MSTP MD-PhD Program
Frequently asked questions.

- Program Structure
How long does it take to complete both degrees?
The average length of time before graduation is 7.5 years; generally students will take 6 years or 8 years depending on the nature of their graduate research. Students generally complete and defend their PhD thesis before completing their clinical rotations in the last 1 – 2 years.
Can I do one degree before the other?
As above, nearly all students will complete their PhD requirements 1 – 2 years before their MD requirements. An important advantage of combined degree training is the breadth that the first 1 – 2 years of medical school provides for graduate research. Students must pass part I of the National Board Medical Licensing Examination before commencing full-time laboratory research. Occasionally circumstances will arise when an individual student's training is best served by deviating from this "traditional" plan; these situations require approval and monitoring by the graduate advisor and the MSTP Directors.
How will I be supported during my training?
Stanford MSTP students are fully supported through the entire program, tuition, health insurance and stipend, by a combination of funds from a National Institute of Health training grant, individual graduate programs, and School of Medicine funds.
Are there laboratory rotations?
One of the ways in which we try to make the total time of training less than the sum normally taken to complete MD and PhD degrees is by encouraging MSTP students to choose a potential thesis advisor without a yearlong set of rotations through different laboratories. During the first year of the program, students meet with departmental chairs and research faculty and participate in research seminars and group meetings, so that the summer following the first year can be spent working full-time in a laboratory whose goals, approaches, and personnel are already familiar. In most cases, MSTP students choose this laboratory as the place to carry out their thesis research.
Can I get advanced placement credit for graduate coursework?
MSTP students fulfill the same curricular requirements as "straight MD" and "straight PhD" students. Some PhD Programs may permit substitution of previous graduate course work (or MD courses) for their PhD requirements; this is individual to the program and the student.
Are MSTP students required to complete the MD Scholarly Concentration (SC) program?
The MSTP is a combined effort between the MD program and the PhD programs. All trainees are required to fulfill all requirements for both the MD and PhD degrees. The single exception is the MD program requirement for a Scholarly Concentration. For dual degree MD-PhD students, the PhD substitutes for this requirement.
Will I have special opportunities as an MSTP student?
Yes! In addition to individual regular advising meetings with the Program Directors, we hold seminars, courses, and lunches with guest speakers, covering important topics of professional development and translational medicine. The MSTP community also meets annually for the MSTP Scientific Conference, to present research, and to share clinical experiences, advice and above all support.
Will I have special responsibilities as an MSTP student?
Of course! Besides the challenge of balancing graduate and medical training, we ask all MSTP students to play an integral role in the recruitment, education, and evaluation of incoming MSTP applicants.

Graduate Programs
Can I get a PhD outside the Medical School?
Yes. One of the unique aspects of the Stanford MSTP is its close affiliation with departments in other Schools, including Engineering (Bioengineering, Chemical, Computer Science, Electrical) and Humanities and Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Statistics).
Can I get a PhD in a clinical department?
The PhD must be conferred by a degree-granting department or program, and most clinical departments do not grant PhD degrees. However, most scientists in clinical departments either have joint appointments with basic science departments or are members of interdepartmental programs such as Cancer Biology, Neurosciences, or Immunology, and the only restriction regarding thesis advisors is that they must be members of the Academic Council.
Can I apply to the MSTP and get a PhD in a social science?
If you are a current Stanford MD student and have previously been admitted to a social science PhD program, you may apply to the MSTP for funding. Admitted PhD candidates may apply through the MSTP internal admissions process.
Are there teaching requirements?
The MSTP itself has no specific teaching requirements, but some PhD programs do.
How will my training differ from other "straight PhD" students?
The short answer is, "It won't." PhD training for MSTP students is just as rigorous and intensive as for students outside the MSTP. However, MSTP students don't spend their first year rotating through different laboratories, and most MSTP students complete their preclinical medical school curriculum before starting full-time laboratory research.
- Admissions Process
How many applicants do you interview and admit?
On average, we invite about 60 students for interviews or about 1 in 9 of those students who submit a secondary application. About 8 - 10 students begin the MSTP every year.
Can I apply to the MSTP after starting medical school?
Yes! One of the unique aspects of the Stanford School of Medicine is its strong emphasis on research, and the MSTP invites current Stanford medical students in their preclinical years, who have made a commitment and contribution to a research-based career, to submit an application for the MSTP. We refer to this as the “internal” application process . Typically, the MSTP admits 1 – 2 internal applicants every year.
Is there an early decision program?
No. We think making a decision about combined medical school and graduate training is challenging enough! Finding a program that best matches an individual student's interests and goals is facilitated by visiting several universities and meeting with a variety of potential research advisors.
How do I find out about the status of my application?
Just ask (we don't mind).
Can I schedule my interview for a different day?
There are 5 – 6 interview days per season; once invited, interviews are scheduled on a first-come, first-served basis. We will try to accommodate requests for other dates if necessary.
I don't know whether to apply for Med School or MSTP?
You should only apply to the MSTP if you are committed to a career in biomedical research; such a commitment should be based, in part, on previous sustained and productive research experience as an undergraduate. If you're not sure, consider working full-time in a laboratory after undergraduate school before deciding whether an MSTP is right for you, or, alternatively, starting as a "straight MD" student, participating in a research project in your 2nd or 3rd year, and possibly applying to the MSTP as an internal applicant (see above).
What does the MSTP Admissions Committee look for?
Besides qualification for admission to the medical school itself, the single most important component of an MSTP application is a previous sustained and productive research experience.
When can I expect to hear about the outcome of my application and/or interview?
Interview season is October – February; interview invitations will be issued 3 – 6 weeks before the scheduled interview date. MSTP admission decisions are made on a modified rolling basis.
Are MSTP applicants considered independently for medical school admission?
The MSTP Admissions Committee is separate from, but closely integrated with, the Medical School Admissions Committee. All applicants to the MSTP are also considered for MD-only admission. If you are not chosen for an MSTP interview, your application is automatically routed for MD-only consideration. If you are chosen for an MSTP interview, you will also be required to participate in the MD admission interview process. These interviews will be scheduled the day before, or day after, your MSTP interviews. If you are not offered admission to the MSTP, you will be considered for MD-only admission.
- Student Life
Can I afford to live in Palo Alto?
Housing costs in the Bay Area are more than other cities. However, every new graduate student is guaranteed housing on campus or at University associated off-campus sites. Almost anyone can afford to live comfortably as a Stanford graduate student solely on stipend support.
Will the program pay for health insurance? What about the rest of my family?
We consider health insurance an essential component of all graduate training programs. The program covers the entire cost for individual students and offers a mechanism for subsidizing dependents.
Isn't there more to do in San Francisco than in Palo Alto?
It depends whether you would rather watch street vendors in Union Square or go hiking in the Los Altos foothills. Seriously, downtown San Francisco is a short train ride away from Stanford, but the two environments offer different (and complementary) experiences. Downtown Palo Alto doesn't have skyscrapers but it does have a thriving economy, a diverse population, and an environment that attracts many students to stay here for postgraduate training and career opportunities. Come see for yourself!
