- About University Overview Catholic, Marianist Education Points of Pride Mission and Identity History Partnerships Location Faculty and Staff Directory Social Media Directory We Soar
- Academics Academics Overview Program Listing Academic Calendar College of Arts and Sciences School of Business Administration School of Education and Health Sciences School of Engineering School of Law Professional and Continuing Education Intensive English Program University Libraries
- Admission Admission Overview Undergraduate Transfer UD Sinclair Academy International Graduate Law Professional and Continuing Education Campus Visit
- Financial Aid Affordability Overview Undergraduate Transfer International Graduate Law Consumer Information
- Diversity Diversity Overview Office of Diversity and Inclusion Equity Compliance Office
- Research Research Overview Momentum: Our Research UD Research Institute Office for Research Technology Transfer
- Life at Dayton Campus Overview Arts and Culture Campus Recreation City of Dayton Clubs and Organizations Housing and Dining Student Resources and Services
- Athletics Athletics Overview Dayton Flyers
- We Soar We Soar Overview Priorities Goals Impact Stories Volunteer Make a Gift
- Schedule a Visit
- Request Info

Explore More
- Academic Calendar
- Event Calendar
- Blogs at UD
- Erma Bombeck Writers' Workshop
Ratatouille

By Renee Burns Lonner
I live in a suburban area of Los Angeles on a street of modest and neatly kept homes with neatly kept yards. My housekeeping standards could be characterized as super-clean but definitely short of psychotic. You would guess that the word “rat” never enters my vocabulary when speaking about my house or yard.
You’d be wrong.
Several years ago, my gardener built a lovely vegetable planter in my back yard, and I planted all kinds of gourmet lettuces, herbs and — my favorite — snow peas. They started to grow and I was thrilled, like a farmer growing actual food to actually eat. I was so proud. Until I went out one morning and the lettuces had been eaten down to the nubs. The next morning the nubs were gone.
My nursery is a second-generation family-owned business and let me tell you, they know their stuff. I went in and described the problem, asked if there were racoons suddenly in the area, and got a look like they thought I was somewhere between an imbecile and a moron.
One of the owners simply said “rats.” I replied, to his total amusement, “Can’t be, rats don’t eat lettuce!” He sighed a patient sigh and said they “eat anything and everything.” Who knew?
Not to be outsmarted by a rodent, at the end of that season, I asked the gardener to build a 4-foot raised vegetable bed and put a little fence around it. (You’re thinking “she’s closer to imbecile than moron.”) That next winter, I planted another round of beautiful lettuces. Same outcome, took less than a week. Now I’m angry. I went to the hardware store and bought chicken wire and crafted a cage for the lettuces — which are by now the most expensive greens in California. Made a small door I could open (with difficulty and some bleeding) to harvest my crop.
What crop? Within a day or two of my construction project and before my cuts healed, same result.
OKAY…THIS MEANS WAR!
My husband, who had been muttering something that may have sounded like “rat traps” for over a year, again offered his services. By this time, I no longer objected on the grounds that it’s inhumane. Instant death by guillotine for those little f**kers sounded perfect.
He set up several traps and calmly announced the first morning after that he had caught two and already disposed of them, and that my new lettuces were undisturbed. My hero!
Over the next week he caught a couple more and then all quiet. His theory was that the “scouts” did not return, and the group got the message to avoid that murderer’s yard! Clearly, they are reading my Nextdoor feed.
Fast forward to this week and my horrifying discovery when I opened the closet in my guest house. Yup, you guessed it — a rat dropping. After I finished screaming to an empty room in an empty guest house, my husband set a trap where the dropping was. Simultaneously I called pest control. This was no longer a job for amateurs. I needed SWAT-style back up.
The company responded to my near hysteria with “We have a special rat guy, Reuben. He’ll solve your problem.” Yes, I needed special forces, THAT was the answer.
When Reuben arrived the next morning, he asked the most bizarre question as he looked at our trap: “Is that peanut butter in the trap organic ?” Wait, WHHAAAT?? I looked at him like one of us had lost their minds and this time it wasn’t me. He added “They won’t eat that organic crap.” Good news for Reuben, neither will I.
The next thing I knew Reuben was on the roof of my guest house. Soon he knocked on my door and when I answered, he had the look of someone who had just slayed a dragon. Which he had.
“I found where he (gender noted) is getting in! Come with me!” I followed him and he excitedly showed me a tiny hole near the foundation of the guest house, then trotted, with his finger pointing, along “the route,” and finally triumphantly showed me the inside landing place. He pointed to rat droppings that were too high for me to see as proof of his detective work.
Now I’m impressed. He was totally smug as he told me the — not minor — cost of his services over the next couple of hours to rodent-proof the guest house. Worth every penny.
As he left, he told me that rats are all over the city, everywhere. Apparently, the Big Apple has nothing on Los Angeles. Every yard has them and yes, they often get into houses. That revelation took care of my embarrassment about the whole situation. Never mind rodent-proof, he has an everything-proof business. Apparently, we all live in rat-infested cities. How reassuring.
One of our friends, to whom I treated this entire story in long form, lives 50 miles from us out in the country on a large property with its own zoo: horses, cats, dogs, tortoise, a bird or two. His smart-ass response when I told him the rat saga was “For heaven’s sake, Renee — get a cat. I’ll give you one of mine.”
— Renee Burns Lonner
Renee Burns Lonner is a consultant for television newsrooms and a licensed psychotherapist based in Los Angeles. Her published work has appeared in many professional publications. During the pandemic she shifted to humor writing, and her work has been published by Medium, LOL Comedy and the Erma Bombeck Writers' Workshop blog. In 2021, she published her first humor book If You Give a Man a Tesla: A Parody and she is currently working on a second humor book to be published in time for the 2024 holiday season. Spoiler alert: the second book has nothing to do with cars and everything to do with one of life’s major milestones.
