated Circuit.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is called the brain of the computer. CPU performs processing and operations work.
- Magnetic Drum: Magnetic Drum is like a cylinder that stores data and cylinder.
- Magnetic Core: Magnetic cores are used to store information. These are arrays of small rings.
- Machine Language: Machine Language is the language that a computer accepts (in the form of binary digits). It is also called low-level programming language.
- Memory: Memory is used to store data, information, and program in a computer.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence deals with creating intelligent machines and behaviors.
Phases of Computer Generations
This long period is often conveniently divided into the subsequent phases called computer generations.
- First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
| Generations of Computer | Time-Period | Evolving Hardware |
|---|---|---|
| First Generation | 1940s – 1950s | Vacuum Tube Based |
| Second Generation | 1950s – 1960s | Transistor Based |
| Third Generation | 1960s – 1970s | Integrated Circuit Based |
| Fourth Generation | 1970s – Present | Microprocessor Based |
| Fifth Generation | Present – Future | Artificial Intelligence Based |
Before the generation of computers, we used calculators, spreadsheets, and computer algebra systems, mathematicians and inventors searched for solutions to ease the burden of calculation.
Below are the 8 Mechanical Calculators before modern computers were invented.
- Abacus (ca. 2700 BC)
- Pascal’s Calculator (1652)
- Stepped Reckoner (1694)
- Arithmometer (1820)
- Comptometer (1887) and Comptograph (1889)
- The Difference Engine (1822)
- Analytical Engine (1834)
- The Millionaire (1893)
First Generation Computers
The technology behind the primary generation computers was a fragile glass device, which was called a vacuum tube. These computers were very heavy and really large. These weren’t very reliable and programming on them was a tedious task as they used low-level programming language and used no OS. First-generation computers were used for calculation, storage, and control purpose. They were too bulky and large that they needed a full room and consume a lot of electricity. Punch cards were used for improving the information for external storage. Magnetic card used . Machine and assembly language is developed.
Examples of some main first-generation computers are mentioned below.
- ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, built by J. Presper Eckert and John V. Mauchly was a general-purpose computer. It had been cumbersome, and large, and contained 18,000 vacuum tubes.
- EDVAC: Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer was designed by von Neumann. It could store data also as instruction and thus the speed was enhanced.
- UNIVAC: Universal Automatic Computer was developed in 1952 by Eckert and Mauchly.
.webp)
Vacuum Tube
Characteristics of First-Generation Computers
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Vacuum tube. |
| Programming language | Machine language. |
| Main memory | and magnetic drums. |
| Input/output devices | Paper tape and punched cards. |
| Speed and size | Very slow and very large (often taking up an entire room). |
| Examples of the first generation | IBM 650, IBM 701, ENIAC, UNIVAC1, etc. |
Second Generation Computers
Second-generation computers used the technology of transistors rather than bulky vacuum tubes. Another feature was the core storage. A transistor may be a device composed of semiconductor material that amplifies a sign or opens or closes a circuit.
Transistors were invented in Bell Labs. The use of transistors made it possible to perform powerfully and with due speed. It reduced the dimensions and price and thankfully the warmth too, which was generated by vacuum tubes. Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, programming language, and input, and output units also came into the force within the second generation.
The programming language was shifted from high level to programming language and made programming comparatively a simple task for programmers. Languages used for programming during this era were FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
.webp)
Characteristics of Second-Generation Computers
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Transistor. |
| Programming language | Machine language and assembly language. |
| Memory | Magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk. |
| Input/output devices | Magnetic tape and punched cards. |
| Power and size | Smaller in size, had low power consumption, and generated less heat (in comparison with the first-generation computers). |
| Examples of the second generation | PDP-8, IBM1400 series, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, CDC 3600, etc. |
Third Generation Computers
During the third generation, technology envisaged a shift from huge transistors to integrated circuits, also referred to as IC. Here a variety of transistors were placed on silicon chips, called semiconductors. The most feature of this era’s computer was speed and reliability. IC was made from silicon and also called silicon chips.
The computer programs was designed to make the machine work. Operating system was a program designed to handle a machine completely. Because of the operating system machine could execute multiple jobs simultaneously. Integrated circuits were used to replace many transistors used in the second generation.
A single IC has many transistors, registers, and capacitors built on one thin slice of silicon. The value size was reduced and memory space and dealing efficiency were increased during this generation. Programming was now wiped out Higher level languages like BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code). Minicomputers find their shape during this era.