- Graduate Program

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Course Directory
PhD in Medicine
Postgraduate Study
- Why Cambridge overview
- Chat with our students
- Cambridge explained overview
- The supervision system
- Student life overview
- In and around Cambridge
- Leisure activities
- Student union
- Music awards
- Student support overview
- Mental health and wellbeing
- Disabled students
- Language tuition
- Skills training
- Support for refugees
- Courses overview
- Department directory
- Qualification types
- Funded studentships
- Part-time study
- Research degrees
- Visiting students
- Finance overview
- Fees overview
- What is my fee status?
- Part-time fees
- Application fee
- Living costs
- Funding overview
- Applying for University funding
- Doctoral training programmes
- External funding and loans
- Colleges overview
- College listing overview
- Accommodation
- Applying overview
- Before you apply
- Entry requirements
- Application deadlines
- How do I apply? overview
- Application fee overview
- Application fee waiver
- Life Science courses
- Terms and conditions
- Continuing students
- Disabled applicants
- Supporting documents overview
- Academic documents
- Finance documents
- Evidence of competence in English
- AI and postgraduate applications
- Terms and Conditions
- Applicant portal and self-service
- After you apply overview
- Confirmation of admission
- Student registry
- Previous criminal convictions
- Deferring an application
- Updating your personal details
- Appeals and Complaints
- Widening participation
- Postgraduate admissions fraud
- International overview
- Immigration overview
- ATAS overview
- Applying for an ATAS certificate
- Current Cambridge students
- International qualifications
- Competence in English overview
- What tests are accepted?
- International events
- International student views overview
- Akhila’s story
- Alex’s story
- Huijie’s story
- Kelsey’s story
- Nilesh’s story
- Get in touch!
- Events overview
- Upcoming events
- Postgraduate Open Days overview
- Discover Cambridge: Master’s and PhD Study webinars
- Virtual tour
- Research Internships
- How we use participant data
- Postgraduate Newsletter
Primary tabs
- Overview (active tab)
- Requirements
- How To Apply
Doctoral studies are carried out by science postgraduates, medical students combining clinical training with the PhD, and clinically qualified doctors undertaking scientific training. The research covers the whole spectrum of medical science from basic biology to clinical therapies.
Along with the specific research training provided in the laboratory in which they work, students receive further training within the department in the form of postgraduate workshops concentrating on research techniques, research seminars both on the Addenbrooke's site and elsewhere in the University, and postgraduate student seminars dealing with generic skills such as intellectual property rights, writing a thesis or paper, and entrepreneurship.
Candidates wishing to take a shorter course of research and write a thesis for the master's after one year may apply for the MPhil in Medical Sciences.
Learning Outcomes
Those who wish to progress to a PhD after completing an MPhil will be required to satisfy their potential supervisor, Head of Department and the Faculty Degree Committee that they have the skills and ability to achieve the higher degree.
The Postgraduate Virtual Open Day usually takes place at the end of October. It’s a great opportunity to ask questions to admissions staff and academics, explore the Colleges virtually, and to find out more about courses, the application process and funding opportunities. Visit the Postgraduate Open Day page for more details.
See further the Postgraduate Admissions Events pages for other events relating to Postgraduate study, including study fairs, visits and international events.
Key Information
3-4 years full-time, 4-7 years part-time, study mode : research, doctor of philosophy, department of medicine, course - related enquiries, application - related enquiries, course on department website, dates and deadlines:.
Some courses can close early. See the Deadlines page for guidance on when to apply.
Easter 2025
Michaelmas 2025, easter 2026, funding deadlines.
These deadlines apply to applications for courses starting in Michaelmas 2025, Lent 2026 and Easter 2026.
Similar Courses
- MD (Doctor of Medicine) MD
- Medical Science (Medicine) MPhil
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology PhD
- Biological Sciences at the Department of Veterinary Medicine PhD
- Biological Science (Pharmacology) by thesis MPhil
Postgraduate Admissions Office
- Admissions statistics
- Start an application
- Applicant Self-Service
At a glance
- Bringing a family
- Current Postgraduates
- Cambridge Students' Union (SU)
University Policy and Guidelines
Privacy Policy
Information compliance
Equality and Diversity
Terms of Study
About this site
About our website
Privacy policy
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
- Student/Faculty Portal
- Learning Hub (Brightspace)
- Continuous Professional Development
- Admissions and Application Process
- Prerequisites and Requirements
- Financial Support
- Curriculum Overview
- Initiative for Maximizing Student Development (IMSD)
- Career Development Internships
- Tracks Overview
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Biomedical Engineering and Physiology
Clinical and Translational Science
- Molecular Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
- Neuroscience
- Regenerative Sciences
- Virology and Gene Therapy
- Find a Mentor
- Student Life Overview
- Student Organizations
- Graduate Student Workspaces
- Events and Programs
- Alumni Perspectives
Clinical and Translational Science Track
Research focus.
across the translational spectrum from discovery to implementation
average amount of time to Ph.D. degree
Guaranteed 5-year internal fellowship
includes full tuition, stipend and benefits
Moving new biomedical discoveries into clinical use as new treatments and cures takes considerable time and resources. A translational scientist is at the forefront of this work, teaming with an integrated group of experts focused on taking knowledge gained through research and translating it for use in health care settings. This bench-to-bedside effort is essential to bridging the gap between basic science and patient care.
The Clinical and Translational Science (CTS) Track within the Ph.D. Program at Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Science is built upon Mayo Clinic's extensive interdisciplinary research and medical environment. It prepares you to lead the biomedical research teams of the future that will rapidly translate discoveries to new treatments and change the paradigms of how we conduct biomedical research.
As a graduate of this program, you’ll be able to conduct research leading to meaningful scientific contributions. In addition, you’ll be prepared to change and improve how biomedical research is conceptualized and implemented.
The Clinical and Translational Science Track allows students to personalize their studies in three areas of emphasis:
- Population-based translational science
- Patient-based translational science
- Laboratory-based translational science
A great strength of the Mayo Clinic CTS track is its focus on providing mentored research experiences for each student. The pre-eminent physicians, scientists, and educators who comprise the faculty at Mayo Clinic are available as mentors or co-mentors for students in the track.
All doctoral students in the CTS track have a common core curriculum. Depending on your area of concentration (laboratory-, patient- or population-based translational science), you’ll select your advanced courses from either track courses or graduate school courses in the basic science disciplines.
- Core required courses
- Track required courses
- Introduction to research projects and methodologies used in the laboratories of clinical/translational investigators
- Completion of three research experiences or laboratory rotations, each lasting eight weeks
- Selection of laboratory for thesis research
- Advanced elective courses (areas of interest)
- Research gathering preliminary data for a thesis research project
- Preparation of a thesis proposal in the format of a grant application
- Selection of faculty for the oral qualifying exam committee, followed by defense of the research proposal in the oral exam (to be completed before the end of the fall quarter)
- Written Comprehensive Examination
- Oral Qualifying Examination (presentation of thesis proposal)
- Ongoing workshops/seminars/journal clubs
- Completion of thesis research and any remaining course requirements
- Selection of your Graduate School Thesis Advisory Committee that will evaluate the proposed direction, specific aims, and experimental strategies of your project, as well as meet with you at least twice a year to discuss your research progress
- Works-in-progress presentation of research project
- Final Oral Examination (thesis defense)
/0x0:512x512/prod01/channel_2/media/mccms/content-assets/academics/biomedical-research-training/phd-program/clinical-translational-science-kelly-kevin-pic-tile.jpg)
I chose the Clinical and Translational Science Track because of the flexibility of the program. Much of your coursework can be whichever topic helps you most for your research, and there are very few restrictions on the principal investigators you can work under. Also, because Mayo provides access to such unique patient populations, I’m able to use a lot of techniques that I wouldn’t be able to at a university or institution.
Kevin Kelly Ph.D. student, Clinical and Translational Science Track
/0x0:512x512/prod01/channel_2/media/mccms/content-assets/academics/biomedical-research-training/phd-program/clinical-translational-science-koleilat-alaa-pic-tile.jpg)
One thing that attracted me to the CTS Track is how supported I felt as a student and the opportunities we have to learn and grow. We’re encouraged to explore career options other than the traditional academic route. I’m interested in translational science, and there have been numerous examples in which discoveries happened at the bench and ended up as clinical trials here at Mayo.
Alaa Koleilat, Ph.D. 2020 graduate of the Ph.D. Program, Clinical and Translational Science Track
/0x0:512x512/prod01/channel_2/media/mccms/content-assets/academics/biomedical-research-training/medical-scientist-training-program-mstp/MD-PhD-Joseph.jpg)
Mayo Clinic draws students and patients from all over the world, which creates a unique educational environment. It also emphasize patient needs, which shapes the way that students learn and interact with other professionals. The small class size and primary focus on biomedical sciences contributes to the welcoming, energetic and collaborative environment. The leaders of all the programs I am associated with are clearly invested in my success.
Josiane Joseph M.D.-Ph.D. student, Clinical and Translational Science Track
- "BLOOM: Beta-lactam Optimization and Outcomes Management," Erin Barreto (Mentor: Andrew Rule, M.D.)
- "Differentiating types of dementia using extracellular vesicles," Maria Esperanza Bregendahl (Mentor: Pam J. McLean, Ph.D.)
- "Investigating Sulfatase 2 effects on the tumor microenvironment in hepatobiliary cancers," Tayla Brooks (Mentor: Lewis. R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- "Defining racial differences in hedgehog-associated breast cancer risk biomarkers in normal breast biopsies," Jennifer Cabezas (Mentor: Derek Radisky, Ph.D.)
- "Cytokine Mediated Death and Survival in Multiple Myelom," Allison (Allie) Carr (Mentor: Adrian T. Ting, Ph.D.)
- "Peripheral multi-omics biomarkers of Alzheimer’s and related phenotypes," Xuan Chen (Mentor: Nilufer Taner, M.D., Ph.D.)
- "Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Left Heart Diseases," Ahmed Fayyaz (Mentor: Margaret M. Redfield, M.D.)
- "Using focused ultrasound (FUS) to enhance the delivery of intravenous umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSC) in chronic spinal cord injured rats," Abdul Karim (AK) Ghaith (Mentors: Mohamad Bydon M.D., and Anthony J. Windebank M.D.)
- "The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in Systemic Stress Response in Zebrafish," Robin Heider (Mentor: Karl J. Clark, Ph.D.)
- "Utilizing long-read sequencing to unravel the clinical heterogeneity in motor neuron diseases and undiagnosed genetic disorders," Angita (AJ) Jain (Mentor: Marka M. Van Blitterswijk, M.D., Ph.D.)
- "Unraveling the Immunological Basis of Lobular Involution Stagnation in Breast Cancer Development," Jaida Lue (Mentor: Derek Radisky, Ph.D.)
- "Artificial intelligence derived voice biomarkers for the detection and management of cardiovascular disease," Jaskanwal Deep (Jas) Sara (Mentor: Amir Lerman, M.D.)
- "Characterization of Mitochondrial DNA variations, heteroplasmic levels, and deletion frequency in Pacbio’s continuous long reads," Ngan Tran (Mentor: Owen Ross, Ph.D.
- "Unrefined: Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis burden and potential interventions in x population," Caitlin VanLith (Mentor: Lewis. R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- "Data Independent Acquisition of Small Molecule Signatures to Characterize Inborn Errors of Metabolism," Rachel Wurth (Mentor: Devin Oglesbee, Ph.D.)
- "Developing Strategies to address health disparities for first generation regenerative medicine treatments," Mohamed (Mo) Addani (Mentor: Zubin Master, Ph.D.)
- "Utility of Methylated DNA Markers for the Diagnosis of Malignant Pancreatic Biliary Strictures," Matthew Cooley (Mentor: Lewis. R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- "Electrical stimulation of hippocampus and amygdala modulates human ventral temporal cortex in distinct ways," Harvey Huang (Mentor: Dora Hermes, Miller Ph.D.)
- "Senolytics and antifibrotic treatment for chronic spinal cord injury," Vagisha Kulsreshtha (Mentors: James Kirkland M.D., Ph.D., and Isobel A. Scarisbrick Ph.D.)
- "HDAC1/OLIG2/STAT5 transcriptional complex facilitates GSC-mediated invasion and tumorigenesis," Auna’y Miller (Mentor: Nhan L. Tran, Ph.D.)
- "Transcriptional adaptation as a possible mechanism underlying amyotrophic lateral sclerosis," Adriana (Adri) Morales Gomez (Mentor: Nathan Staff M.D., Ph.D.)
- "Single Cell Landscape of Infiltrating Immune Cells in Cholangiocarcinoma," Hannah Stumpf (Mentor: Sumera I. Ilyas, M.B.B.S.)
- "Developing a Value-Based Hybrid Care Model for Stroke Patients," Stephanie Zawada (Mentor: Bart M. Demaerschalk, M.D.)
- “Improving Facial Paralysis Surgical Outcomes: Targeting Facial Nerve Regeneration,” Marissa Suchyta (Mentor: Samir Mardini, M.D.)
- “Regenerative Capabilities of Extracellular Vesicles in Myocarditis,” Danielle Beetler (Mentor: DeLisa Fairweather, Ph.D.)
- “Machine Learning-Aided Biomarker Discovery and Precision Genomics for Gallbladder Cancer,” Linsey Jackson (Mentor: Lewis R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- “Pathway Discovery in Neurodegenerative Diseases by Integration of Multi-omics Data,” Yuhao (Harry) Min (Mentor: Nilufer Taner, M.D., Ph.D.)
- “Investigating Uterine Fibroids in Women of Color: A Translational Approach,” Minerva Orellana (Mentors: Felicity T. Enders, Ph.D. and Elizabeth (Ebbie) A. Stewart, M.D.)
- “Natural Language Processing Aided Discovery of Adverse Symptoms during Fertility Procedures,” Karen DSouza (Mentor: Megan A. Allyse, Ph.D.)
- “Understanding and Promoting Student Wellbeing Through Social-Emotional Behavioral Programming,” Catherine Knier (Mentor: Dr. Anthony J. Windebank, M.D, and Christopher K. Pierret, Ph.D.)
- “Reducing the Burden of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among Migrant Populations: Improving Prevention and Outcomes Through Disease Modeling,” Kenneth Valles (Mentor: Lewis R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- “Living Systematic Reviews and Guideline Updates in Areas with Rapidly Evolving Evidence,” Irbaz Bin Riaz (Mentor: M. Hassan Murad, M.D.)
- “Sex Differences in Mitochondria During Acute cvb3 Myocarditis,” Damian Di Florio (Mentor: DeLisa Fairweather, Ph.D.)
- “The Role of Convection-Enhanced Delivery for Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma,” Erica Power (Mentor: David J. Daniels, M.D., Ph.D)
- “Subcutaneous Combination Biodevice for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes,” Ethan Law (Mentor: Quinn P. Peterson, Ph.D.)
- “Technologies to Enable Closed-loop Neurochemical Control in Deep Brain Stimulation,” Aaron Rusheen (Mentor: Kendall H. Lee, M.D., Ph.D.)
- “Functional Validation in Unsolved Rare Disease Patients as a Method of Providing and Clarifying Diagnosis,” Brad Bowles (Mentor: Karl J. Clark, Ph.D. and Eric W. Klee, Ph.D.)
- “The Role of Glypican-3 Isoforms in the Development of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Liver Cancer Therapy,” Aarti Koluri (Mentor: Lewis R. Roberts, M.B., Ch.B., Ph.D.)
- “Clinical Implementation of Tobacco Cessation Treatment among Cancer Patients,” Josh Ohde, Ph.D. (Mentor: David O. Warner, M.D.)
- “Metabolic Abnormalities Associated with Disease Alter Progenitor Cell Function and Precede Tissue Deterioration,” Josiane Joseph (Mentor: Jason D. Doles, Ph.D.)
- “Breast Cancer Mode of Detection Varies by Breast Density and Stage at Diagnosis in Population Based Cohort,” Susanna Basappa (Mentor: Lila J. Rutten, Ph.D.)
Your future
Many graduates of the Clinical and Translational Science Track choose to pursue postdoctoral training regardless of whether they intend to pursue careers in academia or industry. Other students choose to enter advanced training programs, such as genetics fellowships.
Meet the directors
Clinical and translational science is a rapidly developing area of science. Advances in technology and the way we approach and treat diseases or other conditions have set the stage for improved human health.
Our program combines the clinical and scientific resources of Mayo Clinic, where you’ll graduate with an understanding of how research is translated to health care, and ready to carry out research that accelerates medical discoveries into better health.
/prod01/channel_2/media/mccms/content-assets/academics/biomedical-research-training/phd-program/curriculumx2ftracks/318X318-Felicity-Enders.jpg)
Felicity Enders, Ph.D.
Clinical and Translational Science Track Director Professor of Biostatistics Phone: 507-538-4970 Email: [email protected] View research interests
/prod01/channel_2/media/mccms/content-assets/academics/biomedical-research-training/phd-program/curriculumx2ftracks/318X318-Marina-Walther-Antonio.jpg)
Marina Walther-Antonio, Ph.D.
Clinical and Translational Science Track Associate Director Assistant Professor of Surgery Phone: 507-293-7070 Email: [email protected] View research interests
/prod01/channel_2/media/mccms/content-assets/academics/biomedical-research-training/phd-program/512X512-WF626117_0003.jpg)
Anthony Windebank, M.D.
Clinical and Translational Science Track TL1 Principal Investigator Professor of Neurology Phone: 507-284-4716 Email: [email protected] View research interests
Browse a list of Clinical and Translational Science Track faculty members
MEMP PhD Program
Hst’s memp phd program, is this program a good fit for me.
HST’s Medical Engineering and Medical Physics (MEMP) PhD program offers a unique curriculum for engineers and scientists who want to impact patient care by developing innovations to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease. We're committed to welcoming applicants from a wide range of communities, backgrounds, and experiences.
How is HST’s MEMP PhD program different from other PhD programs?
As a MEMP student, you’ll choose one of 11 technical concentrations and design an individualized curriculum to ground yourself in the foundations of that discipline. You’ll study medical sciences alongside MD students and become fluent in the language and culture of medicine through structured clinical experiences. You’ll select a research project from among laboratories at MIT, Harvard, affiliated hospitals and research institutes , then tackle important questions through the multiple lenses of your technical discipline and your medical training. As a result, you will learn how to ask better questions, identify promising research areas, and translate research findings into real-world medical practice.
What degree will I earn?
You’ll earn a PhD awarded by MIT or by the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences.
What can I do with this degree?
Lead pioneering efforts that translate technical work into innovations that improve human health and shape the future of medicine.
How long will it take me to earn a PhD in HST’s MEMP program?
Similar to other PhD programs in MIT's School of Engineering, the average time-to-degree for MEMP PhD students is less than six years.
What are the degree requirements?
Science / engineering.
Choose one of the established concentration areas and select four courses from the approved list for the chosen area. Current MEMP concentration areas are:
- Aeronautics & Astronautics
- Biological Engineering
- Brain & Cognitive Sciences
- Chemical Engineering
- Computer Science
- Electrical Engineering
- Materials Science & Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Nuclear Engineering
Harvard MEMPs fulfill Basic Science/Engineering Concentration and Qualifying Exam through their collaborating department (SEAS or Biophysics).

Biomedical Sciences and Clinical Requirements
Biomedical sciences core.
- HST030 or HST034: Human Pathology
- HST160: Genetics in Modern Medicine
- HST090: Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
Restricted Electives - two full courses required*
- HST010: Human Anatomy
- HST020: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology*
- HST100: Respiratory Pathophysiology**
- HST110: Renal Pathophysiology**
- HST130: Introduction to Neuroscience
- HST162: Molecular Diagnostics and Bioinformatics*
- HST164: Principles of Biomedical Imaging*
- HST175: Cellular & Molecular Immunology
* May combine two half-courses to count as one full course **Must choose at least one of HST100, HST110
Clinical Core
- HST201: Intro. to Clinical Medicine I and HST202: Intro. to Clinical Medicine II
- HST207: Intro. to Clinical Medicine
PhD Thesis Guide
Letter of intent #1:.
Research advisor and topic. Due by April 30 of 2nd year.
Letter of Intent #2:
Tentative thesis committee. Due by April 30 of 3rd year.
Thesis proposal:
Defended before thesis committee. Due by April 30 of 4th year.
Final Thesis:
Public defense and submission of final thesis document.
Harvard MEMPs must an electronic copy of the final thesis including the signed cover sheet. Harvard MEMPs should not register for HST.ThG.
Qualifying Exam
TQE: Technical qualification based on performance in four concentration area courses and Pathology
OQE: Oral examination to evaluate ability to integrate information from diverse sources into a coherent research proposal and to defend that proposal
Professional Skills
Hst500: frontiers in (bio)medical engineering and physics.
Required spring of first year
HST590: Biomedical Engineering Seminar
Required fall semester of first year. Minimum of four semesters required; one on responsible conduct of research and three electives. Topics rotate.
Required for all MEMP students. (Biophysics students may substitute MedSci 300 for HST590 term on responsible conduct of research.)
Professional Perspectives
Required once during PhD enrollment
What can I expect?
You’ll begin by choosing a concentration in a classical discipline of engineering or physical science. During your first two years in HST, you’ll complete a series of courses to learn the fundamentals of your chosen area.
In parallel, you’ll become conversant in the biomedical sciences through preclinical coursework in pathology and pathophysiology, learning side-by-side with HST MD students.
With that foundation, you’ll engage in truly immersive clinical experiences, gaining a hands-on understanding of clinical care, medical decision-making, and the role of technology in medical practice. These experiences will help you become fluent in the language and culture of medicine and gain a first-hand understanding of the opportunities for — and constraints on — applying scientific and technological innovations in health care.
You’ll also take part in two seminar classes that help you to integrate science and engineering with medicine, while developing your professional skills. Then you’ll design an individualized professional perspectives experience that allows you to explore career paths in an area of your choice: academia, medicine, industry, entrepreneurship, or the public sector.
A two-stage qualifying examination tests your proficiency in your concentration area, your skill at integrating information from diverse sources into a coherent research proposal, and your ability to defend that research proposal in an oral presentation.
Finally, as the culmination of your training, you’ll investigate an important problem at the intersection of science, technology, and medicine through an individualized thesis research project, with opportunities to be mentored by faculty in laboratories at MIT, Harvard, and affiliated teaching hospitals.
Interested in applying? Learn about the application process here.

HST MEMP grad Carmen Martin Alonso looks ahead to a bright future as a medical researcher
- Accessibility Options:
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Search
- Skip to footer
- Office of Disability Services
- Request Assistance
- 305-284-2374
- High Contrast
- School of Architecture
- College of Arts and Sciences
- Miami Herbert Business School
- School of Communication
- School of Education and Human Development
- College of Engineering
- School of Law
- Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science
- Miller School of Medicine
- Frost School of Music
- School of Nursing and Health Studies
- The Graduate School
- Division of Continuing and International Education
- People Search
- Class Search
- IT Help and Support
- Privacy Statement
- Student Life

- Search Site
- Main College
- College News
Biomedical Engineering
- Chemical, Environmental and Materials Engineering
- Civil and Architectural Engineering
- Electrical and Computing Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
- Letter from the Chair
- Department Clusters
- Undergraduate
- Imaging, Optics, & Lasers
- Biomechanics, Microfluidics, Biomaterials and Tissue
- Neural Engineering, Signals, & Instrumentation
- News and Events
- Advisory Board
- PhD Students
- Certificate Program
- Medical Physics Program
- Student Publications
- History and Current Enrollment
PhD in Medical Physics
- Listening Exercise
- Communications
- graduate programs
PhD in Medical Physics | College of Engineering | University of Miami
The PhD in Medical Physics Program focuses on training students’ research ability and experience in the field of medical physics with an emphasis on radiation therapy, in addition to the course work required by the MS in Biomedical Engineering – Medical Physics Program. Students graduating from the program are required to take the American Board of Radiology (ABR) exam and to apply for medical physics residency programs. Students are encouraged to seek academic positions after graduating from the program.
Students will complete required coursework by the program and will join research projects in the Department of Radiation Oncology, or other collaborative departments or clinical sites. PhD students in the program will take two qualify exams. The first one is the general qualify exam required by the Department of Biomedical Engineering, usually after two-semester study and before the third semester starts. The second qualify exam is required by the Medical Physics Graduate Program, usually after all coursework has been completed.
The Medical Physics curriculum is designed to provide students with the technical and intellectual skills required for successful careers in the field of medical physics. In addition to the coursework required by the Biomedical Engineering PhD program, PhD students enrolled in the medical physics program must successfully complete 32 medical physics course credits, at least 12 credits in research dissertation (BME 830/840) in the field of medical physics, and other requirements by the BME PhD program. Students who received MS in Medical Physics degree from other CAMPEP-accredited programs can transfer the medical physics coursework credits.
| Course # | Title | Credits |
| (Choose One of the Following) | ||
| BME 601 | Unified Medical Sciences I | 3 |
| BME 603 | Unified Medical Sciences III | 3 |
| BME 602 | Unified Medical Sciences II | 3 |
| BME 620 | Medical Imaging Systems (X-ray, CT) | 3 |
| BME 621 | Medical Imaging Systems (MRI, NMI, Ultrasound) | 3 |
| BME 681 | Radiation Biology and Physics | 3 |
| BME 682 | Radiation Therapy Physics | 3 |
| BME 683 | Radiation Protection | 3 |
| BME 701 | Ethics and Professionalism for Engineers and Medical Physicists | 1 |
| BME 729 | Advanced Medical Imaging | 3 |
| BME 781 | Radiation Dosimetry and Physics | 3 |
| BME 783 | Radiation Therapy Clinical Rotation | 3 |
| BME 784 | Medical Physics Journal Club | 1 |
| TOTAL MEDICAL PHYSICS COURSE CREDITS | 32 | |
| BME 830/840 | Doctoral Dissertation Research | 12+ |

- 1251 Memorial Drive McArthur Engineering Building Coral Gables , FL 33146
- 305-284-2445 305-284-2445
- Academic Calendar
- Alumni & Friends
- Medical Center
- Hurricane Sports
- Parking & Transportation
- social-facebook
- social-twitter
- social-youtube
- social-instagram
- social-linkedin
Copyright: 2024 University of Miami. All Rights Reserved. Emergency Information Privacy Statement & Legal Notices
Individuals with disabilities who experience any technology-based barriers accessing the University’s websites or services can visit the Office of Workplace Equity and Inclusion .
Announcements
Updates on campus events, policies, construction and more.
- Dean’s 2023 State of the School address available online
- Notice of data security incident
- COVID-19: Medical Campus updates
close
Information for Our Community
Whether you are part of our community or are interested in joining us, we welcome you to Washington University School of Medicine.
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Alumni & Friends
- Administrators
- Researchers
- Job Seekers
Huang named head of pathology & immunology
Physician-scientist renowned for expertise in human brain development, degeneration
by Marta Wegorzewska • September 12, 2024
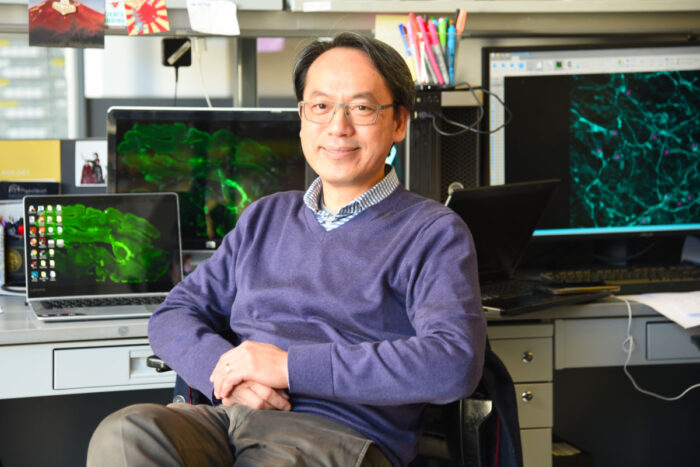

Eric J. Huang, MD, PhD, a leader in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, will head the Department of Developmental Pathology & Immunology at WashU Medicine beginning in January.
Eric J. Huang, MD, PhD, a renowned physician-scientist specializing in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, has been named the Edward Mallinckrodt Professor and head of the Department of Pathology & Immunology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. His appointment begins Jan. 1.
Huang comes to WashU Medicine from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), where he is a professor and vice chair of research for the Department of Pathology. His appointment was announced by David H. Perlmutter, MD , executive vice chancellor for medical affairs, the George and Carol Bauer Dean of the School of Medicine, and the Spencer T. and Ann W. Olin Distinguished Professor.
“We are so fortunate to have Dr. Huang, an exceptionally talented physician-scientist, join our leadership team and the WashU Medicine community,” Perlmutter said. “With his leadership and expertise, we see enormous potential to advance the clinical practice and science in anatomic pathology, laboratory medicine and immunology with revolutions in imaging technologies and by applying artificial intelligence and the precision medicine paradigm to our efforts, which altogether will enhance our long-standing legacy as one of the most – if not the most – accomplished faculties in pathological and immunological sciences.”
Trained as a developmental biologist, Huang has made seminal discoveries in unraveling the complexities of human brain development. His laboratory focuses on understanding the processes involved in how the brain develops in utero and in infancy. In recent studies, he has identified how the human brain continuously produces specialized cells – GABAergic interneurons – during the prenatal period and then incorporates them into brain networks during infancy. His studies also have revealed how blood vessel cells develop in the prenatal human brain and how misguided immune cells increase the risk of brain hemorrhage in premature infants, helping to pave the way for future therapeutics to stop brain bleeds in preterm infants.
Huang’s research also focuses on understanding the drivers of frontotemporal dementia, the second most common cause of dementia in people under age 65. Work from his laboratory uncovered that over-reactive microglia – immune cells responsible for protecting the brain from infection and disposing of dead cells – promote excessive pruning of brain cell connections. He also found that such cells work with other brain cells called astrocytes to cause the damage to and loss of neurons implicated in frontotemporal dementia.
His research is funded by six major grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
“It is an honor to join WashU Medicine in this role,” Huang said. “I am excited by the opportunity to build upon the strengths of a department that is leading the field in clinical innovation and research. WashU Medicine has a strong collaborative culture, which I aim to continue fostering within the department and with other disciplines. I am eager to support early-career faculty in becoming independent investigators and advancing our commitment to the success of trainees.”
Huang’s research has been published in top-tier journals, including Science, Nature and Cell, among others. His scientific accomplishments also have been recognized throughout his career. As a junior faculty member, he received the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers. Most recently, he was elected as an academician to Academia Sinica, a leading academic institution in Taipei, Taiwan. He also is known as a dedicated mentor to PhD and MD/PhD students, postdoctoral trainees and early-career faculty.
Huang earned his medical degree from the National Taiwan University College of Medicine before completing his doctoral studies at the Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences in New York. He completed residency training in anatomic pathology, and fellowship training in neuropathology at UCSF, where he also stayed to complete a Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s postdoctoral fellowship. In 2000, he joined UCSF’s faculty.
Huang will succeed Richard J. Cote, MD , who has led the department since 2019. Cote will continue his research at WashU Medicine, where he studies tumor progression and response to therapy, and as a pathologist focusing on breast and genitourinary cancer diagnoses in patients seen at Siteman Cancer Center, based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and WashU Medicine.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
Editors' Picks

September 12, 2024
9-story Siteman Cancer Center building designed for patient comfort, convenience.
Medical Campus & Community, News Release
September 10, 2024
Patients inspired design of state-of-the-art building on Washington University Medical Campus.
News Release
July 31, 2024
Study in hamsters indicates vaccines targeting nose, mouth may be key to controlling spread of respiratory infections.
Why Pursue an MD-PhD?
New section.
Just some of the reasons why people choose a career as a physician-scientist.
- The career of a physician-scientist is unique. There are few comparable careers that allow one to experience the passion of solving a patient's medical struggles while pursuing research that may define the mechanism of that patient’s disease and may ultimately translate into a clinical cure for the disease.
- MD-PhD trainees are research scientists who solve mechanisms underlying disease, combined with their passion to treat patients in a clinical setting.
- MD-PhD training efficiently integrates the scientific and medical education of the physician-scientist.
- During the PhD training years, MD-PhD students take the coursework and formal training in research methodology that are important for the development of the research scientist.
- Most MD-PhD programs provide trainees with a stipend and tuition scholarships. This financial support recognizes the time that a student must spend in training for the MD-PhD career. The extent of financial support varies among programs and may only support U.S. citizens and permanent residents.
Areas of Research Interest for MD-PhD Training
- Most MD-PhD candidates earn their PhD in biomedical laboratory disciplines such as cell biology, biochemistry, genetics, immunology, pharmacology, physiology, neuroscience, and biomedical engineering.
- Some MD-PhD Programs also allow trainees to do their graduate work in fields outside of laboratory disciplines, including computational biology, economics, epidemiology, health care policy, anthropology, sociology, or the history of medicine.
- The spectrum of graduate degree programs offered is an important element to consider when applying to specific MD-PhD Programs.
- @AAMCpremed
Helpful tools and information regarding medical MD-PhD programs.
Information about applying to MD-PhD programs, emphasizing the application process during COVID-19.
Information about MD-PhD programs, emphasizing the career and application process.
Learn about MD-PhD Programs from program leaders.
Upcoming short presentations will describe features of MD-PhD training, alumni careers, and detailed logistics of the application process.
Emily battled viral encephalitis for years during college, and now as a MD/PhD student, she reminds premeds that it's okay to ask for help.
Cesar couldn't apply to medical school when he first graduated from college due to his undocumented status. Now he's in a MD-PhD program and hopes to practice in the Southwest where there's a high need for Spanish-speaking physicians.
- History, Facts & Figures
- YSM Dean & Deputy Deans
- YSM Administration
- Department Chairs
- YSM Executive Group
- YSM Board of Permanent Officers
- FAC Documents
- Current FAC Members
- Appointments & Promotions Committees
- Ad Hoc Committees and Working Groups
- Chair Searches
- Leadership Searches
- Organization Charts
- Faculty Demographic Data
- Professionalism Reporting Data
- 2022 Diversity Engagement Survey
- State of the School Archive
- Faculty Climate Survey: YSM Results
- Strategic Planning
- Mission Statement & Process
- Beyond Sterling Hall
- COVID-19 Series Workshops
- Previous Workshops
- Departments & Centers
- Find People
- Biomedical Data Science
- Health Equity
- Inflammation
- Neuroscience
- Global Health
- Diabetes and Metabolism
- Policies & Procedures
- Media Relations
- A to Z YSM Lab Websites
- A-Z Faculty List
- A-Z Staff List
- A to Z Abbreviations
- Terms, Privacy & Notices
- Dept. Diversity Vice Chairs & Champions
- Dean’s Advisory Council on Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer and Intersex Affairs Website
- Minority Organization for Retention and Expansion Website
- Office for Women in Medicine and Science
- Committee on the Status of Women in Medicine Website
- Director of Scientist Diversity and Inclusion
- Diversity Supplements
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recruitment
- By Department & Program
- News & Events
- Executive Committee
- Aperture: Women in Medicine
- Self-Reflection
- Portraits of Strength
- Mindful: Mental Health Through Art
- Event Photo Galleries
- Additional Support
- MD-PhD Program
- PA Online Program
- Joint MD Programs
- Advanced Health Sciences Research
- Clinical Informatics & Data Science
- Clinical Investigation
- Medical Education
- Visiting Student Programs
- Special Programs & Student Opportunities
- Residency & Fellowship Programs
- Center for Med Ed
- Organizational Chart
- Leadership & Staff
- Committee Procedural Info (Login Required)
- Faculty Affairs Department Teams
- Recent Appointments & Promotions
- Academic Clinician Track
- Clinician Educator-Scholar Track
- Clinican-Scientist Track
- Investigator Track
- Traditional Track
- Research Ranks
- Instructor/Lecturer
- Social Work Ranks
- Voluntary Ranks
- Adjunct Ranks
- Other Appt Types
- Appointments
- Reappointments
- Transfer of Track
- Term Extensions
- Timeline for A&P Processes
- Interfolio Faculty Search
- Interfolio A&P Processes
- Yale CV Part 1 (CV1)
- Yale CV Part 2 (CV2)
- Samples of Scholarship
- Teaching Evaluations
- Letters of Evaluation
- Dept A&P Narrative
- A&P Voting
- Faculty Affairs Staff Pages
- OAPD Faculty Workshops
- Leadership & Development Seminars
- List of Faculty Mentors
- Incoming Faculty Orientation
- Faculty Onboarding
- Past YSM Award Recipients
- Past PA Award Recipients
- Past YM Award Recipients
- International Award Recipients
- Nominations Calendar
- OAPD Newsletter
- Fostering a Shared Vision of Professionalism
- Academic Integrity
- Addressing Professionalism Concerns
- Consultation Support for Chairs & Section Chiefs
- Policies & Codes of Conduct
- First Fridays
- Faculty Facing Caregiving Need
- Fund for Physician-Scientist Mentorship
- Grant Library
- Grant Writing Course
- Mock Study Section
- Research Paper Writing
- Establishing a Thriving Research Program
- Funding Opportunities
- Join Our Voluntary Faculty
- Child Mental Health: Fostering Wellness in Children
- Faculty Resources
- Research by Keyword
- Research by Department
- Research by Global Location
- Translational Research
- Research Cores & Services
- Program for the Promotion of Interdisciplinary Team Science (POINTS)
- CEnR Steering Committee
- Experiential Learning Subcommittee
- Goals & Objectives
- Faculty & Staff
- Issues List
- Print Magazine PDFs
- Print Newsletter PDFs
- YSM Events Newsletter
- Social Media
- Patient Care
INFORMATION FOR
- Residents & Fellows
- Researchers
Surgery Post-COVID: No Need to Wait More Than 2 Weeks, New Study Says
Postponing operations following a positive COVID-19 test may be creating unnecessary delays in elective surgeries, new findings suggest.
In the early days of the pandemic, the American Society of Anesthesiologists recommended delaying nonurgent surgeries by up to seven weeks following SARS-CoV-2 infection. These guidelines were based on research at the time that showed that COVID-19 was associated with an increased risk of post-operative difficulties including pulmonary complications.
Now, in the midst of the latest wave — predominantly driven by subvariants of Omicron known as FLiRT and LB.1 — many medical institutions continue to take conservative measures even though the newest infections have tended to be milder.
A new study shows that there is no significant benefit in delaying surgeries longer than two weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection. The researchers published their findings in Annals of Surgery on August 1.
“The same mandate for postponing surgery that was necessary before isn’t supported by the most recent evidence,” says Ira Leeds, MD , assistant professor of surgery at Yale School of Medicine, who was the study’s first author.
Following the onset of the pandemic, elective surgeries came to a screeching halt. “For the first six months to a year of the COVID-19 pandemic, unless there was a true urgency, cases were being routinely delayed based on local policies supported by society guidelines at the time,” says Leeds.
Later on, as these procedures went back on the schedule, surgeons grappled with how to provide patients with the beneficial outcomes of surgery while minimizing the risk of COVID-related post-operative complications. Given that both surgery and COVID-19 can place stress on organs such as the heart and lungs, surgeons took great precautions.
“The data at the time suggested that among those who were seriously ill from COVID-19, there were long-term sequelae [condition following prior disease/injury],” says Leeds. For example, these patients faced greater risks associated with mechanical ventilation and blood clots.
The same mandate for postponing surgery that was necessary before isn’t supported by the most recent evidence. Ira Leeds, MD
However, when later waves of COVID-19 eased in severity, surgeons had little guidance on whether weeks-long delays were still protecting patients, especially those who had mild or asymptomatic infections.
Surgery within two weeks of infection associated with adverse outcomes
In its latest study, Leeds’ team used Veterans Affairs administrative data from April 2020 to September 2022 to identify more than 80,000 patients who had undergone an inpatient surgical procedure. The most common surgeries patients underwent were hernia repairs and knee replacements. Of this cohort, 16,000 had a positive COVID-19 test before surgery. The researchers divided these patients into groups based on the number of days between the most recent positive test and the date of surgery. Then, they matched patients in the COVID-positive and control groups based on factors including which disease they were being treated for, which procedure they underwent, and which medical center they visited.
The researchers compared mortality within 90 days and post-operative complications within 30 days. Their analysis revealed that there were no significant differences between the groups—with the exception of those who had tested positive within two weeks before their surgery. These patients were the only ones who had a higher risk of mortality and post-operative complications [BI1] —including cardiopulmonary complications, blood clots, and post-operative infections—compared to the controls.