Who's Publishing What: 101 True Tales from the Terminal
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key things to know about U.S. election polling in 2024

Confidence in U.S. public opinion polling was shaken by errors in 2016 and 2020. In both years’ general elections, many polls underestimated the strength of Republican candidates, including Donald Trump. These errors laid bare some real limitations of polling.
In the midterms that followed those elections, polling performed better . But many Americans remain skeptical that it can paint an accurate portrait of the public’s political preferences.
Restoring people’s confidence in polling is an important goal, because robust and independent public polling has a critical role to play in a democratic society. It gathers and publishes information about the well-being of the public and about citizens’ views on major issues. And it provides an important counterweight to people in power, or those seeking power, when they make claims about “what the people want.”
The challenges facing polling are undeniable. In addition to the longstanding issues of rising nonresponse and cost, summer 2024 brought extraordinary events that transformed the presidential race . The good news is that people with deep knowledge of polling are working hard to fix the problems exposed in 2016 and 2020, experimenting with more data sources and interview approaches than ever before. Still, polls are more useful to the public if people have realistic expectations about what surveys can do well – and what they cannot.
With that in mind, here are some key points to know about polling heading into this year’s presidential election.
Probability sampling (or “random sampling”). This refers to a polling method in which survey participants are recruited using random sampling from a database or list that includes nearly everyone in the population. The pollster selects the sample. The survey is not open for anyone who wants to sign up.
Online opt-in polling (or “nonprobability sampling”). These polls are recruited using a variety of methods that are sometimes referred to as “convenience sampling.” Respondents come from a variety of online sources such as ads on social media or search engines, websites offering rewards in exchange for survey participation, or self-enrollment. Unlike surveys with probability samples, people can volunteer to participate in opt-in surveys.
Nonresponse and nonresponse bias. Nonresponse is when someone sampled for a survey does not participate. Nonresponse bias occurs when the pattern of nonresponse leads to error in a poll estimate. For example, college graduates are more likely than those without a degree to participate in surveys, leading to the potential that the share of college graduates in the resulting sample will be too high.
Mode of interview. This refers to the format in which respondents are presented with and respond to survey questions. The most common modes are online, live telephone, text message and paper. Some polls use more than one mode.
Weighting. This is a statistical procedure pollsters perform to make their survey align with the broader population on key characteristics like age, race, etc. For example, if a survey has too many college graduates compared with their share in the population, people without a college degree are “weighted up” to match the proper share.
How are election polls being conducted?
Pollsters are making changes in response to the problems in previous elections. As a result, polling is different today than in 2016. Most U.S. polling organizations that conducted and publicly released national surveys in both 2016 and 2022 (61%) used methods in 2022 that differed from what they used in 2016 . And change has continued since 2022.
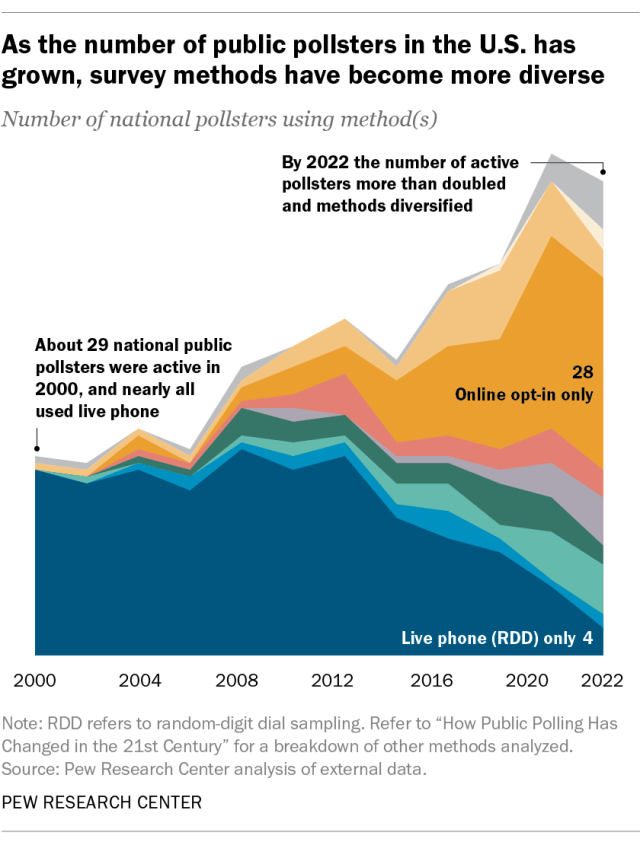
One change is that the number of active polling organizations has grown significantly, indicating that there are fewer barriers to entry into the polling field. The number of organizations that conduct national election polls more than doubled between 2000 and 2022.
This growth has been driven largely by pollsters using inexpensive opt-in sampling methods. But previous Pew Research Center analyses have demonstrated how surveys that use nonprobability sampling may have errors twice as large , on average, as those that use probability sampling.
The second change is that many of the more prominent polling organizations that use probability sampling – including Pew Research Center – have shifted from conducting polls primarily by telephone to using online methods, or some combination of online, mail and telephone. The result is that polling methodologies are far more diverse now than in the past.
(For more about how public opinion polling works, including a chapter on election polls, read our short online course on public opinion polling basics .)
All good polling relies on statistical adjustment called “weighting,” which makes sure that the survey sample aligns with the broader population on key characteristics. Historically, public opinion researchers have adjusted their data using a core set of demographic variables to correct imbalances between the survey sample and the population.
But there is a growing realization among survey researchers that weighting a poll on just a few variables like age, race and gender is insufficient for getting accurate results. Some groups of people – such as older adults and college graduates – are more likely to take surveys, which can lead to errors that are too sizable for a simple three- or four-variable adjustment to work well. Adjusting on more variables produces more accurate results, according to Center studies in 2016 and 2018 .
A number of pollsters have taken this lesson to heart. For example, recent high-quality polls by Gallup and The New York Times/Siena College adjusted on eight and 12 variables, respectively. Our own polls typically adjust on 12 variables . In a perfect world, it wouldn’t be necessary to have that much intervention by the pollster. But the real world of survey research is not perfect.
Predicting who will vote is critical – and difficult. Preelection polls face one crucial challenge that routine opinion polls do not: determining who of the people surveyed will actually cast a ballot.
Roughly a third of eligible Americans do not vote in presidential elections , despite the enormous attention paid to these contests. Determining who will abstain is difficult because people can’t perfectly predict their future behavior – and because many people feel social pressure to say they’ll vote even if it’s unlikely.
No one knows the profile of voters ahead of Election Day. We can’t know for sure whether young people will turn out in greater numbers than usual, or whether key racial or ethnic groups will do so. This means pollsters are left to make educated guesses about turnout, often using a mix of historical data and current measures of voting enthusiasm. This is very different from routine opinion polls, which mostly do not ask about people’s future intentions.
When major news breaks, a poll’s timing can matter. Public opinion on most issues is remarkably stable, so you don’t necessarily need a recent poll about an issue to get a sense of what people think about it. But dramatic events can and do change public opinion , especially when people are first learning about a new topic. For example, polls this summer saw notable changes in voter attitudes following Joe Biden’s withdrawal from the presidential race. Polls taken immediately after a major event may pick up a shift in public opinion, but those shifts are sometimes short-lived. Polls fielded weeks or months later are what allow us to see whether an event has had a long-term impact on the public’s psyche.
How accurate are polls?
The answer to this question depends on what you want polls to do. Polls are used for all kinds of purposes in addition to showing who’s ahead and who’s behind in a campaign. Fair or not, however, the accuracy of election polling is usually judged by how closely the polls matched the outcome of the election.
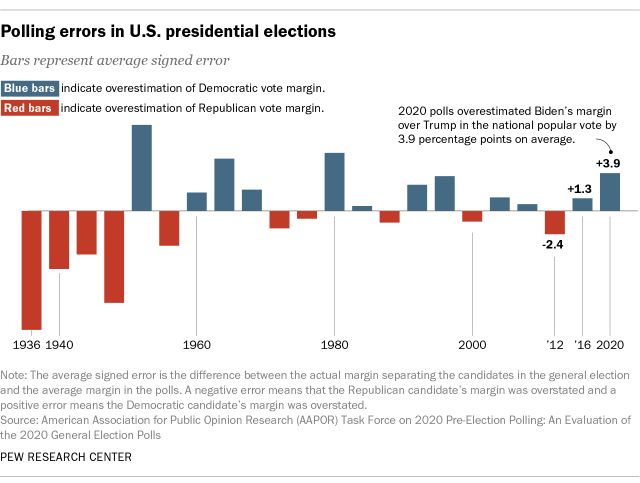
By this standard, polling in 2016 and 2020 performed poorly. In both years, state polling was characterized by serious errors. National polling did reasonably well in 2016 but faltered in 2020.
In 2020, a post-election review of polling by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) found that “the 2020 polls featured polling error of an unusual magnitude: It was the highest in 40 years for the national popular vote and the highest in at least 20 years for state-level estimates of the vote in presidential, senatorial, and gubernatorial contests.”
How big were the errors? Polls conducted in the last two weeks before the election suggested that Biden’s margin over Trump was nearly twice as large as it ended up being in the final national vote tally.
Errors of this size make it difficult to be confident about who is leading if the election is closely contested, as many U.S. elections are .
Pollsters are rightly working to improve the accuracy of their polls. But even an error of 4 or 5 percentage points isn’t too concerning if the purpose of the poll is to describe whether the public has favorable or unfavorable opinions about candidates , or to show which issues matter to which voters. And on questions that gauge where people stand on issues, we usually want to know broadly where the public stands. We don’t necessarily need to know the precise share of Americans who say, for example, that climate change is mostly caused by human activity. Even judged by its performance in recent elections, polling can still provide a faithful picture of public sentiment on the important issues of the day.
The 2022 midterms saw generally accurate polling, despite a wave of partisan polls predicting a broad Republican victory. In fact, FiveThirtyEight found that “polls were more accurate in 2022 than in any cycle since at least 1998, with almost no bias toward either party.” Moreover, a handful of contrarian polls that predicted a 2022 “red wave” largely washed out when the votes were tallied. In sum, if we focus on polling in the most recent national election, there’s plenty of reason to be encouraged.
Compared with other elections in the past 20 years, polls have been less accurate when Donald Trump is on the ballot. Preelection surveys suffered from large errors – especially at the state level – in 2016 and 2020, when Trump was standing for election. But they performed reasonably well in the 2018 and 2022 midterms, when he was not.
During the 2016 campaign, observers speculated about the possibility that Trump supporters might be less willing to express their support to a pollster – a phenomenon sometimes described as the “shy Trump effect.” But a committee of polling experts evaluated five different tests of the “shy Trump” theory and turned up little to no evidence for each one . Later, Pew Research Center and, in a separate test, a researcher from Yale also found little to no evidence in support of the claim.
Instead, two other explanations are more likely. One is about the difficulty of estimating who will turn out to vote. Research has found that Trump is popular among people who tend to sit out midterms but turn out for him in presidential election years. Since pollsters often use past turnout to predict who will vote, it can be difficult to anticipate when irregular voters will actually show up.
The other explanation is that Republicans in the Trump era have become a little less likely than Democrats to participate in polls . Pollsters call this “partisan nonresponse bias.” Surprisingly, polls historically have not shown any particular pattern of favoring one side or the other. The errors that favored Democratic candidates in the past eight years may be a result of the growth of political polarization, along with declining trust among conservatives in news organizations and other institutions that conduct polls.
Whatever the cause, the fact that Trump is again the nominee of the Republican Party means that pollsters must be especially careful to make sure all segments of the population are properly represented in surveys.
The real margin of error is often about double the one reported. A typical election poll sample of about 1,000 people has a margin of sampling error that’s about plus or minus 3 percentage points. That number expresses the uncertainty that results from taking a sample of the population rather than interviewing everyone . Random samples are likely to differ a little from the population just by chance, in the same way that the quality of your hand in a card game varies from one deal to the next.
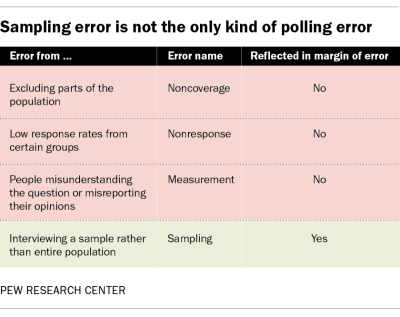
The problem is that sampling error is not the only kind of error that affects a poll. Those other kinds of error, in fact, can be as large or larger than sampling error. Consequently, the reported margin of error can lead people to think that polls are more accurate than they really are.
There are three other, equally important sources of error in polling: noncoverage error , where not all the target population has a chance of being sampled; nonresponse error, where certain groups of people may be less likely to participate; and measurement error, where people may not properly understand the questions or misreport their opinions. Not only does the margin of error fail to account for those other sources of potential error, putting a number only on sampling error implies to the public that other kinds of error do not exist.
Several recent studies show that the average total error in a poll estimate may be closer to twice as large as that implied by a typical margin of sampling error. This hidden error underscores the fact that polls may not be precise enough to call the winner in a close election.
Other important things to remember
Transparency in how a poll was conducted is associated with better accuracy . The polling industry has several platforms and initiatives aimed at promoting transparency in survey methodology. These include AAPOR’s transparency initiative and the Roper Center archive . Polling organizations that participate in these organizations have less error, on average, than those that don’t participate, an analysis by FiveThirtyEight found .
Participation in these transparency efforts does not guarantee that a poll is rigorous, but it is undoubtedly a positive signal. Transparency in polling means disclosing essential information, including the poll’s sponsor, the data collection firm, where and how participants were selected, modes of interview, field dates, sample size, question wording, and weighting procedures.
There is evidence that when the public is told that a candidate is extremely likely to win, some people may be less likely to vote . Following the 2016 election, many people wondered whether the pervasive forecasts that seemed to all but guarantee a Hillary Clinton victory – two modelers put her chances at 99% – led some would-be voters to conclude that the race was effectively over and that their vote would not make a difference. There is scientific research to back up that claim: A team of researchers found experimental evidence that when people have high confidence that one candidate will win, they are less likely to vote. This helps explain why some polling analysts say elections should be covered using traditional polling estimates and margins of error rather than speculative win probabilities (also known as “probabilistic forecasts”).
National polls tell us what the entire public thinks about the presidential candidates, but the outcome of the election is determined state by state in the Electoral College . The 2000 and 2016 presidential elections demonstrated a difficult truth: The candidate with the largest share of support among all voters in the United States sometimes loses the election. In those two elections, the national popular vote winners (Al Gore and Hillary Clinton) lost the election in the Electoral College (to George W. Bush and Donald Trump). In recent years, analysts have shown that Republican candidates do somewhat better in the Electoral College than in the popular vote because every state gets three electoral votes regardless of population – and many less-populated states are rural and more Republican.
For some, this raises the question: What is the use of national polls if they don’t tell us who is likely to win the presidency? In fact, national polls try to gauge the opinions of all Americans, regardless of whether they live in a battleground state like Pennsylvania, a reliably red state like Idaho or a reliably blue state like Rhode Island. In short, national polls tell us what the entire citizenry is thinking. Polls that focus only on the competitive states run the risk of giving too little attention to the needs and views of the vast majority of Americans who live in uncompetitive states – about 80%.
Fortunately, this is not how most pollsters view the world . As the noted political scientist Sidney Verba explained, “Surveys produce just what democracy is supposed to produce – equal representation of all citizens.”
- Survey Methods
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
- Voter Files

Scott Keeter is a senior survey advisor at Pew Research Center .

Courtney Kennedy is Vice President of Methods and Innovation at Pew Research Center .
How do people in the U.S. take Pew Research Center surveys, anyway?
How public polling has changed in the 21st century, what 2020’s election poll errors tell us about the accuracy of issue polling, a field guide to polling: election 2020 edition, methods 101: how is polling done around the world, most popular.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact Samantha Putterman, PolitiFact
Leave your feedback
- Copy URL https://www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/fact-checking-warnings-from-democrats-about-project-2025-and-donald-trump
Fact-checking warnings from Democrats about Project 2025 and Donald Trump
This fact check originally appeared on PolitiFact .
Project 2025 has a starring role in this week’s Democratic National Convention.
And it was front and center on Night 1.
WATCH: Hauling large copy of Project 2025, Michigan state Sen. McMorrow speaks at 2024 DNC
“This is Project 2025,” Michigan state Sen. Mallory McMorrow, D-Royal Oak, said as she laid a hardbound copy of the 900-page document on the lectern. “Over the next four nights, you are going to hear a lot about what is in this 900-page document. Why? Because this is the Republican blueprint for a second Trump term.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about “Trump’s Project 2025” agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn’t claim the conservative presidential transition document.
“Donald Trump wants to take our country backward,” Harris said July 23 in Milwaukee. “He and his extreme Project 2025 agenda will weaken the middle class. Like, we know we got to take this seriously, and can you believe they put that thing in writing?”
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, Harris’ running mate, has joined in on the talking point.
“Don’t believe (Trump) when he’s playing dumb about this Project 2025. He knows exactly what it’ll do,” Walz said Aug. 9 in Glendale, Arizona.
Trump’s campaign has worked to build distance from the project, which the Heritage Foundation, a conservative think tank, led with contributions from dozens of conservative groups.
Much of the plan calls for extensive executive-branch overhauls and draws on both long-standing conservative principles, such as tax cuts, and more recent culture war issues. It lays out recommendations for disbanding the Commerce and Education departments, eliminating certain climate protections and consolidating more power to the president.
Project 2025 offers a sweeping vision for a Republican-led executive branch, and some of its policies mirror Trump’s 2024 agenda, But Harris and her presidential campaign have at times gone too far in describing what the project calls for and how closely the plans overlap with Trump’s campaign.
PolitiFact researched Harris’ warnings about how the plan would affect reproductive rights, federal entitlement programs and education, just as we did for President Joe Biden’s Project 2025 rhetoric. Here’s what the project does and doesn’t call for, and how it squares with Trump’s positions.
Are Trump and Project 2025 connected?
To distance himself from Project 2025 amid the Democratic attacks, Trump wrote on Truth Social that he “knows nothing” about it and has “no idea” who is in charge of it. (CNN identified at least 140 former advisers from the Trump administration who have been involved.)
The Heritage Foundation sought contributions from more than 100 conservative organizations for its policy vision for the next Republican presidency, which was published in 2023.
Project 2025 is now winding down some of its policy operations, and director Paul Dans, a former Trump administration official, is stepping down, The Washington Post reported July 30. Trump campaign managers Susie Wiles and Chris LaCivita denounced the document.
WATCH: A look at the Project 2025 plan to reshape government and Trump’s links to its authors
However, Project 2025 contributors include a number of high-ranking officials from Trump’s first administration, including former White House adviser Peter Navarro and former Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson.
A recently released recording of Russell Vought, a Project 2025 author and the former director of Trump’s Office of Management and Budget, showed Vought saying Trump’s “very supportive of what we do.” He said Trump was only distancing himself because Democrats were making a bogeyman out of the document.
Project 2025 wouldn’t ban abortion outright, but would curtail access
The Harris campaign shared a graphic on X that claimed “Trump’s Project 2025 plan for workers” would “go after birth control and ban abortion nationwide.”
The plan doesn’t call to ban abortion nationwide, though its recommendations could curtail some contraceptives and limit abortion access.
What’s known about Trump’s abortion agenda neither lines up with Harris’ description nor Project 2025’s wish list.
Project 2025 says the Department of Health and Human Services Department should “return to being known as the Department of Life by explicitly rejecting the notion that abortion is health care.”
It recommends that the Food and Drug Administration reverse its 2000 approval of mifepristone, the first pill taken in a two-drug regimen for a medication abortion. Medication is the most common form of abortion in the U.S. — accounting for around 63 percent in 2023.
If mifepristone were to remain approved, Project 2025 recommends new rules, such as cutting its use from 10 weeks into pregnancy to seven. It would have to be provided to patients in person — part of the group’s efforts to limit access to the drug by mail. In June, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected a legal challenge to mifepristone’s FDA approval over procedural grounds.
WATCH: Trump’s plans for health care and reproductive rights if he returns to White House The manual also calls for the Justice Department to enforce the 1873 Comstock Act on mifepristone, which bans the mailing of “obscene” materials. Abortion access supporters fear that a strict interpretation of the law could go further to ban mailing the materials used in procedural abortions, such as surgical instruments and equipment.
The plan proposes withholding federal money from states that don’t report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention how many abortions take place within their borders. The plan also would prohibit abortion providers, such as Planned Parenthood, from receiving Medicaid funds. It also calls for the Department of Health and Human Services to ensure that the training of medical professionals, including doctors and nurses, omits abortion training.
The document says some forms of emergency contraception — particularly Ella, a pill that can be taken within five days of unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy — should be excluded from no-cost coverage. The Affordable Care Act requires most private health insurers to cover recommended preventive services, which involves a range of birth control methods, including emergency contraception.
Trump has recently said states should decide abortion regulations and that he wouldn’t block access to contraceptives. Trump said during his June 27 debate with Biden that he wouldn’t ban mifepristone after the Supreme Court “approved” it. But the court rejected the lawsuit based on standing, not the case’s merits. He has not weighed in on the Comstock Act or said whether he supports it being used to block abortion medication, or other kinds of abortions.
Project 2025 doesn’t call for cutting Social Security, but proposes some changes to Medicare
“When you read (Project 2025),” Harris told a crowd July 23 in Wisconsin, “you will see, Donald Trump intends to cut Social Security and Medicare.”
The Project 2025 document does not call for Social Security cuts. None of its 10 references to Social Security addresses plans for cutting the program.
Harris also misleads about Trump’s Social Security views.
In his earlier campaigns and before he was a politician, Trump said about a half-dozen times that he’s open to major overhauls of Social Security, including cuts and privatization. More recently, in a March 2024 CNBC interview, Trump said of entitlement programs such as Social Security, “There’s a lot you can do in terms of entitlements, in terms of cutting.” However, he quickly walked that statement back, and his CNBC comment stands at odds with essentially everything else Trump has said during the 2024 presidential campaign.
Trump’s campaign website says that not “a single penny” should be cut from Social Security. We rated Harris’ claim that Trump intends to cut Social Security Mostly False.
Project 2025 does propose changes to Medicare, including making Medicare Advantage, the private insurance offering in Medicare, the “default” enrollment option. Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks and can also require prior authorization, meaning that the plan can approve or deny certain services. Original Medicare plans don’t have prior authorization requirements.
The manual also calls for repealing health policies enacted under Biden, such as the Inflation Reduction Act. The law enabled Medicare to negotiate with drugmakers for the first time in history, and recently resulted in an agreement with drug companies to lower the prices of 10 expensive prescriptions for Medicare enrollees.
Trump, however, has said repeatedly during the 2024 presidential campaign that he will not cut Medicare.
Project 2025 would eliminate the Education Department, which Trump supports
The Harris campaign said Project 2025 would “eliminate the U.S. Department of Education” — and that’s accurate. Project 2025 says federal education policy “should be limited and, ultimately, the federal Department of Education should be eliminated.” The plan scales back the federal government’s role in education policy and devolves the functions that remain to other agencies.
Aside from eliminating the department, the project also proposes scrapping the Biden administration’s Title IX revision, which prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. It also would let states opt out of federal education programs and calls for passing a federal parents’ bill of rights similar to ones passed in some Republican-led state legislatures.
Republicans, including Trump, have pledged to close the department, which gained its status in 1979 within Democratic President Jimmy Carter’s presidential Cabinet.
In one of his Agenda 47 policy videos, Trump promised to close the department and “to send all education work and needs back to the states.” Eliminating the department would have to go through Congress.
What Project 2025, Trump would do on overtime pay
In the graphic, the Harris campaign says Project 2025 allows “employers to stop paying workers for overtime work.”
The plan doesn’t call for banning overtime wages. It recommends changes to some Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, regulations and to overtime rules. Some changes, if enacted, could result in some people losing overtime protections, experts told us.
The document proposes that the Labor Department maintain an overtime threshold “that does not punish businesses in lower-cost regions (e.g., the southeast United States).” This threshold is the amount of money executive, administrative or professional employees need to make for an employer to exempt them from overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act.
In 2019, the Trump’s administration finalized a rule that expanded overtime pay eligibility to most salaried workers earning less than about $35,568, which it said made about 1.3 million more workers eligible for overtime pay. The Trump-era threshold is high enough to cover most line workers in lower-cost regions, Project 2025 said.
The Biden administration raised that threshold to $43,888 beginning July 1, and that will rise to $58,656 on Jan. 1, 2025. That would grant overtime eligibility to about 4 million workers, the Labor Department said.
It’s unclear how many workers Project 2025’s proposal to return to the Trump-era overtime threshold in some parts of the country would affect, but experts said some would presumably lose the right to overtime wages.
Other overtime proposals in Project 2025’s plan include allowing some workers to choose to accumulate paid time off instead of overtime pay, or to work more hours in one week and fewer in the next, rather than receive overtime.
Trump’s past with overtime pay is complicated. In 2016, the Obama administration said it would raise the overtime to salaried workers earning less than $47,476 a year, about double the exemption level set in 2004 of $23,660 a year.
But when a judge blocked the Obama rule, the Trump administration didn’t challenge the court ruling. Instead it set its own overtime threshold, which raised the amount, but by less than Obama.
Support Provided By: Learn more
Educate your inbox
Subscribe to Here’s the Deal, our politics newsletter for analysis you won’t find anywhere else.
Thank you. Please check your inbox to confirm.

RFK Jr. won't be able to remove himself from ballots in Michigan and Wisconsin

Robert F. Kennedy Jr. will be unable to remove himself from the ballots in the key swing states of Michigan and Wisconsin, election officials confirmed Tuesday, days after he ended his independent presidential campaign and endorsed former President Donald Trump.
Kennedy is on the ballot in Michigan as a candidate for the Natural Law Party , which nominated him at its convention this year. Cheri Hardmon, a spokesperson for the Michigan secretary of state's office, confirmed that "minor party candidates cannot withdraw, so his name will remain on the ballot in the November election."
In Wisconsin, the state election commission met Tuesday to certify ballot access for presidential and vice presidential candidates. Even though Kennedy asked to withdraw his nomination petition as an independent candidate, the commission voted to decline the request, according to an archived video of the proceedings published by WisconsinEye , a nonprofit public affairs network.
"The statute liter a lly sa ys , 'Any person who files nomination papers and qualifies to appear on the ballot may not decline nomination. The name of that person shall appear upon the ballot except in case of death of the person,'" Ann Jacobs, the chair of the commission, told another commissioner struggling with the idea of keeping someone on the ballot who didn't want to move forward with his or her candidacy.
"You're giving me this touchy-feely: 'I feel like this shouldn't be the law.' The law in this case is crystal clear," she added. "I don't disagree with you — it's weird, but I don't see we have any discretion here."
In Nevada, however, a court ordered on Tuesday that Kennedy would not appear on the ballot in the fall. The ruling came as part of a lawsuit Kennedy filed while he was still an active candidate attempting to secure a spot on the ballot. But the court order shows the two sides agreed to drop the case.
In his speech Friday dropping out of the race and backing Trump, Kennedy said he would work to remove his name from ballots in states where he could play a spoiler role.
"In about 10 battleground states where my presence would be a spoiler, I'm going to remove my name, and I've already started that process and urge voters not to vote for me," Kennedy said.
"Our polling consistently showed by staying on the ballot in the battleground states, I would likely hand the election over to the Democrats, with whom I disagree on the most existential issues," he added.
But Kennedy added that he wouldn't remove his name from ballots in "red" or "blue" states in the hope of giving his supporters a chance to vote for him without affecting the results of the election. Kentucky Secretary of State Michael Adams, for instance, announced Monday that Kennedy would be placed on the ballot in the solidly Republican state.
It's unlikely Kennedy will draw significant numbers of votes in states where he remains on the ballot, as he's no longer actively campaigning and is supporting a different candidate. But his decision to drop out had been seen as a marginal boost to Trump, as he had been more likely to pull from voters who would choose Trump in a head-to-head matchup with Vice President Kamala Harris
Ben Kamisar is a national political reporter for NBC News
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
This Is Who Kamala Harris Fails

By Hala Alyan
Dr. Alyan is a clinical psychologist and professor in New York City.
As a Palestinian American, I’ve watched with growing apprehension the recent rebranding and memeification of Kamala Harris: Look! Here’s a woman who does jubilant dances, is firmly intelligent, has the same guffaw as your mother. It’s endearing. It’s refreshing.
I’m not immune to the charms of American mythology. I spent much of my childhood in Midwestern suburbia, bred on rom-coms and the glittering spectacle of professional wrestling. I, too, love the promise of a third act, a swooping hero, the prop of a good soundtrack. But for me to lean into the powerful marketing of the current vice president as a bastion of hope requires enormous amnesia — not only of this administration’s complicit funding of Palestinian slaughter but also of Ms. Harris’s track record on criminal reform , immigration and law enforcement .
Because even in those Midwestern suburbs I was also Palestinian, raised on stories of the nakba, land theft, a boy burned alive , a young American woman mangled by an Israeli bulldozer , the searing image of a man trying to protect his son from flying bullets . Ms. Harris’s viral quote on existing in your context is handy here: Palestinian Americans and their allies are bringing a context to this election. They carry a hope for ending Palestinian oppression that feels almost futile but irresponsible to abandon, and a memory that extends past a few glitzy weeks.
The Democratic National Convention was a visually and sonically arresting display, full of bright-eyed, stirring speeches on race, identity, democracy — including a moving speech by the parents of an Israeli hostage — and talk of social justice and liberation. It began with a land acknowledgment. And yet the word Palestine was only held, briefly, in the mouths of non-Palestinians. Mentions of a cease-fire in Gaza were urgent but vague, as though one would be midwifed via fervent prayer rather than the sober reconsideration of our nation’s active participation and funding of the current onslaught.
The most generous read of Ms. Harris vis-à-vis Palestinians is that she has inherited — versus had an active role in — a disastrous foreign policy on Gaza, and now must contend with hundreds of thousands of ambivalent voters who oppose it. There is no doubt Ms. Harris is more articulate than President Biden on the issue. In her speech accepting the Democratic nomination, she spoke of Palestinians’ devastation, their displacement, their hunger, their right to “freedom” and “self-determination.” “The scale of suffering is heartbreaking,” she said.
I appreciate Ms. Harris’s broken heart. What I’d appreciate more is a direct naming of who is killing and starving Palestinians, acts that are neither inevitable nor without a perpetrator. I’d appreciate the upholding of international law through sanctions and an arms embargo. It’s hard to abide the passive framing of Palestinian death in the same speech that reasserts a nuclear power’s right to defend itself — a “defense” that in the past few months has included both American and Israeli representatives calling to level Gaza, mobs rioting to defend the rights of soldiers accused of raping a Palestinian prisoner , and bombs shredding hundreds of starving children in refugee camps.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Academic proofreading and editing
Our editors ensure that your documents are error-free and impactful, with flawless grammar, polished academic language, and proper formatting.
Which document can we edit for you?
What happy customers say about us, 4.6/5 (2,346 reviews).
Very trustworthy and extremely efficient
I had an academic document proofread by the papertrue team. They not only corrected numerous grammar and spelling issues, they also advised on certain expressions according to my target audience. And the best, they did so over night... extremely fast, extremely good, and trustworthy service. Will be coming here again for the next publication.
Even my tutor can not find these errors
Thank you for editing my document on time. The editor pointed my attention to my commonly made mistakes; missing words, incorrect spelling and grammatical inconsistencies throughout the document. I was happy to receive both a tracked and a clean version of the edited document. I will happily recommend PaperTrue to my friends, and I will myself come back on a later occasion.
I have been using their services for 1 years now, and the only word that could describe this Papertrue is excellent. English is my second language, and every time, when I send my paper, I learn a lot from their feedback, comments and suggestions. Also, every my email have been answered very quickly. A very good value for money.
Great proofreading and editing!
PaperTrue has done a great editing/Proofreading on my friend's thesis. The thesis was accepted promptly without any further query or demand for amendment. We really appreciate their work.
Best editing service ever!
PaperTrue is the most helpful proofreader I experienced. They are fast, professional and careful. With their help, my paper got A or A-! so excited! Thanks to PaperTrue, I can have more time on other subjects, which really saved my life! Very much appreciated their professional assistance. Thanks a million!
Wonderful services
The proofreaders and editors at papertrue did a wonderful job of improving my dissertation. Almost all the errors were gone and the sentences were reworded to make its style more academic. I will tell my friends at the university about your high quality proofreading.
Review of Thesis - Effect of Nanopolymers in Paints
I found Paper True on the internet and decided to use them because of their high star rating and tremendous reviews that were relevant to what I needed. My German niece asked me to review her thesis and after struggling with it for over 8 hours and 6 pages later I knew I needed help. Paper True delivered within 2 days, the time frame I gave them. Not only did they deliver a document with all corrections and helpful comments suggested on the side(Tracked) but another one that was already corrected (Clean). The Thesis was 100% better and I was thrilled.
PaperTrue is a life saver
PaperTrue allowed me to expedite my writing process and helped me hand my paper in on time. I took a nap after sending my paper in and wake up to a well edited final draft. It's a lifesaver for college students!
Good option for ESL
Since English isn't my first language, I needed a professional proofreading service, just for my peace of mind. After some research I found PaperTrue, found some good reviews and tried it. It is a great service on a fair price. I would come back for more :)
How it works
In the news, we're trusted around the world, 52,000 clients served, 180 million words edited, 60,000 documents edited, 2014 year of establishment.
© All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self publishing services
- Dissertation
- Research paper
- Journal article
- Admission essay
- Personal statement
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Legal document
- Job Applicant
- Résumé
- Cover letter
- Partner with us
- Case studies
5% Off On AI + Professional Editing Services!
Avail our in-depth, accurate and fast AI + Professional editing services at an even more affordable price.
Get My 5% Discount Now
Your Discount Code has been emailed to you!
If you would like to place your order now, your discount code is also provided below. Use the button to copy the code, then click here to place your order.
Discount Code : Copy
Discount Code Copy
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Essay Writing

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource begins with a general description of essay writing and moves to a discussion of common essay genres students may encounter across the curriculum. The four genres of essays (description, narration, exposition, and argumentation) are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres, also known as the modes of discourse, have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the wide spread use of these genres and students’ need to understand and produce these types of essays. We hope these resources will help.
The essay is a commonly assigned form of writing that every student will encounter while in academia. Therefore, it is wise for the student to become capable and comfortable with this type of writing early on in her training.
Essays can be a rewarding and challenging type of writing and are often assigned either to be done in class, which requires previous planning and practice (and a bit of creativity) on the part of the student, or as homework, which likewise demands a certain amount of preparation. Many poorly crafted essays have been produced on account of a lack of preparation and confidence. However, students can avoid the discomfort often associated with essay writing by understanding some common genres.
Before delving into its various genres, let’s begin with a basic definition of the essay.
What is an essay?
Though the word essay has come to be understood as a type of writing in Modern English, its origins provide us with some useful insights. The word comes into the English language through the French influence on Middle English; tracing it back further, we find that the French form of the word comes from the Latin verb exigere , which means "to examine, test, or (literally) to drive out." Through the excavation of this ancient word, we are able to unearth the essence of the academic essay: to encourage students to test or examine their ideas concerning a particular topic.
Essays are shorter pieces of writing that often require the student to hone a number of skills such as close reading, analysis, comparison and contrast, persuasion, conciseness, clarity, and exposition. As is evidenced by this list of attributes, there is much to be gained by the student who strives to succeed at essay writing.
The purpose of an essay is to encourage students to develop ideas and concepts in their writing with the direction of little more than their own thoughts (it may be helpful to view the essay as the converse of a research paper). Therefore, essays are (by nature) concise and require clarity in purpose and direction. This means that there is no room for the student’s thoughts to wander or stray from his or her purpose; the writing must be deliberate and interesting.
This handout should help students become familiar and comfortable with the process of essay composition through the introduction of some common essay genres.
This handout includes a brief introduction to the following genres of essay writing:
- Expository essays
- Descriptive essays
- Narrative essays
- Argumentative (Persuasive) essays

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework

3 Strong Argumentative Essay Examples, Analyzed
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.
Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A high-school-level essay of 300 words (considered one page) costs $11. 9. MyPerfectWords. This is an essay writing service with grammar and plagiarism checks, where you need to key in the topic and the relevant prompt. The essay writer then refers to multiple resources to write an essay using AI.
In a test of character, Trump shows his true grift. In his disorientation, the GOP nominee and former president retreats to his instincts. ... an essay by conservative writer Rich Lowry titled ...
Desiree Miller's anthology, 101 True Tales from the Terminal, was inspired by a social media post she wrote about her fun interactions in Atlanta's airport as she awaited her flight to Dayton, Ohio, to the 2022 Erma Bombeck Writers' Workshop. Read More. Home. 300 College Park Dayton, Ohio 45469 937-229-1000. [email protected].
Confidence in U.S. public opinion polling was shaken by errors in 2016 and 2020. In both years' general elections, many polls underestimated the strength of Republican candidates, including Donald Trump. These errors laid bare some real limitations of polling. In the midterms that followed those ...
Vice President Kamala Harris, the Democratic presidential nominee, has warned Americans about "Trump's Project 2025" agenda — even though former President Donald Trump doesn't claim the ...
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. will be unable to remove himself from the ballots in the key swing states of Michigan and Wisconsin, election officials confirmed Tuesday, days after he ended his independent ...
For the past six months, former President Donald Trump has been sitting on a social media fortune that he couldn't touch. That will change very soon.
The most generous read of Ms. Harris vis-à-vis Palestinians is that she has inherited — versus had an active role in — a disastrous foreign policy on Gaza, and now must contend with hundreds ...
Basic essay structure: the 3 main parts of an essay. Almost every single essay that's ever been written follows the same basic structure: Introduction. Body paragraphs. Conclusion. This structure has stood the test of time for one simple reason: It works. It clearly presents the writer's position, supports that position with relevant ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you'll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true. In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs.
Papertrue! True! True! True! My experience with papertrue.com was great. I came across their site from the high ratings. And the high ratings proved to be true. Once I got onto their site, I was immediately helped by a papertrue.com Rep, a live person, who helped answer my questions and walked me through the process. That was a big plus!
3. Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay is a type of essay that aims to persuade the reader to adopt a particular stance based on factual evidence and is one of the most common forms of college essays. 4. Expository essays. An expository essay is a common format used in school and college exams to assess your understanding of a specific ...
a sentence at the end of the introduction paragraph that summarizes what you will be writing about in your essay. true or false: a thesis statement is not detailed at all. false. true or false: A thesis statement is 1-2 sentences long. true. true or false: A thesis statement should include the main points that you will express in your essay.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Here are the eight steps to write an essay: Stage 1: Planning. 1. Pick an appropriate research topic. In certain cases, your teacher or professor may assign you a topic. However, in many cases, students have the freedom to select a topic of their choice.
What makes an essay argumentative is the method of convincing: An argumentative essay uses fact-based evidence and unquestionable logic to prove that its thesis is true. Persuasive essays do this, too, but tend to be more emotional and less formal. Argumentative essays focus more on concrete empirical data, whereas persuasive essays appeal more ...
Step 2: Pick one of the things you wrote down, flip your paper over, and write it at the top of your paper, like this: This is your thread, or a potential thread. Step 3: Underneath what you wrote down, name 5-6 values you could connect to this. These will serve as the beads of your essay.
When applying for college, you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities. For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay. College application prompt. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure.
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate assignment before you ...
When you're writing a persuasive essay, you need more than just an opinion to make your voice heard. Even the strongest stance won't be compelling if it's not structured properly and reinforced with solid reasoning and evidence. Learn what elements every argumentative essay should include and how to structure it depending on your audience in this easy step-by-step guide.
Best editing service ever! PaperTrue is the most helpful proofreader I experienced. They are fast, professional and careful. With their help, my paper got A or A-! so excited! Thanks to PaperTrue, I can have more time on other subjects, which really saved my life! Very much appreciated their professional assistance. Thanks a million!
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Essays are shorter pieces of writing that often require the student to hone a number of skills such as close reading, analysis, comparison and contrast, persuasion, conciseness, clarity, and exposition. As is evidenced by this list of attributes, there is much to be gained by the student who strives to succeed at essay writing.
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
There are 4 modules in this course. This class is the chance to create your personal essay or extend into a full memoir -- from planning and structure to bold narrative brushstrokes to the layering of significant detail. You will develop the opportunity to find your voice and see it come alive, amplified and improved, on the page.
Argumentative Essay Example 2. Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through female Anopheles mosquitoes. Each year, over half a billion people will become infected with malaria, with roughly 80% of them living in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
This college essay tip is by Abigail McFee, Admissions Counselor for Tufts University and Tufts '17 graduate. 2. Write like a journalist. "Don't bury the lede!" The first few sentences must capture the reader's attention, provide a gist of the story, and give a sense of where the essay is heading.