.webp)
Integrated Circuit
Characteristics of Third-Generation Computers
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Integrated circuits (ICs). |
| Programming language | High-level language. |
| Memory | Large magnetic core, magnetic tape/disk. |
| Input/output devices | Magnetic tape, monitor, keyboard, printer, etc. |
| Examples of the third generation | IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, NCR 395, B6500, UNIVAC 1108, etc. |
Fourth Generation Computers
In 1971 First microprocessors were used, the large-scale of integration LSI circuits built on one chip called microprocessors. The advantage of this technology is that one microprocessor can contain all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on one chip. LSI placed thousands of transistors onto a single chip.
The computers using microchips were called microcomputers. This generation provided even smaller size of computers, with larger capacities. That’s not enough, then Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits replaced LSI circuits. The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the pc from the central processing unit and memory to input/ output controls on one chip and allowed the dimensions to reduce drastically. VLSI placed several hundred thousand transistors on a single silicon chip. This silicon chip is known as the micro processor.
Technologies like multiprocessing, multiprogramming, time-sharing, operating speed, and virtual memory made it a more user-friendly and customary device. The concept of private computers and computer networks came into being within the fourth generation.

Microprocessor
Characteristics of Fourth-Generation Computers
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Very-large-scale integration (VLSI) and the microprocessor (VLSI has thousands of transistors on a single microchip). |
| Memory | semiconductor memory (such as , etc.). |
| pointing devices, optical scanning, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc. | |
| Examples of the fourth generation | IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, Alter 8800, etc. |
Fifth Generation Computers
The technology behind the fifth generation of computers is AI. It allows computers to behave like humans. It is often seen in programs like voice recognition, area of medicine, and entertainment. Within the field of game playing also it’s shown remarkable performance where computers are capable of beating human competitors.
The speed is the highest, size is the smallest and area of use has remarkably increased within the fifth generation computers. Though not a hundred percent AI has been achieved to date but keeping in sight the present developments, it is often said that this dream also will become a reality very soon.
To summarize the features of varied generations of computers, it is often said that a big improvement has been seen so far because of the speed and accuracy of functioning care, but if we mention the dimensions, it’s been small over the years. The value is additionally diminishing and reliability is increasing.

AI-Based Computers
Characteristics of Fifth-Generation Computers
| Characteristics | Components |
|---|---|
| Main electronic component | Based on artificial intelligence, uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method (ULSI has millions of transistors on a single microchip and the Parallel processing method use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously). |
| Language | Understand natural language (human language). |
| Size | Portable and small in size. |
| Input/output device | Trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognize voice/speech), light scanner, printer, keyboard, monitor, mouse, etc. |
| Example of the fifth generation | Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc. |
FAQs on Generations of Computer
1. what are the 5 types of generation of computer.
The five generations of computers are: 1. First Generation (1940s-1950s): Characterized by vacuum tubes and punched cards. Examples: ENIAC, UNIVAC. 2. Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Transistors replaced vacuum tubes, allowing smaller and more efficient computers. Introduction of high-level programming languages. Examples: IBM 1401, IBM 7094. 3. Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Integrated circuits (ICs) replaced transistors, leading to smaller and faster computers. Introduction of operating systems. Examples: IBM System/360, DEC PDP-11. 4. Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s): Microprocessors brought computing power to individual users. Introduction of personal computers. Examples: IBM PC, Apple Macintosh. 5. Fifth Generation (1980s-Present): Focus on parallel processing, artificial intelligence (AI), and natural language processing. Development of supercomputers and expert systems. Ongoing advancements in AI and machine learning. Examples: IBM Watson, Google’s DeepMind.
2. What is Gen Z technology?
Gen Z technology encompasses the digital tools and platforms that define the experiences of individuals born roughly between the mid-1990s and early 2010s. This generation is characterized by its seamless integration of smartphones, social media, online collaboration, and video content into daily life, shaping their communication, learning, and entertainment habits.
3. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines. It involves programming computers to think, learn, and perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence, such as problem-solving and decision-making. AI encompasses subfields like machine learning and natural language processing, with applications ranging from virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles.
4. What was the First Computer?
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), completed in 1945, is widely regarded as the first electronic general-purpose computer.
5. Who is Known as the Father of Computers?
Charles Babbage is known as the Father of Computers for his pioneering work on the concept of a programmable mechanical computer in the 19th century.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Programming
- How to Get a Free SSL Certificate
- Best SSL Certificates Provider in India
- Elon Musk's xAI releases Grok-2 AI assistant
- What is OpenAI SearchGPT? How it works and How to Get it?
- Content Improvement League 2024: From Good To A Great Article
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
PDF | On Oct 21, 2019, Ishaq Zakari and others published History of computer and its generations. | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Fifth Generation Computers. Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence. Are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition. The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality. The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop ...