The study offers evidence that previous guidelines for delaying surgery are no longer beneficial to patients—preventing them from receiving timely care while offering no further protection from COVID-related complications. “If someone is being hospitalized for COVID a week before their surgery, and they can wait a couple of weeks, then, yes, they should,” says Leeds. “But anything more than two weeks was not associated with better surgical outcomes.”
Featured in this article
- Ira Leeds, MD, FACS, FASCRS Assistant Professor of Surgery (Colon and Rectal); Assistant Professor, Biomedical Informatics & Data Science; Clinical Member, Cancer Prevention and Control Program - Yale Cancer Center; Clinical Fellow, Clinical Epidemiology Research Center (CERC), Department of Veterans Affairs

COMMENTS
Deciding to pursue an MD-PhD dual degree is a long-term commitment, but for a medical student with a passion for research, it's a rewarding path. ... PhD research—after completing two years of medical school—at the University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine, Drayton Harvey applied to 30 MD-PhD programs.
Funding. The Harvard/MIT MD-PhD Program at Harvard Medical School (HMS) has been sponsored in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through its Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) since 1974. All MD-PhD student applicants to our program compete on equal footing for MSTP support, regardless of scientific interest.
Stanford Health Policy offers a PhD program which promises to educate students who will be scholarly leaders in the field of health policy, and will be highly knowledgeable about the theoretical and empirical approaches that can be applied in the development of improvements in health policy and the health care system. These students will be ...
MD-PhD Application Timeline. AMCAS application opens: May preceding the year of expected entry. Applicants interviewed: October-March. Final decisions sent to applicants: December-March. Applicants revisit program (s) to decide where to matriculate: March-April. MD-PhD programs start: June-August. Are you considering a MD-PhD program?
The Doctor of Medicine-Doctor of Philosophy (MD-PhD) is a dual doctoral program for physician-scientists, combining the professional training of the Doctor of Medicine degree with the research program of the Doctor of Philosophy degree.. In the United States, the National Institutes of Health currently provides 50 medical schools with Medical Scientist Training Program grants that ...
There are nine HMS-based PhD programs. Students in these programs are all enrolled in the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (GSAS):
Whether you're preparing for graduate school or applying now, the Mayo Clinic experience for biomedical science Ph.D. students is different. Program highlights: Research training by leading investigators in fields ranging from molecules to populations, all in the context of exceptional health care. Embedded within a top academic medical ...
Almost all MD-PhD students spend time during this final 18-month period engaged in basic, translational or clinical research: they may return to their thesis lab, structure a short research experience to learn a new skill, or participate in clinical research related to the specialty in which they plan to match.
All interviews (MD and MD-PhD) are conducted virtually. "Non-traditional" MD-PhD interviews. January-February. Notification of acceptance to MD-PhD Program. March 15. Second Look for Admitted Students (in-person) March/April. Acceptance response deadline. April 30.
The Harvard/MIT MD-PhD Program Daniel C. Tosteson Medical Education Center 260 Longwood Avenue, Suite 168 Boston, MA 02115 Phone: 617-432-0991 [email protected]
The short answer is, "It won't." PhD training for MSTP students is just as rigorous and intensive as for students outside the MSTP. However, MSTP students don't spend their first year rotating through different laboratories, and most MSTP students complete their preclinical medical school curriculum before starting full-time laboratory research.
PhD in Medicine. Doctoral studies are carried out by science postgraduates, medical students combining clinical training with the PhD, and clinically qualified doctors undertaking scientific training. The research covers the whole spectrum of medical science from basic biology to clinical therapies. Along with the specific research training ...
Throughout graduate school, there are scheduled times when students must reach certain milestones. Biomedical scientists can use their knowledge of biomedical research in a wide variety of ways. Biomedical scientists bridge the gap between the basic sciences and medicine. The PhD degree is the gateway to a career in biomedical research.
The career of each MD-PhD graduate is uniquely based upon research and clinical interests, but follows the general path: MD-PhD training: 7-8 years (See Education and Training for more information). Specialty and subspecialty clinical and research training (residency/fellowship): 3-7 Years.
"Utilizing long-read sequencing to unravel the clinical heterogeneity in motor neuron diseases and undiagnosed genetic disorders," Angita (AJ) Jain (Mentor: Marka M. Van Blitterswijk, M.D., Ph.D.) "Unraveling the Immunological Basis of Lobular Involution Stagnation in Breast Cancer Development," Jaida Lue (Mentor: Derek Radisky, Ph.D.)
The M.D./Ph.D. Program is committed to accepting and training the leaders of tomorrow. Our medical school training is excellent, and our campus provides an extraordinary breadth of research opportunities. The School of Medicine has over $200 million in NIH funding, and the campus at UC Davis has over 90 graduate groups engaged in broad areas of ...
Funding. The Harvard/MIT MD-PhD Program at Harvard Medical School (HMS) has been sponsored in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through its Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) since 1974. All MD-PhD student applicants to our program compete on equal footing for MSTP support, regardless of scientific interest.
How is HST's MEMP PhD program different from other PhD programs? As a MEMP student, you'll choose one of 11 technical concentrations and design an individualized curriculum to ground yourself in the foundations of that discipline. You'll study medical sciences alongside MD students and become fluent in the language and culture of medicine ...
About the Program. The Medical Scientist Training Program at Baylor College of Medicine is designed for highly motivated students. The successful applicant should have both an excellent scholastic record and sustained potential in research. Exposure to both laboratory bench work and clinical care in private practice, academic medicine or ...
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program.
MD-PhD programs provide training for the dual degree by integrating research and clinical training experiences where students learn to conduct hypothesis driven research in a mentored environment. There are over 100 MD-PhD programs affiliated with U.S. medical schools, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences partially supports ...
Medical school typically lasts four years, but three-year accelerated programs have been emerging. Once someone receives either an M.D. or D.O. degree, they go on to the next phase of their ...
In addition to the coursework required by the Biomedical Engineering PhD program, PhD students enrolled in the medical physics program must successfully complete 32 medical physics course credits, at least 12 credits in research dissertation (BME 830/840) in the field of medical physics, and other requirements by the BME PhD program.
About Washington University School of Medicine. WashU Medicine is a global leader in academic medicine, including biomedical research, patient care and educational programs with 2,900 faculty. Its National Institutes of Health (NIH) research funding portfolio is the second largest among U.S. medical schools and has grown 56% in the last seven years.
MD-PhD training efficiently integrates the scientific and medical education of the physician-scientist. During the PhD training years, MD-PhD students take the coursework and formal training in research methodology that are important for the development of the research scientist. Most MD-PhD programs provide trainees with a stipend and tuition ...
MD-PhD Program. PA Program. PA Online Program. Joint MD Programs ... isn't supported by the most recent evidence," says Ira Leeds, MD, assistant professor of surgery at Yale School of Medicine, who was the study ... However, when later waves of COVID-19 eased in severity, surgeons had little guidance on whether weeks-long delays were still ...
We are introducing OpenAI o1, a new large language model trained with reinforcement learning to perform complex reasoning. o1 thinks before it answers—it can produce a long internal chain of thought before responding to the user.