- English ESL Worksheets
- Grammar Topics
- Past simple tense

2,947 Past simple tense English ESL worksheets pdf & doc
Simple Past – Free Exercise
Complete the sentences with the simple past of the verbs in brackets.
- William (visit) his grandparents last weekend. regular verb → add ed
- Jane (arrive) an hour ago. regular verb that ends in e → add a d
- We (go) to Bob's birthday party yesterday. irregular verb, 2nd verb form (go- went -gone)
- I (be) on holiday last week. irregular verb, 2nd verb form (be- was/were -been) for I/he/she/it we use was
- She (see) fire. irregular verb, 2nd verb form (see- saw -seen)
Make the sentences negative.
- I phoned Lucy last night. → I Lucy last night. didn’t + infinitive
- You cleaned your room. → You your room. didn’t + infinitive
- Olivia worked as an actress. → Olivia as an actress. didn’t + infinitive
- We looked for the treasure. → We for the treasure. didn’t + infinitive
- He spoke Spanish. → He Spanish. didn’t + infinitive
Make simple past questions using the words in brackets.
- (you/dance) at the party last night? did + subject + infinitive
- (she/do) her homework? did + subject + infinitive
- (Robert/work) at the post office? did + subject + infinitive
- (they/help) you with the washing-up? did + subject + infinitive
- When (I/say) that? question word + did + subject + infinitive
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
Past simple exercises PDF
- English grammar PDF
- PDF worksheets
- Mixed PDF tests
- Present tenses
- Past tenses
- Future tenses
- Present perfect
- Past perfect
- Future perfect
Irregular verbs
- Modal verbs
- If-conditional
- Passive voice
- Reported speech
- Time clauses
- Relative clauses
- Indirect questions
- Question tags
- Imperative sentence
- Gerund and infinitive
- Direct | indirect object
Past simple tense
- Online exercises
- Grammar rules PDF
English grammar books PDF
PDF book 1: English grammar exercises PDF
PDF book 2: English grammar rules PDF
Past simple exercises + PDF worksheets
PDF exercises to download for free:
Past simple verbs PDF 1
Key with answers 1
- Dear Jane, How are you doing? Yesterday I ___ (do) my homework, ___ (tidy) my bedroom and ___ (decide) to go out.
Past simple verbs PDF 2
Key with answers 2
- cast, catch, cost, cut The goalkeeper ___ the ball. Our holiday in the Caribbean ___ a fortune.
Past simple was, were PDF 3
Key with answers 3
- A: ___ I often ill when I was a child? B: Not really. You ___ healthier than your brother.
Past simple was, were PDF 4
Key with answers 4
- Samuel, I hear you ___ eighteen years old last week. Yes, I ___ . I had a big birthday party.
Past simple questions PDF 5
Key with answers 5
- (Bill | arrive | on time) Did Bill arrive on time?
Past simple questions PDF 6
Key with answers 6
- Did your students their homework? or Did your students do their homework?
Past simple positive + negative PDF 7
Key with answers 7
- The Beatles were formed in London in 1960. The Beatles ___ (not be) formed in London. They ___ (start) to play together in Liverpool in 1960.
Past simple negative PDF 8
Key with answers 8
- I ___ (not have) a good day yesterday. I ___ (cannot) stay in bed late, because it was Monday and I had to go to school again.
Past simple vs. Past continuous exercises PDF
Past simple vs. Past perfect exercises PDF
Past simple vs. Present perfect exercises PDF
Past simple passive exercises PDF
Online exercises with answers:
- Complete sentences with regular and irregular verbs.
Past simple - irregular verbs 1
- Choose correct verbs from the list to complete sentences.
Past simple - irregular verbs 2
- Complete sentences with verbs in brackets.
- Correct the information in the general knowledge.
- Complete the story. (Blue Monday)
- Choose the correct questions.
- Regular and irregular verbs, negative forms and questions (three exercises).
Grammar rules PDF:
Past simple and continuous PDF rules
We add -ed to the base form of a verb to make regular past simple forms: work - worked, jump - jumped . It is the same for all persons, singular and plural.
Positive statement: I listened, he listened Negative statement: I did not listen (I didn't listen), he did not listen (he didn't listen) Question: Did you listen? Negative question: Did you not listen? (Didn't you listen?)
Spelling rules
We add -d (not -ed) to the verbs that end with -e: like - liked. If the verb ends with a consonant and -y, we change -y into -i: carry - carried, try - tried. But: play - played , because this verb ends with a vowel and -y.
If the verb has only one syllable and ends with a vowel and a consonant, we double the consonant to keep the same pronunciation: stop - stopped . The same rule applies to the verbs that end with -l: travel - travelled .
All the irregular verbs have different forms: go - went, buy - bought, cut - cut etc.
We use did to make past simple questions: I cried. - Did you cry? He slept. - Did he sleep?
We do not use the auxiliary verb did with the verb to be and modal verbs. Were you a student? Was he in London? I was not at home. He was not happy. Could you sing? Could he come? I could not swim. He could not stay.
Wh- questions
The auxiliary verb did is not used in questions beginning with wh- pronouns (who, which) in case that the pronoun is the subject of the question. Who met you? (who is the subject) Which train arrived on time? (which train is the subject) But: Who did you meet? Which train did you miss? (who and which train are the objects)
The negative question normally shows a surprise. Didn't you know it?
Negative forms
We use did not or didn't to make negative forms: You did not come. Julia didn't do her homework.
- All PDF exercises and grammar rules from this website.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Simple Past Tense | Examples & Exercises
Simple Past Tense | Examples & Exercises
Published on August 22, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on October 23, 2023.
The simple past tense is a verb form used to refer to an action or series of actions that were completed in the past.
The simple past tense of regular verbs is formed by adding “-ed” to the infinitive form of the verb (e.g., “cook” becomes “cooked”). Most verbs in the simple past take the same form regardless of the subject (e.g., “He worked/we worked”).
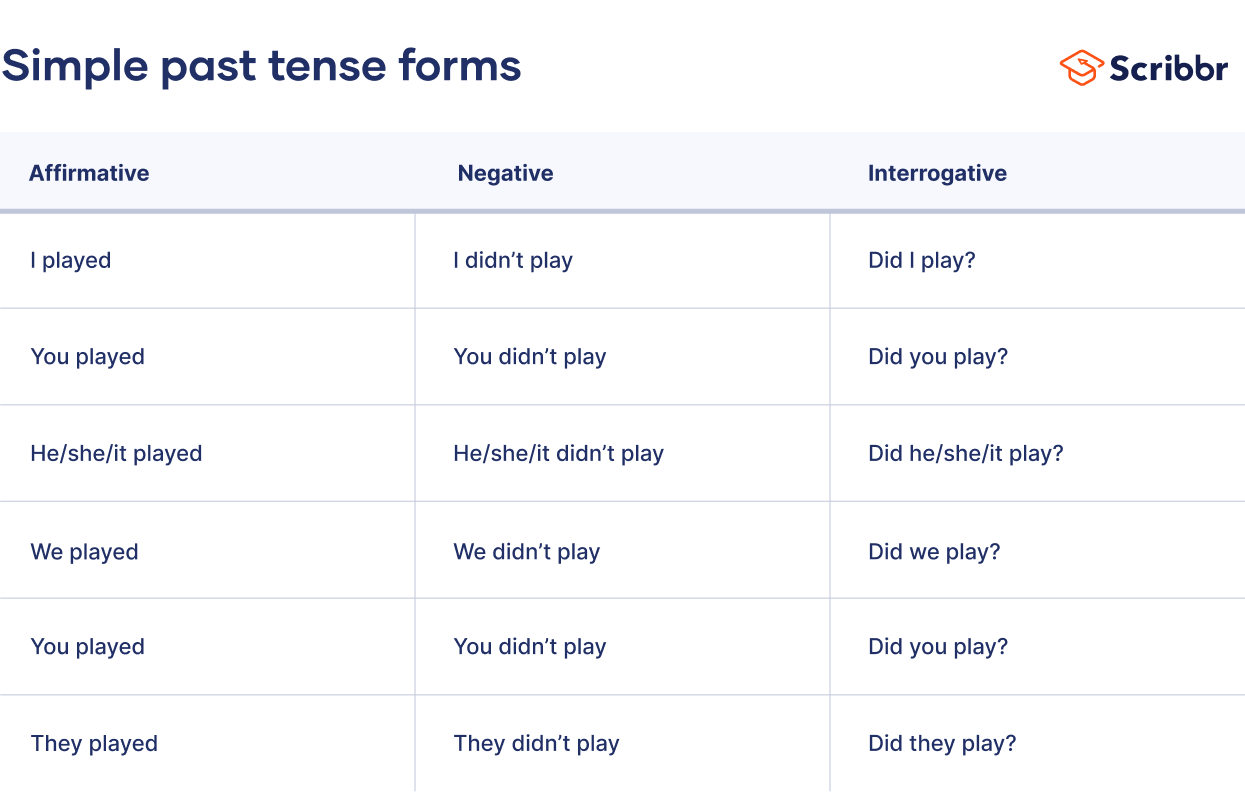
Table of contents
How to use the simple past, present perfect vs. past simple, simple past vs. past perfect, how to form negatives, how to form questions, how to form the passive voice, exercises: simple past tense, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions about the simple past tense.
The simple past tense (also called the past simple or preterite ) is used to describe an action or series of actions that occurred in the past.
The past simple of regular verbs is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the infinitive (e.g., “talk” becomes “talked”).
Irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern: some take the same form as the infinitive (e.g., “put”), while others change completely (e.g., “go” becomes “went”).
Most verbs in the simple past tense don’t follow subject-verb agreement (i.e., they don’t change form depending on the subject).
Ariana rented a car and drove to the coast.
We visited a museum, walked the Champs-Élysées, and dined at a fancy restaurant.
Forming the simple past
The simple past of regular verbs is usually formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the verb (e.g., “guess” becomes “guessed”). However, this can vary depending on the verb’s ending.
| -e | -add “d” | love; loved |
| short verbs, where the last three letters follow a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern | -double the last letter and add “-ed” | stop; stopped plan; planned |
| long verbs with a stressed syllable at the end, where the last three letters follow a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern | -double the last letter and add “-ed” | prefer; preferred admit; admitted |
| Consonant + y | -ied (replacing the “y”) | try; tried |
Irregular verb: “be”
The stative verb “be” in the simple past tense is used to describe unchanging past conditions (e.g., “My father was a good man”) and temporary past situations (e.g., “The children were tired”). Unlike other verbs in the simple past, “be” changes form depending on the subject, as shown in the table below.
| I | was |
| You | were |
| He/she/it | was |
| We | were |
| You | were |
| They | were |
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Both the present perfect and past simple tenses are used to refer to past action. However, they serve different purposes:
- The present perfect is used to refer to an action that began in the past and may continue or to an action that took place in the past and has present consequences.
- The past simple is typically used to describe an action that was completed in the past and is not ongoing.
I have run a marathon before. [I may run a marathon again]
I was a vegetarian when I was younger.
While the past simple is used to describe an action or series of actions that occurred in the past, the past perfect is used to indicate that an action was completed before another past action began.
In the past simple tense, negative statements are formed by adding “did not” (or the contraction “didn’t”) between the subject and the infinitive form of the verb.
For the verb “be,” negative statements are formed by adding “was not/were not” (or the contractions “wasn’t/weren’t”) after the subject .
To ask a yes–no question using the simple past, add “did” before the subject and the infinitive form of the verb.
To ask a question starting with a wh-word (an interrogative pronoun like “who” or an interrogative adverb like “where”), follow the same word order as above, but add the pronoun or adverb at the start of the sentence.
Why did Eva leave so early?
Passive sentences are ones in which the subject is not the person or thing performing the action. Instead, the subject is the person or thing being acted upon.
In the past simple, passive constructions are formed using a subject , “was”/“were,” and the past participle of the verb.
Maria was ignored by the salesman.
Practice using the simple past correctly with the exercises below. In the blank space in each sentence, fill in the correct simple past form based on the subject and verb specified (e.g., “[he / talk]” becomes “he talked”). Some answers may also be negative statements or questions.
- Practice questions
- Answers and explanations
- __________ [you / go] to the shop this morning.
- __________ [they / play] a board game.
- __________ [my son / not / study] for the exam.
- __________ [the band / rehearse] every day this week.
- __________ [I / plan] to be home by six!
- When __________ [you / travel] to France?
- The simple past form of the irregular verb “go” is “went.”
- The simple past form of the regular verb “play” is “played.”
- In the simple past tense, negative statements are formed by adding “did not” (or the contraction “didn’t”) between the subject (“my son”) and the infinitive form of the verb (“study”).
- The simple past form of the regular verb “rehearse” is “rehearsed.”
- For short verbs, where the last three letters follow a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern (e.g., “plan”), you double the final consonant and add “-ed.”
- To ask a question starting with a wh-word, add the wh-word at the start of the sentence, followed by “did,” the subject (“you”), and the infinitive form of the verb (“travel”).
If you want to know more about commonly confused words, definitions, common mistakes, and differences between US and UK spellings, make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Sentence structure
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
The simple past tense of the verb “read” is “read” (e.g., “I read a book last week”).
While “read” is spelled the same in both its past and present forms, its pronunciation differs depending on the tense :
- The simple present form is pronounced “reed.”
- The simple past form is pronounced “red.”
The simple past tense of the verb “teach” is “taught” (e.g., “You taught me a lesson”).
While the simple past of a regular verb is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the infinitive (e.g., “talk” becomes “talked”), irregular verbs like “teach” don’t follow a specific pattern.
The simple past tense of the verb “go” is “went” (e.g., “Ava went to Spain”).
While the simple past of a regular verb is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the infinitive (e.g., “jump” becomes “jumped”), irregular verbs like “go” don’t follow a specific pattern.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, October 23). Simple Past Tense | Examples & Exercises. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/simple-past-tense/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, simple present tense | examples, use & worksheet, present continuous tense | examples & exercises, present perfect continuous | examples & exercises, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
The Simple Past of Regular and Irregular Verbs
Table of contents, what is the simple past tense, the simple past of regular and irregular verbs, the simple past of regular verbs.
| Verb + ed |
|---|
| The Infinitive | The Simple Past |
|---|---|
| live | lived |
| start | started |
| die | died |
| visit | visited |
| play | played |
| watch | watched |
| phone | phoned |
| marry | married |
The Simple Past Of Irregular verbs
For example, the verbs “was, wrote” are irregular past forms. “ Was ” is the simple past of “ to be ,” and “ wrote ” is the simple past of “ write .”
| The Infinitive | The Simple Past |
|---|---|
| be | was/were |
| come | came |
| do | did |
| drive | drove |
| give | gave |
| go | went |
| meet | met |
| run | ran |
| see | saw |
| speak | spoke |
| swim | swam |
| write | wrote |
The Simple Past Of Regular And Irregular Verbs (Form And Use)
The forms of the simple past tense, 1. the affirmative form of the simple past:.
| I, you, he, she, it, we, they | tennis last Sunday. |
| the movie last Saturday. | |
| the report two days ago. | |
| the homework yesterday evening. |
2. The Interrogative Form of the Simple Past:
| AUXILARY VERB “DID” + SUBJECT + BASE FORM OF THE VERB |
|---|
| Did you have lunch? |
| Did | I, you, he, she, it, we, they | play tennis? |
| watch the movie? | ||
| write the report? | ||
| do the homework? |
The Negative Form of the Simple Past
| I did not/didn’t have lunch |
| I, you, he, she, it, we, they | tennis last Sunday. | |
| the movie last Saturday. | ||
| the report two days ago. | ||
| the homework yesterday evening. |
The Use of the Simple Past
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer
learnEnglish-online
Learn English Online for Free
Main navigation
Simple past.
The simple past a common verb tense in English. It is for actions in the past. This lesson shows you how to use the simple past correctly and gives you examples. You can find the exercises at the bottom of the page .
Let’s start with regular and irregular verbs:
Simple Past Verbs
Two types of verbs are used in the simple past: Regular and Irregular .
Regular Verbs
To make a regular verb in the past tense, ad “ ed ” to the base verb.
| Play | Play |
| Talk | Talk |
| Watch | Watch |
Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs don’t end in “ ed ”. They have different endings. For example:
The Verb to Be
“ Be ” is an irregular verb with more than one conjugation in the past:
| I | Was |
| You | Were |
| He/She/It | Was |
| We | Were |
| They | Were |
Here are some example sentences with “be” in the simple past.
- I was tired yesterday.
- They were hungry this morning.
Here is a list of common irregular verbs and their past tense forms:
| Be | Was, Were |
| Can | Could |
| Have | Had |
| Do | Did |
| Go | Went |
| Say | Said |
| Take | Took |
| Make | Made |
| Know | Knew |
| Eat | Ate |
| Run | Ran |
Simple Past Structure
You can form this verb tense with this structure:
| Subject + Verb (Past) + Object |
Here are some examples:
- I played baseball.
- She finished the game.
- He went home.
- They ate lunch.
The verb is the same for all subjects.
- They played
Now let’s see when to use the simple past verb tense.
Simple Past Uses
Completed Actions in the Past
Use the simple past to talk about actions that are finished in the past.
- She went to the movie theatre yesterday.
- He ate breakfast at 8:30 this morning.
- Susan finished her homework last night.
Past Status
Use “was” and “were” to talk about past status.
- He was a teacher 5 years ago. He is not anymore.
- They were tired last night.
- It was hot last week. Now it is cold.
Past Routines
Activities that happened many times in the past also use simple past.
- I worked every day last week.
- She watched television very often when she was a child.
- The kids always walked home from school.
Simple Past Questions
Yes/No questions in the simple past are like questions in the simple present. You can ask Did questions and Be questions.
Use “Did” to form questions with other verbs.
| Did + Subject + Base Verb |
- Did you eat yesterday?
- Did she watch the movie?
- Did Charles leave ?
Use “Did” with all subjects:
- Did they walk to the store?
- Did you finish the game?
- Did she like the book?
- Did Greg and Tony play soccer last night?
Also, make sure the verb is in its simple form. After “ did “, the verb is in present form.
- Did Sandra and Jim go home?
- Did she buy new shoes?
To answer these questions, use the following two options:
- Yes, I did.
- No, I did not.
Here is an example conversation with questions using “ did ”:
Tom: Did you bring your jacket?
Kelly: No, I did not.
Tom: Did you bring a sweater?
Kelly: Yes, I did.
Use the verb “ be ” with adjectives and nouns . “ Be ” is a verb, so you do not need another verb. Here is the structure:
| Be (in past) + Subject + Adjective/Noun |
- Were you hungry last night?
- Was she a teacher last year?
- Was it cold last week?
Be is conjugated as “ was ” or “ were ”:
| I | Was |
| You | Were |
| She | Was |
| He | Was |
| It | Was |
| We | Were |
| They | Were |
WH questions in the past are the same as WH questions in the present. They are formed as follows:
| WH + Did + Subject + Verb |
- Where did you go last night?
- What did you eat for breakfast yesterday?
- When did you wake up this morning?
| WH + Was/Were + Subject + Noun/Adjective |
- Where was the party last night?
- When was the game yesterday?
- Who was the champion at the tournament?
Here is a sample conversation with “wh” questions in the past:
James: Hi Doug, How was your weekend?
Doug: It was good, thanks.
James: What did you do?
Doug: I went to a restaurant for dinner.
James: Where did you go?
Doug: I went to Super Pizza.
James: How was it?
Doug: The pizza was delicious.
Simple Past Negative Sentences
There is a special structure to use when making negative statements in the past. There are two types of negative sentences with simple past: Did and Be .
| Subject + Did + Not + Verb (in present) |
- I did not eat yesterday.
- She did not wear a hat last night.
- We did not go to a restaurant.
“Did not” is contracted as “didn’t”.
- He didn’t listen to the teacher.
- We didn’t go to the concert.
Be is conjugated as “was” and “were”. These negative sentences are used for past status.
| Subject + Be + Not + Adjective/Noun |
- I was not tired yesterday.
- We were not quiet in class.
- Jeremy was not awake at 7:00 am this morning.
Simple Past Time Phrases
There are many words used to show an activity is in the past. Here are the 2 most important:
Ago is used with a measure of time to show when something happened. It goes after the measure of time:
| Time + Ago |
- He arrived 30 minutes ago .
- She lived in San Francisco 5 years ago .
- They left 2 hours ago .
Last means a time before the current time. It goes before the unit of time:
| Last + Time |
- He worked at McDonald’s last
- They ate Italian food last week.
Simple Past Exercises
Are you ready to check your understanding of the simple past? Try these simple past exercises:
Simple Past Test
Simple past test 2, simple past questions test, simple past questions test 2, simple past verbs test.
You can also practice with this listening activity that uses a song by The Beatles:
Simple Past Listening Exercise
And here is a reading activity:
Simple Past Reading
More grammar lessons and tests.
- Conditionals
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Gerunds and Infinitives
- Modal Verbs
- Passive Voice
- Prepositions
- Rather and Prefer
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Verb Tenses
Start Your Free English Course Today!
Grammar Writing Listening Reading Vocabulary
IELTS TOEFL TOEIC Business English

- Kindergarten-Numbers
- Grade 1-Counting
- Grade 1-Addition
- Grade 1-Subtraction
- Grade 1-Multiplication
- Grade 1-Division
- Creative Writing Prompts
- Famous Cities
- Eslways.com

- Aladdin and the Magic Lamp
- Alice in Wonderland
- Beauty and the Beast
- Gingerbread Man
- Hansel and Gretel
- Jack and the Beanstalk
- Little Red Riding Hood
- Puss in Boots
- Sleeping Beauty
- Snow White
- Rumpelstiltskin
- The Bremen Town Musicians
- The Elves and the Shoemaker
- The Emperor's New Clothes
- The Frog Prince
- The Golden Goose
- The Tin Soldier
- Tom Thumb

- Classroom Language
- Describing People
- Environment
- Giving Directions
- Greeting People

- Privacy Policy
- Term of Use
- Report a Mistake

- 4th of July
- Accessories
- Action Verbs
- American/British English
- Animal Sounds
- Autumn/Fall
- Baby Animals
- Bathroom Objects
- Bedroom Objects
- Body Movement Verbs
- Body Parts
- Children Games
- Chinese Zodiac Signs
- Classroom Objects
- Classroom Verbs
- Clothes and Accessories
- Computer Parts
- Cooking Verbs
- Countries/Nationalities
- Daily Routines
- Days of the Week
- Detective Stories
- Easter Holiday
- Extreme Sports
- Face Parts
- Family Members
- Farm Animals
- Fast Food
- Father's Day
- Feelings/Emotions
- Films/Movies
- Food and Drinks
- Free Time Activities
- Gardening Tools
- Hand Tools
- Health Problems
- Holiday Types
- Household Chores
- Jobs/Occupations
- Junk Food
- Kitchen Appliances
- Kitchen Utensils
- Living Room Objects
- Means of Transport
- Mother's Day
- Musical Instruments
- Nationalities
- New Year's Eve
- Office Objects
- Opposite Adjectives
- Ordinal Numbers
- Party Types
- Personal Care Products
- Places in a City
- Places in a House
- Places at School
- School Subjects
- School Supplies
- Sea Animals
- Solar System
- Sports Verbs
- St. Patrick's Day
- Stationery Objects
- Thanksgiving
- TV Programmes
- Valentine's Day
- Weather Conditions
- Wild Animals
- Zodiac Signs
- Ability / Inability
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Because/Because Of
- Comparatives
- Conditionals
- Conjunctions
- Contractions
- Countables/Uncountables
- Demonstratives
- Determiners
- Frequency Adverbs
- Future Tenses
- Gerunds and Infinitives
- Imperative Mood
- Irregular Verbs
- Modal Verbs
- Must/Have To
- Participles
- Parts of Speech
- Passive Voice
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense
- Phrasal Verbs
- Plural Nouns
- Possessive Adjectives
- Prepositions
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Punctuation Marks
- Quantifiers
- Regular Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Reported Speech
- Sense Verbs
- Stative Verbs
- Subject/Verb Agreement
- Subordination
- Tag Questions
- Time Adverbs
- Used to
- Verb Tenses
- Verb To Be
- Wish Clauses
- Word Order

Past Simple Tense ESL Multiple Choice Questions Worksheet
Past Simple ESL Reading Comprehension Questions Worksheet

Past Simple ESL Reading Comprehension Exercises Worksheet
Past simple tense esl printable speaking activity cards, past simple tense esl word order exercise worksheet.

Past Simple Tense ESL Printable Writing Activity Worksheet

Past Simple Tense ESL Worksheets

Past Simple ESL Dialogue Comprehension Exercises Worksheet

Past Simple ESL Gap Fill Exercise Worksheet

Past Simple Was Were ESL Grammar Exercises Test Worksheet

Past Simple Regular Verbs ESL Grammar Test Worksheet

Past Simple Irregular Verbs ESL Grammar Test Worksheet

Past Simple Tense ESL Printable Board Game
The Past Simple Tense
Perfect english grammar.

(also called the simple past tense)
Click here to learn about how to USE the past simple.
It's similar to the present simple because it has different rules for the verb 'be', which becomes 'was' or 'were':
The Past Simple with 'be'
Here's how to make the positive:
| I cold |
| you tired |
| he in the garden |
| she late |
| it sunny |
| we on holiday |
| they hungry |
To make the negative with 'be', just add 'not':
| I was sleepy | I was sleepy |
| you were on the bus | you were on the bus |
| he was at school | he was at school |
| she was beautiful | she was beautiful |
| it was cold | it was cold |
| we were at work | we were at work |
| they were tired | they were tired |
Here's an exercise to practise the positive and negative forms with 'be'
To make a question, just like the present simple, we change the position of 'was / were' and the subject.
Here are the past simple 'yes / no' questions with 'be':
| sleepy? |
| late? |
| at the cinema? |
| kind? |
| hot? |
| hungry? |
| at work? |
And the 'wh' questions with 'be' (the question word just goes at the beginning, everything else is the same):
| why sleepy? |
| where ? |
| when at the cinema? |
| how ? |
| how ? |
| why hungry? |
| when at work? |
And here's an exercise for 'wh' and 'yes / no' questions

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
The Past Simple (Simple Past) with Other Verbs
The positive:
We usually make the positive by adding '-ed' to the infinitive. For example, 'play' becomes 'played'. However, there are some irregular verbs , for example 'go' becomes 'went' and 'run' becomes 'ran'.
(Here's some help if you are not sure how to pronounce '-ed' at the end of a verb).
| I (regular) |
| you (regular) |
| he (regular) |
| she (regular) |
| it (regular) |
| we (irregular) |
| they (irregular) |
Click here for a list of 50 common irregular verbs (PDF file)
Click here for an exercise about irregular verbs in this verb tense
Click here for another irregular verb exercise
In the negative there aren't any irregular verbs. All verbs use 'did not (didn't) + infinitive':
| I walk | I walk |
| you play | you play |
| he cook | he cook |
| she listen | she listen |
| it rain | it rain |
| we eat | we eat |
| they drink | they drink |
Here's an exercise about the negative form
Questions are also very easy. Just put 'did' before the subject, and the infinitive after it.
Here are the 'yes / no' questions:
| I ? |
| you ? |
| he ? |
| she ? |
| it ? |
| we ? |
| they ? |
And here's an exercise about 'yes / no' questions
To make a 'wh' question, of course, put the question word at the beginning of the sentence:
| where I ? |
| what you ? |
| what he ? |
| why she ? |
| when it ? |
| where we ? |
| how they ? |
And here's an exercise about 'wh' questions
Here are some exercises about making all the forms: Mixed Exercise 1 Mixed Exercise 2 Mixed Exercise 3 Mixed Exercise 4
Click here to learn about when we use this tense

Past Simple Tense: How to Use It, With Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
On this page:
Simple past tense definition
The simple past tense is a verb tense that is used to describe completed actions or events that occurred in the past. The simple past tense is commonly used in storytelling and narration, as well as in conversations about past experiences. In this article, we will explain how to use the simple past and provide examples to help you understand it better.
When to use the simple past tense?
1. Actions That Occurred in the Past The simple past tense is commonly used to describe actions that happened in the past. For example:
- I walked to the store.
- They studied English last night.
- She ate pizza for dinner.
2. Completed Actions Completed ActionsThe simple past tense is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. For example:
- I finished my homework before dinner.
- They left for the airport at 5am.
- She visited her grandparents last weekend.
3. Sequences of Events in the Past The simple past tense can also be used to describe a sequence of events that occurred in the past. For example:
- I woke up, brushed my teeth, and ate breakfast.
- They arrived at the party, greeted their friends, and danced all night.
- She got dressed, packed her bags, and left for the airport.
4. Past Habits or States The simple past tense can be used to describe habits or states in the past. For example:
- I always drank coffee in the morning.
- They lived in New York City for ten years.
- She had curly hair when she was a child.
5. Specific point in the past To talk about a specific point in the past. For example:
- He finished his project last night at 10 pm.
How to form the simple past tense?
The simple past tense is formed using the past form of the main verb. The structure of a simple past form is as follows:
Subject + past form of the verb
The formation of the simple past tense depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular:
1. For regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to the base form of the verb to form the past simple tense. For example:
- walk (base form) -> walked (past simple)
- play (base form) -> played (past simple)
- watch (base form) -> watched (past simple)
2. For irregular verbs, the simple past form is different from the base form of the verb and must be learned individually. Some common irregular verbs and their past simple forms include:
- go (base form) -> went (past simple)
- eat (base form) -> ate (past simple)
- see (base form) -> saw (past simple)
- do (base form) -> did (past simple)
Note that there are some verbs that are both regular and irregular, depending on their meaning. For example:
- “learned” (regular) and “learnt” (irregular) are both used in different regions and contexts.
Also, it’s important to remember that the verb “be” has two different past simple forms: “was” (for the singular pronouns: I, he, she, it) and “were” (for the plural pronouns: we, you, they).
Here are some examples of the past simple tense in use:
- Regular verb: “She played tennis yesterday.”
- Irregular verb: “He went to the store last night.”
- Irregular verb: “I saw a movie last weekend.”
- Regular verb: “We walked to the park.”
- Irregular verb: “They did their homework before dinner.”
How to make a negative form?
To make a negative sentence in the past simple tense, you need to use the auxiliary verb “did” and the negative particle “not” (or “n’t”). The formula forming the simple past is:
Subject + did not (didn’t) + base form of the verb + object
For example:
- I did not (didn’t) go to the party last night.
- He did not (didn’t) finish his homework on time.
- They did not (didn’t) visit their grandparents over the weekend.
Note that the contracted form “didn’t” is more commonly used in spoken English.
Also, for regular verbs, the negative form is formed by adding “-not” (or “-n’t”) to the auxiliary verb “did” and using the base form of the verb. For example:
- I did not (didn’t) walk to the store.
- She did not (didn’t) play soccer last weekend.
- They did not (didn’t) watch a movie yesterday.
How to make a question form?
You can read more here about the question form
Can I use the simple past tense to talk about ongoing actions in the past?
No, the past simple tense is not used to talk about ongoing actions in the past. It is used to describe a completed action or event that happened at a specific time in the past. If you want to talk about an action that was in progress in the past, you should use the past continuous tense.
For example, if you want to describe an action that was ongoing in the past, you could say “I was reading a book,” using the past continuous tense. If you were to use the past simple tense, it would imply that you had already finished reading the book, and would say “I read a book” use the simple past instead.
Can I use the simple past tense to talk about future events from a past perspective?
No, the simple past tense is not typically used to talk about future events, even from a past perspective. It is primarily used to describe completed actions or events that occurred at a specific point in the past.
If you want to talk about a future event from a past perspective, you would typically use the past perfect tense. For instance, “By the time I arrived at the party, the cake had already been cut,” suggests that the cake was cut before the speaker arrived at the party.
Alternatively, you could use the present perfect tense to describe a future event that has already been planned or arranged. For instance, “I have reserved a table at the restaurant for tomorrow night,” suggests that the reservation has already been made for a future event.
What are some common irregular verbs in the simple past tense?
In English, there are many irregular verbs, which means their past tense and past participle forms do not follow the rules of the regular -ed ending pattern. Here are some common irregular verbs in the simple past tense:
- have -> had
- say -> said
- make -> made
- come -> came
- take -> took
It is important to remember that irregular verbs do not follow a specific rule, so they need to be memorized.
Are there any exceptions or special cases when using the simple past tense?
Yes, there are a few exceptions and special cases when using the simple past tense in English:
- Modal verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) do not have a past tense form. Instead, their past meaning is expressed through the use of the perfect infinitive (e.g. could have, should have, would have).
- The verb “to be” has two past tense forms: “was” for the singular subjects (I, he, she, it) and “were” for the plural subjects (we, you, they).
- Some verbs have the same past simple form as their base form. For instance, “cut” is the past simple form of “cut,” and “put” is the past simple form of “put.”
- The simple past tense is sometimes used in conditional sentences to express a hypothetical situation that is unlikely or impossible. For example, “If I had known you were coming, I would have baked a cake.”
- In reported speech , the simple past tense is often used to report a past action or event. For example, “She said she saw the movie yesterday.” Here, the original statement might have been “I saw the movie yesterday,” but in the reported speech, the simple past tense “saw” is changed to “said she saw.”
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
https://first-english.org
Simple past worksheet - English online exercises
- English year 1
- Tenses English
- English year 2
- English year 3
- English year 4
- You are learning...
- Simple past
- 01 Simple Past rules
- 02 Simple Past - to be
- 03 Simple Past - to be
- 04 Simple Past - to be
- 05 Past regular verbs
- 06 Past regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- 07 past irregular verbs
- 08 past irregular verbs
- 09 simple past questions
- 10 simple past questions
- 11 simple past questions
- 12 crossword Simple Past
- 13 crossword Simple Past
- 14 crossword Simple Past
- 15 crossword Simple Past
- 16 crossword Simple Past
- 17 past - present crossword
- 18 past - present crossword
- 19 simple past worksheets
- 40 more exercises
- English Tenses
- Simple Present Tense
- Simple Past Tense
- Present Perfect
- Past Perfect
- Future Perfect
- Going-to-Future
- Continuous Tenses
- Present Continuous
- Past Continuous
- Present Perfect Progr.
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Future 1 Continuous
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Comparison of Tenses
- If clauses - Conditional
- Passive exercises
- Reported Speech
Simple past worksheets
Simple past worksheet exercises.
1 Simple Past rules and explanations PDF 2 Simple Past regular verbs PDF exercises 3 Simple Past exercises answers PDF 4 Simple Past reguar verbs worksheet PDF 5 Simple Past regular verbs answers PDF 6 Simple Past regular verbs worksheet PDF 7 Simple Past regular verbs secrets answers PDF 8 Simple Past reguar verbs worksheet PDF 9 Simple Past irregular verbs secrets answers PDF
Irregular verbs - worksheets
10 Simple Past irregular verbs 11 Simple Past irregular verbs answers 12 Simple Past irregular verbs 13 Simple Past irregular verbs answers 14 Simple Past to be 15 Simple Past to be answers ▶ These exercises as free online exercises
Signal words Simple Past - worksheets
16 Simple Past signal words worksheet PDF 17 Simple Past signal words answers 'to be' PDF 18 Simple Past signal words word order worksheet PDF 19 Simple Past signal words answers PDF 20 Simple Past signal words exercises worksheet PDF 21 Simple Past signal words answers - PDF ▶ These exercises as free online exercises
Questions simple past - worksheets
22 Simple Past did exercises PDF 23 Simple Past questions did answers - PDF worksheet 24 Simple Past did exercises PDF 25 Simple Past questions did answers - PDF worksheet 26 Simple Past questions with did 27 Simple Past questions answers PDF 28 Simple Past questions with was/were PDF worksheet 29 Simple Past questions answers - PDF 30 Simple Past worksheet did - was/were 31 Simple Past worksheet did - was/were PDF 32 Simple Past worksheet did - was/were 33 Simple Past worksheet did - answers PDF
Simple Past negatives - worksheets
34 Simple Past negative exercise PDF 35 Simple Past negative answers - PDF worksheet 36 Simple Past negative exercises PDF 37 Simple Past negative answers - PDF worksheet 38 Simple Past negative 39 Simple Past negatives answers PDF 40 Simple Past negative PDF worksheet 41 Simple Past negative answers - PDF 42 Simple Past negative worksheet 43 Simple Past worksheet answers PDF

Simple Past mixed exercises pdf
44 Simple Past mixed exercise PDF 45 Simple Past mixed answers - PDF worksheet 46 Simple Past mixed exercises crossword PDF 47 Simple Past answers - PDF worksheet 48 Simple Past mixed exercises crossword 49 Simple Past answers PDF 50 Simple Past crossword crossword PDF worksheet 51 Simple Past answers - PDF
Online exercises Simple Past
01 Simple Past rules 02 Simple Past exercises 03 Simple Past regular verbs 04 Simple Past 05 Simple Past exercises 06 Simple Past exercises 07 Simple Past irregular verbs 08 Simple Past 09 Simple Past irregular verbs 10 Simple Past examples 11 Simple Past exercise
12 To be Simple Past 13 To be Simple Past 14 To be Simple Past 15 To be to be exercise
Simple Past worksheet - exercises
Simple Past English Tenses and English grammar worksheets, grammar rules, grammar exercises. English Simple past worksheet review to help advanced level English classes and students review for all major tenses.
Past Simple tense

The Past Simple tense is sometimes called the "preterite tense". We can use several tenses and forms to talk about the past, but the Past Simple tense is the one we use most often.
In this lesson we look at the structure and use of the Past Simple tense, followed by a quiz to check your understanding.
How do we make the Past Simple tense?
There are two basic structures for the Past Simple tense:
1. Positive sentences
| subject | + | main verb |
2. Negative and question sentences
| subject | + | auxiliary | + | main verb |
| conjugated in Past Simple | ||||
Look at these examples with the main verbs go (irregular) and work (regular):
| subject | auxiliary verb | main verb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | I | went | to school. | ||
| You | worked | very hard. | |||
| - | She | did | not | go | with me. |
| We | did | not | work | yesterday. | |
| ? | Did | you | go | to London? | |
| Did | they | work | at home? |
From the above table, notice the following points...
For positive sentences:
- There is no auxiliary verb .
- The main verb is conjugated in the Past Simple, invariable: -ed (or irregular)
For negative and question sentences:
- The auxiliary is conjugated in the Past Simple, invariable: did
- The main verb is invariable in base form: base
- For negative sentences, we insert not between the auxiliary verb and main verb.
- For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
- "Why didn't you go to the party?" / "I did go."
- It did seem a bit strange.
- After drinking it I did in fact feel better.
Past Simple with main verb be
The structure of the Past Simple with the main verb be is:
| subject | + | main verb |
| conjugated in Past Simple | ||
Look at these examples with the main verb be :
| subject | main verb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | I, he/she/it | was | here. | |
| You, we, they | were | in London. | ||
| - | I, he/she/it | was | not | there. |
| You, we, they | were | not | happy. | |
| ? | Was | I, he/she/it | right? | |
| Were | you, we, they | late? |
- There is no auxiliary verb , even for questions and negatives.
- The main verb (be) is conjugated in the Past Simple: was, were
- For negative sentences, we insert not after the main verb.
- For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the main verb.
How do we use the Past Simple tense?
We use the Past Simple tense to talk about an action or a situation - an event - in the past. The event can be short or long .
Here are some short events with the Past Simple:





















IMAGES
COMMENTS
Past simple: all for. 4 exercises to revis. 92226 uses. angelmix. Simple Past- exercis. Just a simple set of. 91060 uses. islandgirl. Simple Present tense. Students write the s. 72888 uses. rmartinandres. THE TREE HOUSE - PAR. Students find in a p. 71321 uses. ladygargara. PAST SIMPLE- Regular. Very easy ws for beg.
A common way to form the simple past is to add -ed to the end of a verb. These verbs are called "regular verbs.". Other verbs have many kinds of changes. They are called "irregular verbs.". The Be verb is a special kind of irregular verb. It has two forms (was and were). It also has diferent sentence patterns.
Past simple - pdf exercises. Past simple - pdf exercises. Worksheet - crossword pdf. Worksheet : affirmative-negative forms. Past simple - exercises. Past simple tense - worksheet. Worksheet : simple past - interrogative. Past simple - worksheets. Past simple - negative.
Exercises Complete the sentences with the simple past of the verbs in brackets. William (visit) his grandparents last weekend. regular verb → add ed; Jane (arrive) an hour ago. regular verb that ends in e → add a d; We (go) to Bob's birthday party yesterday. irregular verb, 2nd verb form (go-went-gone); I (be) on holiday last week. irregular verb, 2nd verb form (be-was/were-been)
Past simple exercises + PDF worksheets. PDF exercises to download for free: Past simple verbs PDF 1. Key with answers 1. Dear Jane, How are you doing? Yesterday I ___ (do) my homework, ___ (tidy) my bedroom and ___ (decide) to go out. Past simple verbs PDF 2. Key with answers 2.
Revised on October 23, 2023. The simple past tense is a verb form used to refer to an action or series of actions that were completed in the past. The simple past tense of regular verbs is formed by adding "-ed" to the infinitive form of the verb (e.g., "cook" becomes "cooked"). Most verbs in the simple past take the same form ...
Put the verbs into the simple past: Last year I (go) to England on holiday. It (be) fantastic. I (visit) lots of interesting places. I (be) with two friends of mine . In the mornings we (walk) in the streets of London. In the evenings we (go) to pubs. The weather (be) strangely fine. It (rain) a lot.
The simple past, also known as the past simple or preterite, is the fundamental form of the past tense. It is used to describe past actions and events that occurred before the present moment. The simple past of regular verbs is formed by adding -ed to the bare infinitive (e.g., play → played, watch → watched, etc.).However, there are hundreds of irregular verbs with various forms (e.g., go ...
Simple past lesson with explanations of the grammar structure including questions, and negatives. Find links to simple past exercises. Skip links. ... Susan finished her homework last night. Past Status. Use "was" and "were" to talk about past status. He was a teacher 5 years ago. He is not anymore.
A fun esl printable grammar test worksheet for learning, teaching and practising past simple tense with irregular verbs. First write the past forms of the irregular verbs. Second rewrite the sentences making them positive. Next rewrite the sentences making them negative. Then answer the questions about yourself.
We make the past simple just like the present simple except we use 'did' instead of 'do / does'. It's really easy because 'did' doesn't change, even with 'he / she / it'. The positive: We usually make the positive by adding '-ed' to the infinitive. For example, 'play' becomes 'played'. However, there are some irregular verbs, for example 'go ...
Past simple - regular verbs. Past simple affirmative - write. Past simple regular - write. Past tenses: -ed / -ied. Negative forms - past simple. Affirmative - negative: write. Interrogative forms - past simple. Affirmative - interrogative: write. Negative - interrogative: write.
The simple past verb tense is used to write about events that happened in the past and are complete. Simple past is an easy choice when the time of the event is given by some time expression. ... For Homework: Choose one of the topics above and write a story in paragraph form (not a list of sentences.) Use the simple past tense in six or more ...
To make a negative sentence in the past simple tense, you need to use the auxiliary verb "did" and the negative particle "not" (or "n't"). The formula forming the simple past is: Subject + did not (didn't) + base form of the verb + object. For example: I did not (didn't) go to the party last night. He did not (didn't) finish ...
Simple past - Exercises. Rony Rodríguez. Member for 4 years 4 months Age: 7+ Level: Grade 8th. Language: English (en) ID: 123254. 23/04/2020. Country code: EC. Country: Ecuador. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Simple past (2013134) From worksheet author: Simple past ...
English Simple past worksheet review to help advanced level English classes and students review for all major tenses. 50 simple past worksheets as pdf, handouts and printable exercises. Exercises free and with help function, teaching materials and grammar rules.
We use the Past Simple tense when: the event is in the past. the event is completely finished. we say (or understand) the time and/or place of the event. In general, if we say the past time or place of the event, we must use the Past Simple tense; we cannot use the present perfect. Here are some more examples:
Simple Past. The simple past (also called past simple, past indefinite or preterite) is a verb tense which is used to show that a completed action took place at a specific time in the past. The simple past is also frequently used to talk about past habits and generalizations. Read on for detailed descriptions, examples, and simple past exercises.
To form the Simple Past Tense for regular verbs, you typically add "-ed" to the base form of the verb. Examples: Walk (Base) → Walked (Simple Past) Play (Base) → Played (Simple Past) Talk (Base) → Talked (Simple Past) In the Simple Past Tense, regular verbs follow a straightforward pattern by adding "-ed" to their base form.
Regular past simple forms are formed by adding - ed to the infinitive of the verb. That seems easy! Yes, but there are some spelling rules. If a verb ends in - e, you add - d. If a verb ends in a vowel and a consonant, the consonant is usually doubled before - ed. If a verb ends in consonant and - y, you take off the y and add - ied.
12/03/2019. Country code: RO. Country: Romania. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Irregular verbs (2013224) From worksheet author: A worksheet to practise the past simple tense. Key included. Thank you.
Irregular verbs 21-30: write. Common irregular verbs 31-40. Verbs 31-40: drag and drop. Irregular verbs 31-40: write. Quiz 1 : irregular verbs 01-15. Quiz 2 : irregular verbs 16-30. Quiz 3 : irregular verbs 31-45. Quiz 4 : irregular verbs 46-60. 90 irregular verbs: 9 pages.
In this lesson, students learn the difference between Past Simple and Past Continuous. They also get the chance to practise using the two tenses in a variety of tasks. A2 / Pre‐Intermediate 60 min Standard Lesson Premium Plan. Unlock these lesson worksheets with the Premium subscription.