1.1 Defi ne computer, and distinguish between analog and digital computer designs, p. 4 1.2 Identify the main types of single user and multi-user computers, p. 5 1.3 Discuss how computers have shaped our current world, p. 10 1.4 List the parts of a complete computer system and discuss the phases of the information processing cycle, p. 20
Computer Systems, Early Computers, Electronic Computers, Generations of Electronic Computers, Mainframe Computers, Mechanical Computers, Microprocessor Architectures, Minicomputers, Parallel Computers, Supercomputers. Contents 1. Early (Non-Electronic) Computing Machines 2. Electronic Computers 2.1. First Generation (1945-1955) 2.2.
Fifth generation computers are in developmental stage which is based on the artificial intelligence. The goal of the fifth generation is to develop the device which could respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will be used in this technology.
The Third Generation, 1964-1979. The third generation officially began in April 1964 with IBM's announcement of its System/360 family of computers. Hardware technology began to use integrated circuits (ICs) which yielded significant advantages in both speed and economy. Operating System development continued with the introduction and ...
e fourth generation computers became more powerful, compact, reliab. e, and affordable. As a result, it gave rise to the personal computer (PC) revolution. This generation also sa. the development of the GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces), mouse, and handheld devices. Despite many advantages, this generation required.
computer, which gets its power by variable programs, with the ability to calculate rapidly, hold lots of information and even learn. We mark computer generations by the logic technology they're built from. We're currently in the fourth generation, called large scale integrated circuit technology. The first generation began
Early Computing Machines. Invention of the Abacus before 1000 BCE, capable of adding and subtracting. Advanced mechanical calculators invented in the 17th century. o Napier's bones. o Pascaline. Turing machine invented in the early 18th century, an abstract machine that simulated computer algorithms. 1956-1963.
Generations of Computer - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the five generations of computers: 1) First generation used vacuum tubes, were large, generated a lot of heat, and were very expensive. 2) Second generation used transistors instead of vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, cheaper, and more reliable.
In comparison to first generation computers, the second generation computer had the following favorable features. 1. Smaller in size as compared to first generation computers 2. More reliable 3. Less heat generated 4. Faster computational speed Disadvantages: Some unfavorable features can also be seen in this generation. 1. Air conditioning ...
1 History of Computers. 1Hi. tory of Comp. ters1.1. IntroductionWe are in the midst of a revolution in technology and in the way. e process information. The computer is at the he. rt of this revolution. Where it will take us is unknown, but we do know that eve. ts are moving rapidly. In fact, virtually everything related to digital computers ...
Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic, or assembly, languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words. High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of COBOL and FORTRAN.
The SSEM (June 1948) was the first such machine to work. The Manchester Mark 1 (Intermediate Version, April 1949) was the first full-sized computer available for use. The completed Manchester Mark 1 (October 1949), with a fast random access magnetic drum, was the first computer with a classic twolevel store.
The electronic computer programmable COLOSSUS was used in cryptanalysis. In 1950, LEO, one of the first electronic computer based on Von Newmann architecture(UAL, UCC, memory, input out devices), was used to inventary mangement. In the prior art, the electronic computers were employed for generating and editing sound images and video.
Generations of Computers Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. Nowadays, generation includes both hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system.
Computer generations are based on when major technological changes in computers occurred, like the use of vacuum tubes, transistors, and the microprocessor. As of 2018, there are five generations of the computer. Types of Computer Generation and examples 1940 - 1956: First Generation - Vacuum Tubes The first generation of computers used ...
Computer Generations Assignment Refined - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the history of computer generations from first to fifth generation. Each generation is characterized by improvements in circuitry size, speed, memory, and reliability due to advancements in technology.
Abstract-In this paper, emphasis has been given on the gradual and continuous advancement of computer from on and before 300BC to 2012 and beyond. During this very long period of time, a simple device like computer has witnessed many significant changes in its manufacturing and development. By and large, the changes are conceptual ...
Introduction to Computer Generations. This development period of electronic computing technology is called Computer Generation. There are five generations of computers identified, although the sixth generation could be in development now in the early 21st century.. During the evolutionary timeline, each generation of computers has improved a lot by undergoing considerable changes in their size ...
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s) Main electronic component - vacuum tube. Main memory - magnetic drums and magnetic tapes. Programming language - machine language. Power - consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat. Speed and size - very slow and very large in size (often taking up ...
First Generation Computers (1940-1956) Second Generation Computers (1956-1963) Third Generation Computers (1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond) Generations of Computer. Time-Period. Evolving Hardware. First Generation.
Assignment Generations of Computer - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the five generations of computers from the 1940s to the 1980s. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were large, expensive, and unreliable. The second generation used transistors, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable.