Cardiovascular Efficacy of Evolocumab in Patients with Obesity: Updates from FOURIER Trial

Session: Smaller trials, trial updates, and other studies on lipid therapy Topic: Drug therapy Speaker: Doctor Y. Kang (Boston, US) Event: ESC Congress 2024
Congress Presentation

About the speaker

Doctor Yu Mi Kang
Harvard Medical School Teaching Hospital, Boston (United States of America) 1 presentation 0 follower
4 more presentations in this session
Apolipoprotein a-i infusions and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction and hyperlipidemia.
Speaker: Doctor C. Gibson (Boston, US)
Alternative LDL cholesterol lowering strategy vs. high-intensity statin strategy: An individual patient data meta-analysis from the randomized RACING and LODESTAR trials
Speaker: Professor M. Hong (Seoul, KR)
A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study of plozasiran in patients with familial chylomicronemia syndrome
Speaker: Professor G. Watts (Perth, AU)
ApoA-I Infusions and Burden of Ischemic Events after Acute Myocardial Infarction
Speaker: Doctor G. Chi (Boston, US)
Access the full session
Smaller trials, trial updates, and other studies on lipid therapy, about the event, esc congress 2024.
30 August - 2 September 2024
Sessions Presentations

ESC 365 is supported by


Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions
(12 reviews)
Andrea M. Nelson, University of West Florida
Katherine Greene, University of West Florida
Copyright Year: 2021
Publisher: University of West Florida Pressbooks
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Carolina Molina-Martin, Adjunct Faculty, Old Dominion University on 6/16/24
This book is comprehensive and informative. In addition to a Table of Contents that provides a breakdown of each of the 18 chapters, a Glossary follows the Table of Contents. Glossary terms are bolded in green and their definitions can be found in... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
This book is comprehensive and informative. In addition to a Table of Contents that provides a breakdown of each of the 18 chapters, a Glossary follows the Table of Contents. Glossary terms are bolded in green and their definitions can be found in the glossary at the end of the book.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The content is very accurate, . It is non biased, and inclusive. The chapters are very thorough and well-written. There are no glaring errors.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The information presented in the text is relevant and is not information that will become outdated, as it is focused on medical terminology.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in very accessible language. Terms are presented with appropriate depth and clarity. Each chapter opens with a list of word parts (prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes) related to the topic. References are included with each chapter.
Consistency rating: 5
The terminology and framework are consistent, Interactive content is built into each chapter. The structure of each chapter is consistent throughout. It starts with learning objectives.
Modularity rating: 5
The book is easy to read. It is written with well defined chapters broken into manageable paragraphs.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Extremely well organized. The order of presentation is overall logical and clear. Pertinent information for the topic of the chapter is covered.
Interface rating: 5
The interactive reinforcement activities require you to click, drag and drop, listen and repeat, flip, and test yourself. No issues were found with the features of the text. The interface is user-friendly, No problems with navigation.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No glaring errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
The text is not culturally insensitive.
This OER book is different from many traditional medical terminology textbooks. Kudos to the authors for all of their hard work on creating such a wonderful book. This resource will serve well future healthcare students and any healthcare profession.
Reviewed by Judith Guetzow, Lecturer II, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 5/22/24
The text offers comprehensive coverage of medical terminology for healthcare professions, presenting terms with appropriate depth and clarity. Each chapter opens with a list of word parts (prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes) related to the... read more
The text offers comprehensive coverage of medical terminology for healthcare professions, presenting terms with appropriate depth and clarity. Each chapter opens with a list of word parts (prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes) related to the topic. Medical terms are prominently displayed in bold green font throughout the chapters, and a useful glossary is provided in the book, aiding students in quickly locating relevant vocabulary. Furthermore, at the end of each body system chapter, a vocabulary list is included, featuring terms associated with that specific system.
The content is accurate, error-free, unbiased, and reflects the latest developments in the field; thus, providing students with reliable information essential for their understanding of medical terminology.
The content is current, ensuring students learn terminology that reflects existing practices. The authors provide a balance between current information and the established principles of medical terminology, ensuring the text remains relevant without quickly becoming obsolete. Its structured format allows for easy updates as medical terminology evolves.
Written in clear and accessible prose, the text provides explanations and context for technical terms, making it suitable for students at all proficiency levels and enhancing overall clarity.
Consistency is maintained throughout the text in both terminology and framework; thus, contributing to its reliability and lucidity. This is conducive to improving students’ comprehension and retention of the medical terms.
The modularity of the text facilitates flexible teaching approaches. The text is organized into eighteen chapters that can be further divided into reduced sections, allowing instructors to assign smaller reading sections without disrupting the flow of the material.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion guiding students through progressively more complex concepts in a clear and discerning manner. As students advance through each body system, they learn the corresponding medical terms, the word parts that form these terms, and the relevant abbreviations specific to each system.
The interface of the textbook is user-friendly, free of significant navigation issues or display problems that could hinder the learning experience. There is a clear presentation of images and charts which enhances the learning experience. Each chapter integrates interactive content such as videos, flashcards, drag-and-drop exercises, and self-tests that are exclusive to the online format. Hyperlinks to the interactive content are provided to users of PDF or EPUB versions of the text. This content was accessible to a diverse range of learners, with closed captioning provided for the videos, and no errors were detected in the captions. Additionally, image descriptions were included for each picture. A minor concern is that certain flashcards lacked the text-to-speech feature.
No grammatical errors were found. The text is grammatically sound and written at a level appropriate for the students, ensuring readability.
The material is free from inappropriate or offensive content.
Overall, the authors created a comprehensive textbook that provides a thorough understanding of medical terminology relating to body systems and pathology, diagnostics, and medical procedures. It would be wonderful if PowerPoints, test banks, and assignments as learning exercises that require students to break down the terms into word parts were included in each chapter. However, I found reading the text and engaging with the interactive activities enjoyable. Reviewing this material has been valuable, as it has piqued my interest in potentially using it for my medical terminology class in the near future.
Reviewed by Gary McIlvain, Professor, Marshall University on 5/21/24
It covers the information very well. It tends to become an anatomy textbook too much. read more
It covers the information very well. It tends to become an anatomy textbook too much.
The accuracy was on par. Again, too much "anatomy book" context for med term.
With anatomy and medical terminology, it rarely changes. So, the text longevity would be good.
The ease of reading the text is great and students would be able to follow it well. It seems to become a better anatomy text than medical terminology or maybe the title should be "applied medical terminology" and it state it focuses on applying it within anatomy.
Yes, but more anatomy textbook than I would use for a med term class.
It is divided by systems, which is a common way to organize a medical terminology text.
It does do a good job applying it to common every day issues (e.g. M.S.)
Great use of drag and drop and flash cards.
I didn't note any errors.
Yes, it did use pictures that depicted varying racx3es, ethnicities, and backgrounds. It is limiting in anatomy pictures to be able to do this...
I would like to see basic pharmacology used in it. I would not currently use this as the only text due to the lack of basic pharmacology. With that added it would be a great text.
Reviewed by Jenni Johnson, Assistant Professor, Marshall University on 5/21/24
This book provides appropriate medical terminology for all regions of the body as well as all healthcare disciplines. It is a great asset for any healthcare profession. read more
This book provides appropriate medical terminology for all regions of the body as well as all healthcare disciplines. It is a great asset for any healthcare profession.
I found no mistakes within the textbook.
The book is extremely relevant and it can be utilized for many years across many healthcare professions. This text is also good for a variety of learning styles by utilizing virtual flash cards and videos with audio.
The textbook is clearly and concisely written
Each chapter follows the same format which makes it very easy to navigate.
This book has 18 chapters and they are clearly outlined. Each chapter is broken up into sections that have an excellent flow that builds learning over time.
Each area is clearly defined
Each chapter and learning tool is easy to navigate and there were no technical issues.
I found no grammatical errors in the text.
There was no cultural bias in this text. It was inclusive of all cultures, and genders and free from religious bias.
I believe this text can be used for a wide variety of future healthcare professions. The flashcards, interactive videos and end of chapter quizzes appeal to all learning styles and assist with retention. Each word is broken down to easily understand the meaning and use of the terminology,
Reviewed by Wendy Schuh, Assistant Professor, Minnesota State University Mankato on 2/8/24
This book is clearly laid out with 18 different chapters covering all of the body systems + obstetrics. There are interactive figures, flash cards, and end of chapter quizzes. Vocabulary words have a linked definition within the text. It would be... read more
This book is clearly laid out with 18 different chapters covering all of the body systems + obstetrics. There are interactive figures, flash cards, and end of chapter quizzes. Vocabulary words have a linked definition within the text. It would be an added benefit to include pronunciation, which is an important component of medical terminology. Videos have a captioning option.
No concerns with accuracy.
References are included with each chapter. Publication date is 2021, and most references are within the last five years. In addition, this content is mostly stable over the years. CrashCourse videos are a little older (2015) but many students are familiar with Hank Green in this format. Information is relevant and easy to process.
Clear chapter content, sections, and headings.
Consistent style of writing, activities, page layout, etc. throughout the book.
Chapters organized in a logical manner. Flashcards and interactive body part activities are wonderful tools, even better since they can be completed multiple times.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The structure of the textbook is sound and consistent with other medical terminology textbooks. A more thorough Table of Contents would allow for easier navigation. It has a good balance of technical and non-technical writing that makes it easy to read and comprehend.
Interface rating: 3
Appealing and interactive. I attempted to take advantage of the “re-use” option below each activity but could not figure it out. Search function does not work well. I tried searching phrases directly from the text, and it would not pull up. The labeling activities were difficult to complete as the drag and drop feature would not scroll. Therefore, it would be useful to have a correct answer option to see the completed figure. It would be helpful to have descriptions included with different e-book options that explain interactive functions with each format.
Very clean and proofed!
Appeared to be culturally inclusive, although it is difficult to assess in this type of resource. No diverse representation of skin color on diagrams.
This is a great textbook that mimics other medical terminology textbooks costing $100+ that don’t have interactive components. There could be some great additions to more effectively use this for a course textbook, such as a question bank, study guides, and suggestions for worksheets and projects to incorporate points into a course framework.
Reviewed by Sharon Schaeffer, Associate Clinical Professor, Bowling Green State University on 4/16/23
Covers major body systems . read more
Covers major body systems .
I did not see any errors during my review.
Medical terminology is a pretty static topic. When students learn how to correctly combine forms, they will be ready to decipher new vocabulary that comes with progress in health care.
Easy to understand.
The depth of content is consistent.
I will allow students to choose their topic of the week after the first 3 chapters are complete. The module system will work well for this design. This design allows students taking A & P or similar courses the opportunity to learn med term at the same time as they are learning in other courses.
Well organized.
I had no challenges linking to and using the added features.
No problems noted.
Inclusive content.
This book will help my students learn the basics of medical terminology as a foundation for building a strong professional vocabulary. I like the interactive activities in this book as it helps learners of different styles. It would be a bonus if there were quiz question banks available. It is not enough of a deal breaker to stop me from using this in my course next Spring semester.
Reviewed by Kristin Meyer, Professor, Drake University on 12/15/22
The text comprehensively covers medical terms in each body system, with a couple of introductory chapters. It covers the span of life with a dedicated obstetrics chapter, which I have not seen in other texts. read more
The text comprehensively covers medical terms in each body system, with a couple of introductory chapters. It covers the span of life with a dedicated obstetrics chapter, which I have not seen in other texts.
No inaccuracies identified.
Medical terminology does not easily or often change, but the text could be easily updated from time to time to include new disease states or terms.
No issues with clarity identified.
Each chapter has a consistent format with link to video overview and active learning activities interspersed throughout.
The organization by body system allows an instructor to assign the appropriate amount of content to correspond with course credit hours.
The online version is easy to navigate. The search function doesn't work as I would expect it to.
Interface rating: 4
The online version is easy to navigate. The pdf download has none of the interactive features. It would be nice if the pdf version could somehow include the active learning exercises in each chapter, with an answer key appendix.
No grammatical errors identified.
Does not appear to be culturally insensitive.
I could easily adopt this text for my web-instructed undergraduate medical terminology class. The interactive features are helpful to engage students. A summary quiz at the end of each chapter would be a nice added feature.
Reviewed by Nancy Bouchard, Adjunct Professor, North Shore Community College on 11/14/22
Very well done. read more
Very well done.
Very accurate and not biased.
If updates are needed, they could be added with ease.
Well written text.
Very consistent.
Very user friendly. Easy to read and assign chapters.
Very organized.
I did not encounter any issues.
None noticed.
Not insensitive or offensive.
My only concern is for the student who has no prior exposure to medical terminology, healthcare training or will not have a clinical role in healthcare. I would not want them to get overwhelmed by the depth of detail in each chapter. I would suggest a section in each chapter that contains exercises for students to test their understanding of the subject matter read, practice correctly writing the terms and the like. Visual learning is only one way for students to absorb content. I would have to create ways to test their understanding to be graded using quizzes, a research project, midterm and final exam. I'm on the fence if the content in the textbook is too deep for only needing a basic understanding of medical terms.
Reviewed by Martha Fabian-Krause, Adjunct Clinical Instructor, Rogue Community College on 9/1/22
Systematic flow of each body system to include root word, prefix, suffix, anatomy, physiology, video and practice in each section. Logical to follow. read more
Systematic flow of each body system to include root word, prefix, suffix, anatomy, physiology, video and practice in each section. Logical to follow.
No issues noted. Very accurate.
Timeless interpretation of terminology would make the on line text need updating only if new medical information becomes available.
Detailed explanations of terminology, anatomy and physiology with pertinent examples and word practice at the end of each body system.
Each section is consistent by acknowledging medical diseases, disorders, and procedures related to the root words. Good follow through in each body system.
This on line book can be assigned in a particular order relevant to other class material and does not need to be completed in any particular time frame. Pleasurable reading.
The format of each section (body system) is in a progressive fashion and is put together with a video near the beginning and word games at the end of each section. Good sequencing noted throughout.
Charts are easy to navigate. There is an identical format what is easy to assimilate.
None noted.
No diversive issues noted. Represents the full spectrum of human anatomy and physiology.
Marvelous understanding of the root words, prefix, suffix and detailed anatomy and physiology. The videos and word matches at the end of each section put the meaning crystal clear.
Reviewed by Carla Tobin, Faculty, Century College on 6/17/22
This textbook covers all of the body systems, the word parts and rules, and prefixes and suffixes. read more
This textbook covers all of the body systems, the word parts and rules, and prefixes and suffixes.
This book is very accurate. No discrepancies or errors were noted in the textbook.
Medical terminology is a subject that does not change over the years. As new diseases and technologies arise, they can easily be incorporated into the content.
The language used in the book is clear and pronunciations of the terminology is provided throughout the e-book. This is an easy to read book for high school or college level students.
The chapters are consistent in there format and organization throughout the textbook. It is easy to follow for the student.
The chapters are broken down into sections which make it easy to read. The videos are shown within the textbook, so the user is not taken to another site. One suggestion would be to have a link to the next chapter at the bottom of the page rather than scrolling up to the top to choose the next chapter from the left side menu.
The organization of this textbook is exactly what you would expect for a Medical Terminology textbook. It is divided into chapters by body system.
There are no apparent issues with the interface. As noted above, the videos are shown within the textbook window, so the user is not taken to another site.
I did not note any grammatical errors in this textbook.
Cultural sensitivity is not really relevant with medical terminology. This language is used in many countries in order to be able to communicate in the same language.
I agree that the best use of this book in the online internet version. This is a very comprehensive medical terminology book. It covers all of the body systems and word building of medical terminology. The chapters provide many opportunities to practice what the student has learned. I liked that each chapter has the learning objectives listed at the beginning. I would have liked to see chapter summaries for the students to study. I think that this book could easily be incorporated into an online class, however, some work would be involved making PowerPoints, homework and quizzes. Overall, this is an excellent Medical Terminology book.
Reviewed by Renee Eaton, Advanced Instructor, Undergraduate Director, Virginia Tech on 5/17/22
Systems-based organization and includes all body systems. read more
Systems-based organization and includes all body systems.
No errors or issues noted
Medical terminology is something that rarely changes. Context activities may change over time, as does disease prevalence and knowledge, but new terms or different terms are not common.
Clear descriptions and use of technical and non-technical language.
The organization is the same across each chapter making the book easy to access and navigate. Language and flow are consistent.
Text is easy to navigate. It may be helpful to provide some in-chapter navigation on the lower menu bar. For example, the previous and next chapters are linked on the left and right margins of the bottom, and chapter components such as diseases / anatomy / etc. could be added to the center. It may not all fit, but even having a couple of navigation points within the chapter would be helpful.
Good organization and order of chapters.
This is one of my greatest difficulties. Navigation within chapters would be helpful. The incorporation of activities, particularly the labeling activities and Medical Terms in Context, are difficult with a regular laptop screen. The text and answer selections are often not on the same screen, making the activity more tedious to complete. Some of the labeling activities also have large images that put the image and answer selections on different screens. The "Did You Know", "Objectives" and colored boxes contain wasted space. They're excessively large especially in the header, and when viewing on a laptop is often half the screen if not more. The PDF version often has issues of inconsistent font size and misalignment of tables.
No grammatical errors found. I appreciated the bold and linked words, with the ability to see definitions with one click. It might be helpful to have a sidebar with the important words and definitions / information in the section, but that might not be feasible with formatting.
Hard to assess for medical terminology.
The best way to use this text is online with solid internet. The PDF version is frustrating as there are no activities or practice opportunities, and there are issues with the organization and appearance such as misaligned tables and font size differences. When internet is good but not great, none of the videos are viewable. The activities and practice opportunities in the online book are very helpful and enjoyable. Their length is appropriate to encourage use and they are strategically placed throughout the chapters. I did have trouble with the search tool, as things I entered went to the glossary but always included the beginning of the glossary. For example, a search for "diplopia" showed the following:
Abdominal Pertaining to the abdomen (National Cancer Institute, n.d.) Abdominoplasty Surgical repair of the abdomen (National Library of Medicine, 2021) Abduction Moving the limb or hand laterally away from the body, or spreading the fingers or toes (Betts et al., 2013) Abductor Moves the bone away from the midline (Betts et al., 2013) Ablation The Read more » Sensory Systems
Learning Objectives Examine the anatomy of the sensory systems Determine the main functions of the sensory systems Differentiate the medical terms of the sensory systems and common abbreviations Discover the medical specialties associated with the sensory systems Recognize common diseases, disorders, and procedures related to the sensory systems Sensory Systems Word Parts Click on prefixes, Read more »
Overall, the authors did a wonderful job of developing a thorough and practical text. I appreciate the thought that went into the interactive nature of the book and the availability to exercises to practice knowledge.
Reviewed by Debra Minzola, Associate Professor, Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania on 3/18/22
This textbook is very inclusive in the content area. It not only discusses the word but breaks down medical terminology to help learners to easily decipher the meaning of a medical term . read more
This textbook is very inclusive in the content area. It not only discusses the word but breaks down medical terminology to help learners to easily decipher the meaning of a medical term .
There was no inaccuracies detected throughout the text.
This text is very relevant and will easily be updated if needed.
This is an easy to read text and would be a valuable resource for new learners. The ebook offers videos and learning activities throughout.
The text is internally consistent with an easy to follow framework.
The modules in this text are easy to navigate and locate specialty sections.
This text is clearly organized and easy to navigate.
There is no significant navigation problems or confusing features.
There is clear grammar throughout the text.
There is no offensive content in this textbook or language that can be viewed as culturally insensitive.
Learning objectives are listed at the introduction of each section followed by a guide on how to break down each system's medical terms. Throughout each section there are diagrams, charts, and additional videos in the ebook which reinforces the content. The book is organized and easy to navigate.
Table of Contents
- 1. Word Parts and Rules
- 2. Prefixes and Suffixes
- 3. Body Terminology
- 4. Sensory Systems
- 5. Integumentary System
- 6. Skeletal System
- 7. Muscular System
- 8. Nervous System
- 9. Cardiovascular System
- 10. Blood Vessels and Blood
- 11. Lymphatic and Immune Systems
- 12. Respiratory System
- 13. Digestive System
- 14. Endocrine System
- 15. Urinary System
- 16. Male Reproductive System
- 17. Female Reproductive System
- 18. Obstetrics
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions is an Open Educational Resource (OER) that focuses on breaking down, pronouncing, and learning the meaning of medical terms within the context of anatomy and physiology. This resource is targeted for Healthcare Administration, Health Sciences, and Pre-Professional students.
About the Contributors
Andrea M. Nelson , PT, DPT, GCS, CLT, University of West Florida
Katherine Greene , MPH, University of West Florida
Contribute to this Page

- Tips & Tricks
- PowerPoint Templates
- Training Programs
- Free E-Courses
Ultimate Guide to Medical Presentations: Templates, Tutorials, Tips and Resources
About medical presentations.
Medical presentations are fundamentally different from other presentation types. In fact, they are one of the toughest type of presentations to design.
Medical slides have research facts, data charts, diagrams and illustrations that demand a totally different approach to design. You need a slide creation method that considers the unique problems you face as a medical presenter. In this guide, you will Tips, Tutorials and resources to get your started with making over your Medical slides.
We will start with some general tips and tricks on creating medical slides and then proceed to step by step tutorials.

Quick Navigation
Tips to create Medical Presentations
PowerPoint Tutorials for Medical Slides
How to Present Lists & Text
How To Showcase Pictures Creatively
How to use animations effectively, creative morph transition ideas, making medical slides easy to understand, powerpoint delivery tips, powerpoint tips & tricks, issue with typical medical slides, medical slides makeover examples, medical powerpoint templates, free medical & healthcare icons, free medical presentation images, more resources for medical presentations, tips to create medical presentations, how to avoid overwhelming audience in technical presentations.
Do you want to improve how you explain concepts in a technical presentation? In this article, you will find a powerful technique called ‘Telescopic explanation’ to make your technical presentations much clearer and more memorable for your audience. To know more, read this post over on PrezoTraining.com

Tips to present Scientific Information
There are two major facets to a presentation: the content and how you present it. Let’s face it, no matter how great the content, no one will get it if they stop paying attention.
Here are some pointers on how to create clear, concise content for scientific presentations – and how to deliver your message in a dynamic way. Find the tips over on Elsevier connect .
Preparing a Research Presentation
If you have never presented a paper at a scientific meeting, or would like to polish your research presentations, this post contains information that will improve your presentation.
This article contains a set of guides and checklists to help you in the preparation of your presentation. Read this post on ACP .
10 Tips for Medical Presentations
Whether you are presenting an audit or a case report at a local meeting, presenting a paper at a conference, presenting a business case to your Trust, or even presenting on a hot topic at your medical interview, you will need to know how to prepare medical slides which attract your audience rather than distract it. This post on ISC Medical provides 10 tips for Medical presentations.
For a 5-Part series on how to make your Medical Slides Clear and Visual , sign up for our Free E-course.
In the following sections, you'll find step by step PowerPoint tutorials & Makeover Ideas to help you makeover different parts of your presentation.
How To Present Lists and Text
Information presentations use a lot of text and bullet list. In this section, you will find some creative ways to design these type of slides.
PowerPoint Tip: How to Present Long Lists on One Slide
If you have a Long Lists of items on One Slide here is a one-click trick on how to do this. Watch the video below to know more.
PowerPoint Trick to Convert Text to Graphics
Find a useful PowerPoint SmartArt Trick to convert Bullet Point Text to Graphics quickly and easily. Learn how to take the graphics to the next level with some creative ideas from Ramgopal.
For a 5-Part series on how to make your Medical Slides Clear and Visual , sign up for our Free e-course.
Get access to exclusive members-only e-courses & downloads.
Medical presentations usually have a lot of pictures. Especially the training and informational slides. Here are some ways in which you can present the pictures in your presentations in a creative way.
Right Way to Showcase Pictures
Learn the benefit of showcasing pictures using SmartArt tool in PowerPoint. In the video below we start with a typical picture Showcase slide used by presenters. Though the slide looks quite attractive in the first glance, there are some issues that makes the slide ineffective. Watch the video below to know more:
Cropping Pictures in PowerPoint
Learn a super easy trick to crop a picture in PowerPoint in a step by step way. This trick will help you crop a picture in the shape you want, in a single click.
A PowerPoint slide with too much content can be overwhelming for the audience. If you learn to sequence the way you present your information, you make it easy for your audience to understand your presentation.
Here are different ways you can use Custom Animations and Morph Transition effects to sequence information.
Animation for Process with Pictures
In this tutorial, you will find how to create a useful and practical slide with pictures and text to show a process or a timeline diagram. Learn how to create and present it to make an impact.
Animation for Highlighting Pictures
Learn to create an Animated Picture Reveal Effect in PowerPoint. Present your important picture with this effect. Watch the video to preview the effect and learn how to create it:
Sequential Fading technique in PowerPoint
This trick is super useful for medical presentations where you need to present an image step by step. Since it is an image you cannot break it up and present it in parts. However with this useful technique you can highlight one part of an image at a time with animation.

For a 5-Part series on how to make your Medical Slides Clear and Visual , sign up for our Free e-course. Get access to exclusive members-only e-courses & downloads.
In PowerPoint for Office 365, Microsoft introduced the Morph Transition. It is an effective way to create animations fast. Here are some ideas on how you can use this feature to create your slides.
Pros & Cons with Morph Transition
Learn how to create an easy animated scales diagram with Morph Transition Effect. This effect is available in PowerPoint for Office 365. You can also sign up & download the original PowerPoint file over at our website .
Morph Transition To Present Pictures
In this video you will find how to use PowerPoint Morph Transition to replace Custom Animations. See how this can be done with this example of a slide with multiple pictures with text.
Convert your boring text-based slides, blog articles or research papers into clear & beautiful visual slides - even if you have zero Design skills, zero PowerPoint skills & very little time - using our ‘4-step Neuro Slide Design System for Medical Presentations’
Watch the video below to learn more:
Ideas to Present Data
Medical presentations also usually contain a component of data. This could be related to statistics or research. In this section, you will find some easy ways to makeover your slides with numbers.
Creating Pie & Donut Charts
Learn how to create a Pie chart in PowerPoint with this step by step tutorial. This video also covers how to adjust the Pie chart settings and also how to add Donut charts.
How to Animate a PowerPoint Table
Learn a trick to Animate a PowerPoint Table. PowerPoint does not have the feature of animating parts of a table.
[Advanced] Conditional Formatting for Charts
Learn to create a PowerPoint conditional formatting chart that changes color and direction of bar chart automatically for negative values. The positive values are displayed in green color and the negative values in red color.
Here are some tips for when you are actually delivering your presentation. Present confidently with these ideas!
Use Presenter View in PowerPoint like a PRO
How to use Presenter View in PowerPoint to present your slides like a PRO (Presentation Delivery Tips). This view is for the presenter only - when the slideshow This requires 2 monitors (your laptop and the projector screen). Even if you want to use Presenter View in 1 monitor it is possible. Learn how with this video.
Use Hidden Slides to Present Confidently
In this video, you will find a PowerPoint Tip on how to use Hidden slides to present confidently. This feature is especially useful when creating business presentations.
PowerPoint Slideshow Shortcuts
Here are some useful PowerPoint Slideshow Shortcuts you can use when delivering your next presentation. Hope you find these PowerPoint tips useful.
If you wish to improve the quality of your medical slides in a reliable way, take a look at the first video over on this page .
Here are some tips and tricks to reduce time taken to create your slides.
Setting Up Quick Access Toolbar
In this PowerPoint tips tutorial, you will find how to set up the Quick Access Toolbar. It is a great time-saving tool for any version of PowerPoint.
Autocorrect Trick to Save Time
Learn this trick to use PowerPoint Auto-correct option to save time and effort in creating your presentations. Write complex medical terminology accurately & easily in PowerPoint!
Get access to exclusive members-only e-courses & offers.
Many of the medical slides you may see may look like this:

These slides are taken from various sources online like Slideshare and YouTube and represent various types of presentations. The common issues with such slides include:
- Issue with readability - due to poor color choices and font sizes
- Unprofessional design - with overlapping content, hard to read diagrams etc.
- Too much content - that overwhelms the audience
It is quite common to see well researched medical content being totally ignored by the audience - because the presentation slides look busy and boring. And… You can’t blame your audience for tuning out of your presentation.
The quality of your slides makes or breaks your medical presentations.
In this section, we'll makeover usual text filled PowerPoint slides into a visual and interesting slides.
The original slides are taken from various sources online like Slideshare and YouTube and represent various types of presentations.
Medical Title Slide
Original title slide:

Title slide after makeover:

Medical Training Presentation Slide
Original training slide:

Training slide after makeover:

Medical Slide With Quote
Original slide with quote:

Quote slide after makeover:

Health and Safety Training Slide

Slide after makeover:

In the Medical Presentations Bundle with Neuro Slide Design Training, you can watch me make over Text-based slides, a Blog article, a Wikipedia article and a 11-page Research paper. I go through each of the 4 steps to transform these text-based documents to clear and beautiful visual slides.
The Bundle includes 900 Fully Editable PowerPoint Templates. Go over and checkout the bundle .
One of the ways to quickly improve the quality of your slides is to use good quality templates create with the needs of medical presenters in mind. Here are some resources...
Free Medical Title Templates
Leawo website provides free medical title templates for download. These templates are suitable for different type of medical presentations. You can preview and download them here .

FPPT website provides similar free title templates for use as well. You can find title templates related to medical and health fields over here on FPPT .

Premium Medical PowerPoint Templates
While free medical PowerPoint Templates are good enough for student or non-critical presentations, if you are consultant or specialist, you may prefer to use high-quality PowerPoint Templates.
Preview Medical PowerPoint Templates Bundle
Create Medical Slides You Feel Proud to Present Using the Breakthrough Slide Design System created using proven Brain research principles. You can preview templates from our Medical Templates Bundle below:
Browse more templates and know more about the Medical PowerPoint Templates Bundle here .
Icons are useful to represent ideas on slides. Here are some useful links for downloading Healthcare and Medical Icons online.
ICONFINDER : This website has a good collection of vector icons without too many ads or links to other websites.. You can search iconfinder by keyword and specifically look for free to use icons. You can also search by types of icons like glyphs, outline, flat, filled outline, 3D and more.
VECTEEZY : This website provides both free and premium icons. The license may require you to provide attribution to the author. There are lot of popups and ads, and the focus in on their premium icons.
POWERPOINT : If you are using Office 365, you can find a lot of free icons right in PowerPoint. There are icons for people, technology and electronics, communication, business, analytics, commerce, education, signs and symbols, arrows, medical and much more. You can edit the fill colors of these icons to customize them.
Make your own icons in PowerPoint
Make your slides look professional and visual with these icons. Icons make it easy for your audience to remember the information you are presenting. Learn the secret to finding icons for free right within PowerPoint.
300+ Editable Icons for PowerPoint

The Medical Presentations Bundle includes 300+ Medical Icons for PowerPoint. You can break these icons into individual components, mix and match them to create custom icons that meet your specific needs. As one of the doctors using this Bundle said, it is a “ ONE STOP SHOP” for every busy medical practitioner.
Medical presentations can be made more interesting and engaging by the addition of relevant images. If you are looking for high-quality free images, here are some suggestions:
FREEIMAGES.COM : Images on this website are free for use for personal and commercial purposes. You can find a range of generic medical and healthcare images here.

PICJUMBO.COM : This site provides free and interesting images for backgrounds.

WIKIPEDIA is a great source for free images and illustrations. However, there are a couple of things to keep in mind when you use images from Wikipedia.
1) Please check the copyright terms for each image. You may need to provide attribution as per their terms.
2) Images may be of different formats, sizes, color schemes and quality.
Here is a collection of images from Wikipedia related to Brain:

150+ Medical Illustrations | 170+ Medical Photos | 150+ Silhouettes

In the Medical Presentations Bundle we have already done the hard work of putting together a large collection of high quality Medical, Pharma and Science photos & editable illustrations to use in your presentations.
Remember, these are not the usual photos of smiling Doctors and pretty handshakes. These are practical medical photos you can use in your medical slides to illustrate your ideas. As one of the doctors using this Bundle said, it is a “ONE STOP SHOP” for every busy medical practitioner.
For a 5-Part series on how to make your Medical Slides Clear and Visual , sign up for our Free e-course. Get access to exclusive members-only e-courses & downloads.
PowerPoint Skills for Medical Professionals Learn the 14 essential PowerPoint techniques that every medical professional needs to know to design clear medical slides. This training is part of Medical Presentations Bundle .
Advanced PowerPoint Video Tutorials Enhance your presentations with these ideas. In this section you will find extensive video tutorials for 2D and 3D Diagrams, Models, Picture Effects, Animations and More… Click here to browse
Enter your text here...
Liked it? Share:
Get 25 Creative PowerPoint Ideas Mini Course & Members-only tips & offers. Sign up for free below:
Medical Dictionary
Search medical terms and abbreviations with the most up-to-date and comprehensive medical dictionary from the reference experts at Merriam-Webster. Master today's medical vocabulary. Become an informed health-care consumer!
Browse the Medical Dictionary
Featured game.

Find the Best Synonym
Test your vocabulary with our 10-question quiz!
Ringo Starr & 'Drum'
Shaquille O'Neal & 'Dominant'
Katy Perry & 'Firework'

How to Use a Dictionary
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

3 types of medical presentations (and how to give them)
Here are some tips for presenting the top three types of medical presentations: lectures, research presentations, and case reports.
Derek Murray
Building presentations

With your long to-do list as a medical professional, giving presentations is probably not a high priority. Yet, medical presentations are inevitable. Are you ready to give them when your job requires it? If so, where do you even start?
We want to make it a little easier for you to present data-heavy medical topics in an easy-to-understand way.
So, let’s dive right in with the top three types of medical presentations.
Key Takeaways:
- Structure your medical presentation into a story to make it memorable.
- Medical presentations can be lectures, research, or case presentations.
- Customize the presentation based on the type and goal.
1. Lectures
Medical lectures educate an audience about a medical topic. They’re one of the most challenging presentations. According to the Learning Pyramid , lectures are the most passive learning techniques, which is also why they have the lowest retention rates.

There are several settings for educational lectures, including:
- Conferences
- University or school lectures
Medical lectures help students or an audience comprehend complex medical information and then turn what they learned into actionable strategies.
For example, you may teach students with little medical knowledge about a new medical concept. But they must understand the topic and be able to recall it for examinations.
Tips for giving medical lectures
How can you turn one of the most challenging presentations into an engaging, memorable lecture? Here are a few tips to ace your educational medical lectures:
- Be interactive : Use Q&As, activities, and open discussions.
- Hand out resources: Give physical booklets students can review after the presentation.
- Use multimedia: Add audio-visual elements like images, video, and audio clips.
- Use simple language: Your audience is learning, so they need simple language and plenty of definitions to understand the topic.
- Make it entertaining: Keep your audience’s attention with a more engaging and entertaining presentation.
UnitedHealth Group incorporated imagery and movement to show rather than tell about mental health in 2022 to boost their engagement on the topic.

2. Research presentations
The most information-heavy medical presentation is the research presentation. Research presentations share findings with experienced medical professionals, usually in conference settings. Some of the audience includes:
- Investigators
- Ph.D. students
- Medical professionals and experienced doctors
Research presentations can also be part of healthcare marketing . You may have to introduce a new process, pharmaceutical, or device to encourage other healthcare professionals to adopt it in their practices.
Tips for giving research presentations
Use these tips to improve your research presentations :
- Speak on a higher level: You’re talking to a knowledgeable audience, so they expect a higher level of research.
- Back all facts with data: Use statistics and research to back all claims.
- Use power poses: Build authority with a confident presentation.
- Grab the audience’s attention: Start your presentation by giving your audience a reason to care, like a problem you want to solve.
- Build up the conclusion: Structure the research in a natural, progressive order that builds up to your conclusion.
- Look at the future: Conclude with how the research findings will impact the future of medicine.
- Visualize data : Simplify findings and data with visuals and charts.
Cardinal Health transformed the complex research for Smart Compression into understandable slides using a mix of graphics and storytelling in their medical presentation.
3. Case reports
Medical professionals must give oral case reports when transferring information between providers or a team. These presentations are very brief and often don’t require visuals.
Sometimes a case is especially unique and offers educational value to others. In that case, presenters should transform their quick oral case reports into a longer presentation that incorporates data and visuals.
Tips for giving case reports
Case reports use a similar structure to oral patient presentations, except with more details about each point. You’ll still want to pack as much information in a short presentation as possible.
- Begin the presentation with a patient overview: Start by introducing the patient, including all relevant demographic details in summarized graphics and lists.
- Present the history of the patient: Describe the patient’s history, why they sought care, and the symptoms they presented in charts and visuals.
- Explore medical information: Dive into the medical details, like treatment and history, using a storytelling structure to connect the information.
- Offer a plan: Outline a treatment plan alongside proof.
Summarize details in charts: You’ll pack a large amount of information in a concise presentation, so use plenty of charts and diagrams to summarize data and simplify outcomes.
Tips for preparing engaging medical presentations
Your medical presentations have highly complex topics rich with data. These topics can easily feel overwhelming or even boring if they don’t have the right structure and appearance.
Here are three medical presentation tips we’ve learned to help you prepare and present high-quality medical presentations that engage AND inform.
Know your audience’s knowledge level
Before building and presenting a medical topic, you must know your audience’s knowledge level. A lecture to a class of first-year college students will sound far different from a presentation to doctors with 10+ years of industry experience.
Build a presentation around your audience’s knowledge, so it’s understandable yet challenging. By taking this extra step, you’ll know what points need more explanation and what topics you can dig deeper into based on your audience’s experience.
Build a structured story
A complex topic becomes easy to understand and follow if you use a storytelling structure . You might ask, “How can a lecture on a new treatment be a story?”
Any time you communicate, it’s a story: You have the challenge to solve, potential solutions to try, and a final winner (like when presenting medical research). You can structure that story in a progressive order or by announcing one primary outcome and providing a list of proofs (like with patient case studies).
Focus on a goal
The goal of medical presentations can be educating, training, or persuading the audience, depending on the type of medical presentation. Knowing your goal guides which data is most relevant to bring your desired outcome.
Communicate at the speed of healthcare with Prezent
Whether you’re preparing a lecture, research presentation, or case report, creating presentation slides is probably far down your priority list. The fast-paced healthcare industry has enough duties vying for attention. So how are you supposed to squeeze in hours to build an engaging presentation?
Prezent has your back. No need to sweat the details as we have already developed leading presentation templates perfect for data-driven presentations. Personalize to your audience’s knowledge and presentation preferences with AI-powered technology. Save time and energy with access to 35,000+ custom-built slide templates designed with key business and pharma storylines in mind.
You’ll have an engaging and clear presentation deck in minutes rather than hours. Take back your time and communicate efficiently with Prezent so you can focus on turning your ideas and insights into action.
Our proof is in our results. Schedule a demo to see the platform in action.
More blog articles

Product launch planning: The roadmap for creating a successful product launch

Why your presentation needs an executive summary

How AI is revolutionizing presentations
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
Medical Presentations: How to Present Effectively on Urgent Topics

In the face of the pandemic that consumed 2020, we saw an uptick in medical presentations. And rightfully so. The world was in a state of panic over the unknown of a new virus, people were craving information, and organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were scrambling to provide data and resources to help address questions and concerns. Whether it was news stories, or medical research, the world needed to understand what we were up against with COVID-19. Naturally, presentations helped to deliver that information. But this isn’t the first time a virus or disease has rattled communities, and it’s certainly not the first time professionals have used medical presentations to educate the masses. Medical presentations are a helpful tool for medical professionals, research clinics, and organizations to help inform and educate their communities on a wide variety of urgent topics. This can include patient treatment, clinical trial research and results, training for medical staff, general education, medical research, or important data regarding diseases.
While medical presentations tend to be fundamentally different from normal presentations in that they include critical and sensitive information, there are still design best practices just like any other deck. That said, what works for a sales pitch might not resonate well with a medical presentation.
Keep these five things in mind when you want to present effectively on urgent medical presentation topics.
Consider your audience
You may be presenting to a group of doctors within your organization to get the team up to speed on new practices, sharing treatment plans with a patient, or educating the community on new health threats. How you structure your medical presentation is not a one-size-fits-all situation. How you talk to internal staff, versus how you would deliver information to a scared patient is not the same. When you’re crafting your message, consider your audience, and tailor the narrative to their overarching concerns and needs.
Keep things straightforward
Unless you’re presenting to third year residents, your audience probably won’t be able to digest complicated medical terminology. It’s important to avoid medical jargon, complex definitions, or overcomplicated explanations that will confuse your audience. Instead, break things down in layman's terms and relate the information back to your audience and how it will affect them. Keeping things straightforward, and clear, will help your audience digest and process the information quicker. The end goal is that your audience leaves with clarity, feeling more educated on the topic and its urgency.
Use icons to reflect the urgency of the situation
The use of visual aids, such as compelling images or meaningful icons, can help paint the picture of urgency in any presentation. Things like clocks, alarms, lightning bolts, or exclamation points can depict emergencies and symbolize something significant in your presentation. The use of impactful visuals will help engage your audience and let them know what they absolutely need to pay attention to. It helps you control the narrative, and highlight any pertinent information or key takeaways.
Beautiful.ai’s free library of hundreds of thousands of images and icons can help take your presentation to the next level. Our custom icons were thoughtfully created by one of our in-house designers, and are a great way to compliment your data and add urgency to your slide .
Hit them with the facts
In most medical presentations, factual data carries the slides. Whether it’s a survey, research results, or statistics about a particular disease, numerical data will help people understand the urgency or severity of the topic. For example, it was common for nearly every COVID-19 presentation or article to include statistics of the percentage of the population infected, which regions were seeing the greatest spikes in cases, death tolls by county, and data relevant to high-risk individuals. While the numbers may not always be fun— especially as they pertain to a pandemic— they paint a clear picture of what the audience needs to understand. Seeing scary statistics can put into perspective just how real the situation is.
Using the proper charts, graphs , or infographics allows you to dictate exactly what information the audience is consuming. Data visualization with infographics can also help the audience understand and retain otherwise complicated data. However, even with the best charts, you can still overwhelm the audience with information. Opt to include only the most relevant info and useful data.
Allow time to process
Regardless of what you’re presenting— big or small— you should leave time at the end for questions. Medical presentations can be paralyzing, and your audience will likely be seeking more answers. Give your audience a minute or two following the presentation to process what they learned, and then give them a chance to ask questions. You may need to elaborate on specific slides, or revisit a piece of data, to help provide clarification. When it comes to urgent topics, you want your audience to leave feeling more knowledgeable and at ease than they were prior to tuning in.

Jordan Turner
Jordan is a Bay Area writer, social media manager, and content strategist.
Recommended Articles
Customer success presentations: how to create decks that will wow your customers and drive upsell and retention, 5 design lessons from the virgil abloh aesthetic, being the voice of the customer: 10 kinds of product marketing presentations and best practices, what are some creative presentation ideas.
Presentation Skills Toolkit for Medical Students
New section.
The ability to design and deliver an effective presentation is an important skill for all learners to develop. The Undergraduate Medical Education Section of the Group on Educational Affairs developed this toolkit as a resource for medical students and health professions trainees as you learn to create and give effective presentations in the classroom, in the clinical setting, and at academic meetings and conferences. In this toolkit, you’ll find helpful resources on developing and delivering formal lectures and presentations, poster and oral abstract presentations, patient presentations, and leading small group sessions.
Please note: Availability of resources may change over time. To suggest edits or updates, email [email protected] .
On this page:
Formal lectures and presentations, posters and abstracts, patient presentations.
- Leading Small Groups
Traditional academic presentations in medicine and the biomedical sciences are necessarily dense with complex content. Thus, slides tend to be wordy, and presenters may use their slides as cue cards for themselves rather than as tools to facilitate learning for their audience. With the necessary resources, medical students (and presenters at all levels) can better identify appropriate learning objectives and develop presentations that help learners meet those objectives. Organization of content, clarity of slide design, and professional delivery are all essential components to designing and giving effective formal presentations.
Achieving all of these elements can make creating and delivering a formal presentation challenging. The strategies and resources below can help you develop a successful formal presentation.

View long description of infographic .
Strategies for success
- Define the objectives of the presentation. Always define learning objectives for each of your lectures to make it clear what knowledge or skills the audience should acquire from your presentation. The best learning objectives define specific, measurable, or observable knowledge or skill gains. Furthermore, consider how to communicate the importance of the topic to your audience and how information should be arranged to best communicate your key points.
- Design an effective slide set. You should begin creating your slides only after defining your objectives and key points. The slides should support your talk but not be your talk. Keep slides simple. The audience should be able to review a slide and grasp key points quickly. Avoid lengthy text and distracting decorative fonts, clip art, graphs, and pictures. If additional wording or images are necessary, consider handouts or alternative methods of sharing this information. Lastly, design your slide deck to emphasize the key points, revisiting your outline as necessary, and summarize concepts at regular intervals throughout your presentation to strengthen knowledge gains.
- Practice your performance. Effective public speaking starts with preparation and practice. Ensure there is enough time to create your lecture and a supporting slide deck. Know your lecture material and slides without prompts! Understand the audience and learning climate (the size and knowledge level of your audience) and be prepared for the venue (virtual, in-person, or both, lecture hall or classroom). Think about what effective audience engagement may look like and how to incorporate audience response systems, polling, etc., into the lecture.
- Create a positive learning environment. Anticipate questions and allocate sufficient time to answer them. Always repeat the questions being asked for the audience’s benefit and to ensure your understanding. Some questions may be challenging, so be prepared and answer honestly. It is acceptable not to know an answer.
- Demonstrate professionalism in presenting. Exhibit professionalism by being punctual and having appropriate time management. Remember that mistakes happen; be kind to yourself and remain calm and collected. Be enthusiastic: If you can enjoy the experience, so will your audience. Finally, be open to feedback following your presentation.
Additional resources
Below is a collection of resources that further address the elements of creating and delivering a formal presentation. Each resource addresses a specific presentation skill or set of skills listed above and can be used to develop your understanding further.
- Healthy Presentations: How to Craft Exceptional Lectures in Medicine, the Health Professions, and the Biomedical Sciences (requires purchase, book). This illustrated book is a practical guide for improving scientific presentations. It includes specific, practical guidance on crafting a talk, tips on incorporating interactive elements to facilitate active learning, and before-and-after examples of improved slide design. (Skills addressed: 1-3)
- American College of Physicians: Giving the Podium Presentation (freely available, website). This guide includes recommendations related to presentation delivery, including tips on what to wear, how to prepare, answering questions, and anticipating the unexpected. (Skills addressed: 3-5)
- The 4 Ps of Giving a Good Presentation (freely available, PDF). This simple guide on public speaking from the University of Hull covers such topics as positive thinking, preparing, practice, and performing. (Skills addressed: 3-5)
- Zoom Guides (freely available, website). This website from the University of California, San Francisco is one of many great resources created by universities for presenting on a virtual platform, specifically Zoom. (Skills addressed: 3-5)
- Writing Learning Objectives (freely available, PDF). This excellent resource from the AAMC defines Bloom’s Taxonomy and provides verbiage for creating learning objectives. (Skill addressed: 1)
- Adult learning theories: Implications for learning and teaching in medical education: AMEE Guide No. 83 (freely available, article). This AMEE Guide explains and explores the more commonly used adult learning theories and how they can be used to enhance learning. It presents a model that combines many of the theories into a flow diagram that can be followed by those planning a presentation. (Skill addressed: 1)
- Assertion-Evidence Approach (freely available, website). This approach to slide design incorporates clear messaging and the strategic combination of text and images. (Skill addressed: 2)
- Multimedia Learning (requires purchase, book). This book outlines the learning theories that should guide all good slide design. It is an accessible resource that will help presenters of all levels create slide decks that best facilitate learning. (Skill addressed: 2)
- Collaborative Learning and Integrated Mentoring in the Biosciences (CLIMB) (freely available, website). This website from Northwestern University shares slide design tips for scientific presentations. Specific tips include simplifying messages and annotating images and tables to facilitate learning. (Skill addressed: 2)
- Clear and to the Point (freely available, online book). This book describes 8 psychological principles for constructing compelling PowerPoint presentations. (Skill addressed: 2)
Return to top ↑
Presenting the results of the research projects, innovations, and other work you have invested in at regional and national meetings is a tremendous opportunity to advance heath care, gain exposure to thought leaders in your field, and put your evidence-based medicine and communication skills into practice in a different arena. Effective scientific presentations at meetings also provide a chance for you to interact with an engaged audience, receive valuable feedback, be exposed to others’ projects, and expand your professional network. Preparation and practice are integral to getting the most out of these experiences.
The strategies and resources below will help you successfully present both posters and abstracts at scientific meetings.
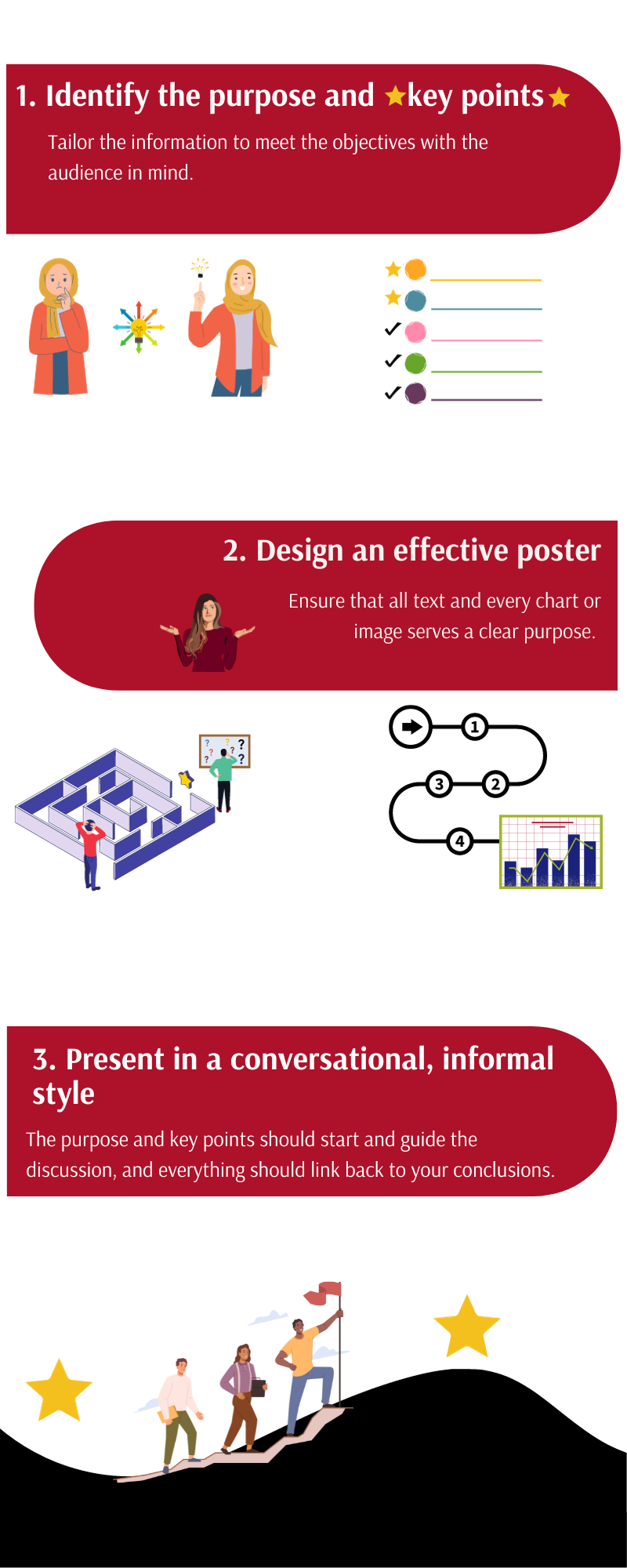
Strategies for success
- Identify a poster’s/abstract’s purpose and key points . Determine the purpose of sharing your work (feedback vs. sharing a new methodology vs. disseminating a novel finding) and tailor the information in your poster or abstract to meet that objective. Identify one to three key points. Keep in mind the knowledge and expertise of the intended audience; the amount of detail that you need to provide at a general vs. specialized meeting may vary.
- Design an effective poster . Design your poster to follow a logical flow and keep it uncluttered. The methods and data should support your conclusions without extraneous information; every chart or image should serve a purpose. Explicitly outline the key takeaways at the beginning or end.
- Present in a conversational, informal style . Imagine you are explaining your project to a colleague. The purpose of your work and key points should guide your presentation, and your explanation of the methods and data should link to your conclusions. Be prepared to discuss the limitations of your project, outline directions for future research, and receive feedback from your audience. Treat feedback as an opportunity to improve your project prior to producing a manuscript.
Additional resources
These resources support the development of the skills mentioned above, guiding you through the steps of developing a poster that frames your research in a clear and concise manner. The videos provide examples that can serve as models of effective poster and abstract presentations.
- How to design an outstanding poster (freely available, article). This article outlines key items for laying out an effective poster, structuring it with the audience in mind, practicing your presentation, and maximizing your work’s impact at meetings. (Skills addressed: 1-3)
- Giving an Effective Poster Presentation (freely available, video). This video shows medical students in action presenting their work and shares strategies for presenting your poster in a conversational style, preparing for questions, and engaging viewers. (Skills addressed: 2,3)
- Better Scientific Poster (freely available, toolkit). This toolkit includes strategies and templates for creating an effective and visually interesting scientific poster. Virtual and social media templates are also available. (Skill addressed: 2)
As with all presentations, it can be very helpful to practice with colleagues and/or mentors before the meeting. This will allow you to get feedback on your project, style, and poster design prior to sharing it with others outside of your institution. It can also help you prepare for the questions you may get from the audience.
Patient presentation skills are valuable for medical students in the classroom and in the care of patients during clinical rotations. Patient presentations are an integral part of medical training because they combine communication skills with knowledge of disease manifestations and therapeutic strategies in a clinical scenario. They are used during active learning in both the preclinical and clinical phases of education and as students advance in training and interact with diverse patients.
Below are strategies for delivering effective patient presentations.

- Structure the presentation appropriately . The structure of your narrative is important; a concise, logical presentation of the relevant information will create the most impact. In the clinical setting, preferences for presentation length and style can vary between specialties and attendings, so understanding expectations is vital.
- Synthesize information from the patient encounter . Synthesis of information is integral for effective and accurate delivery that highlights relevant points. Being able to select pertinent information and present it in an efficient manner takes organization and practice, but it is a skill that can be learned.
- Deliver an accurate, engaging, and fluent oral presentation . In delivering a patient presentation, time is of the essence. The overall format for the presentation is like a written note but usually more concise. Succinctly convey the most essential patient information in a way that tells the patient’s story. Engage your listeners by delivering your presentation in an organized, clear, and professional manner with good eye contact. Presentations will go more smoothly with careful crafting and practice.
- Adjust presentations to meet team, patient, and setting needs . Adaptability is often required in the clinical setting depending on attending preferences, patient needs, and location, making it imperative that you are mindful of your audience.
The resources below provide samples of different types of patient presentations and practical guides for structuring and delivering them. They include tips and tricks for framing a case discussion to deliver a compelling story. Resources that help with adjusting patient presentations based on the setting, such as bedside and outpatient presentations, are also included.
- A Guide to Case Presentations (freely available, document). This practical guide from the Ohio State University discusses basic principles of presentations, differences between written and oral communication of patient information, organization, and common pitfalls to avoid. (Skills addressed: 1-3)
- Verbal Case Presentations: A Practical Guide for Medical Students (freely available, PDFs). This resource from the Augusta University/University of Georgia Medical Partnership provides a practical guide to crafting effective case presentations with an explanation of the goals of each section and additional tips for framing the oral discussion. It also provides a full sample initial history and physical examination presentation. (Skills addressed: 1-4)
- Patient Presentations in Emergency Medicine (freely available, video). This training video for medical students from the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine demonstrates how to tell a compelling story when presenting a patient’s case. The brief video offers handy dos and don'ts that will help medical students understand how best to communicate in the emergency department efficiently and effectively. These skills can also be applied to patient presentations in other specialties. (Skills addressed: 1-4)
Additional information and support on effectively constructing and delivering a case presentation can be found through various affinity support and mentorship groups, such as the Student National Medical Association (SNMA), Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA), and Building the Next Generation of Academic Physicians (BNGAP).
Leading Small Groups
For physicians, working within and leading small groups is an everyday practice. Undergraduate medical education often includes small group communication as well, in the form of problem-based learning groups, journal clubs, and study groups. Having the skills to form, maintain, and help small groups thrive is an important tool for medical students.
Below are strategies to provide effective small group leadership.

- Outline goals/outcomes . Delineating the goals of a meeting ensures that everyone understands the outcome of the gathering and can help keep conversations on track. Listing goals in the agenda will help all participants understand what is to be accomplished.
- Establish ground rules . Establishing explicit procedural and behavioral expectations serves to solidify the framework in which the conversation will take place. These include items such as attendance and how people are recognized as well as the way group members should treat each other.
- Create an inclusive environment . In addition to setting expectations, group leaders can take steps to help all participants feel that their perspectives are valuable. Setting up the room so that everyone sits around a table can facilitate conversations. Having individuals introduce themselves can let the group understand everyone’s background and expertise. In addition, running discussions in a “round-robin style” (when possible) may help every person have an opportunity to express themselves.
- Keep discussions constructive, positive, and on task . As meetings evolve, it can be easy for conversations to drift. Reminding the group of goals and frequently summarizing the discussion in the context of the planned outcomes can help redirect meetings when needed.
- Manage virtual meetings . Online meetings present their own challenges. Adequate preparation is key, particularly working through technological considerations in advance. Explicitly discussing goals and ground rules is even more important in the virtual environment. Group leaders should be more patient with members’ response times and be especially diligent that all participants have an opportunity to be heard.
The resources listed below outline additional helpful points, expanding on the skills described above and providing additional perspectives on managing small group meetings of different types.
- Communication in the Real World: Small Group Communication (freely available, online module). This chapter includes an overview of managing small groups, including understanding the types and characteristics, group development, and interpersonal dynamics. (Skills addressed: 3,4)
- Conversational Leadership (freely available, online book chapter). This short online resource provides guidance for determining group size and seating to best facilitate participation by all group members. (Skill addressed: 4)
- Tips on Facilitating Effective Group Discussion (freely available, PDF). This resource from Brown University provides tips for effective group facilitation, creating an environment conducive for discussions, keeping conversations positive, and managing common problems. Also included is a valuable list of references for further exploration. (Skills addressed: 1-4)
- Facilitating Effective Discussions: Self-Checklist (freely available, online checklist). This checklist from Brown University provides an easy-to-use, practical framework for preparing for, performing, and reflecting on small group facilitation. (Skills addressed: 1-4)
- Sample Guidelines for Classroom Discussion Agreements (freely available, PDF). These guidelines from Brown University give useful tips for managing classroom discussions, including when disagreements occur among group participants. (Skill addressed: 2)
- Fostering and assessing equitable classroom participation (freely available, online article). This online resource from Brown University includes methods to maximize group members’ participation in discussions and to communicate expectations. Also included is a valuable list of references for further exploration. (Skill addressed: 3)
- Facilitating small group learning in the health professions (freely available, online article). The aim of this paper published in BMC Medical Education is to provide students involved in peer/near peer teaching with an overview of practical approaches and tips to improve learner engagement when facilitating small groups. It includes a discussion of the roles of facilitators, strategies for fostering interactions among the group, and methods for resolving common problems. (Skills addressed: 1-4)
- Facilitating a Virtual Meeting (freely available, PDF). This infographic from the University of Nebraska Medical Center includes key points to consider when facilitating an online meeting, including technical considerations, preparation, and follow-up. (Skill addressed: 5)
- Most universities have a communication department with faculty who specialize in small group communication. You may also find that these individuals are a valuable resource.
This toolkit was created by a working group of the Undergraduate Medical Education (UME) Section of the Group on Educational Affairs (GEA).
Working Group Members
- Geoffrey Talmon, MD, University of Nebraska Medical Center
- Jason Kemnitz, EdD, University of South Dakota Sanford School of Medicine
- Lisa Coplit, MD, Frank H. Netter School of Medicine at Quinnipiac University
- Rikki Ovitsh, MD, SUNY Downstate College of Medicine
- Susan Nofziger, MD, Northeast Ohio Medical University
- Amy Moore, MEd, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
- Melissa Cellini, MD, New York Medical College
- Richard Haspel, MD, Harvard Medical School
- Christine Phillips, MD, Boston University School of Medicine
- Arvind Suresh, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth
- Emily Green, PhD, MA, Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University
- Holly Meyer, PhD, MS, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
- Karina Clemmons, EdD, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
- Shane Puckett, EdD, University of South Florida
- Angela Hairrell, PhD, Burnett School of Medicine at Texas Christian University
- Arkene Levy Johnston, PhD, Kiran C. Patel College of Allopathic Medicine
- Sarah Collins, PhD, UT Southwestern Medical Center
- Patrick Fadden, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine
- Lia Bruner, MD, Augusta University - University of Georgia Medical Partnership
- Jasna Vuk, MD, PhD, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
- Pearl Sutter, University of Connecticut School of Medicine
- Kelly Park, Baylor University Medical Center
Effective Presentations: Optimize the Learning Experience With Evidence-Based Multimedia Principles [Incl. Seminar]
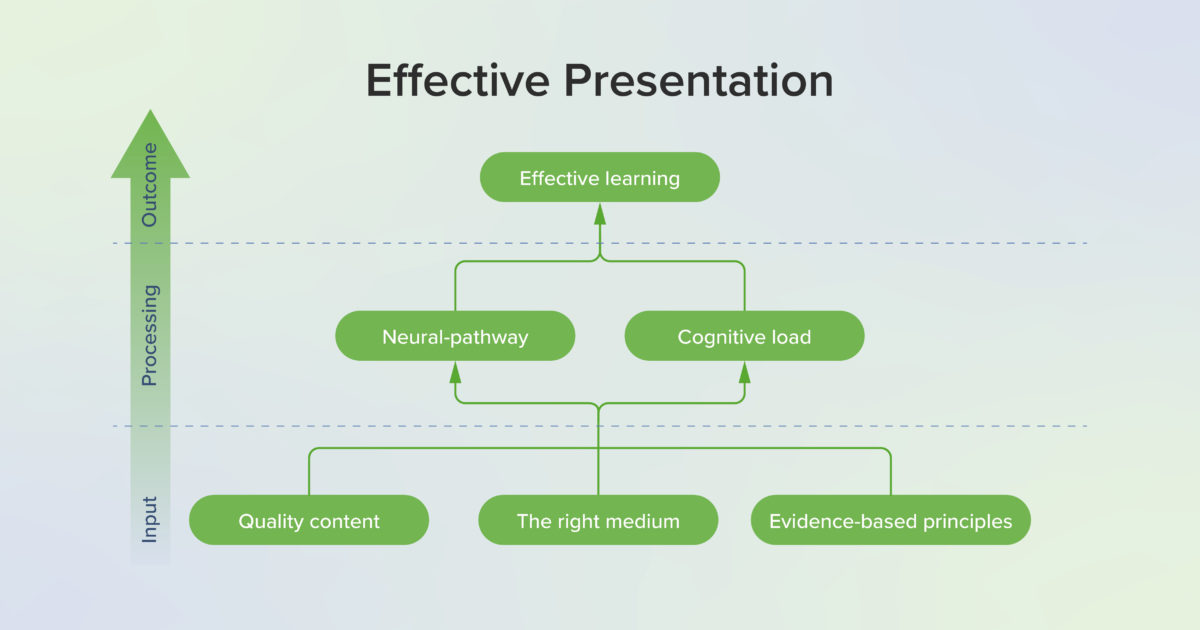
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is an effective presentation.
Professional education requires presentations, from a small discussion or a short video to speaking to a lecture hall with an audience of hundreds. In fact, presentations are at the core of the educational process. With the effort to view all our educational efforts through an evidence-based lens, the construction of an effective presentation needs to undergo the same scrutiny. Whether a presenter intends to share plans, teach educational information, give updates on project progress, or convey the results of research, the extent to which the audience understands and remembers the presentation relies not only on the quality of the content but also the manner in which that content is presented. While the medium of the presentation may range from written content to graphics, videos, live presentations, or any combination of these and more, each of these mediums can be enhanced and made more effective by the use of evidence-based practices for presenting. Regardless of the medium, effective presentations have the same key features: they are appealing, engaging, informative, and concise. Effective presentations gain attention and captivate the audience, but most importantly, they convey information and ideas memorably.
With the integration of technology and online learning, educators have more opportunities than ever to present rich content that enhances and supports student learning. However, these opportunities can be intimidating to educators striving to engage students, as it can be daunting to create visually appealing and informative materials. Additionally, many educators feel pressured by the continued myth of learning styles: the widespread misconception that learning materials should match students’ visual, auditory, or kinesthetic “styles” to optimize learning (1). Despite being featured in many articles and discussions, there is no compelling evidence that matching educational content to learner’s style preferences increases educational outcomes. However, using multiple modes of delivery such as visuals, audio, and active learning has been shown to benefit all learners. In other words, no matter their stated preference, all learners benefit from a variety of media. Using evidence-based principles for multimedia content such as the principles found in Richard Mayer’s multimedia learning as well as the principles of graphic design and universal design supports learning and increases educational outcomes.
Why effective presentations work
What makes a presentation effective? Is an appealing and engaging presentation also an effective one? Research from cognitive science provides a foundation for understanding how verbal and pictorial information are processed by the learner’s mind during a presentation.
Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning
Based in cognitive science research, Mayer’s evidence-based approach to multimedia and cognition has greatly influenced both instructional design and the learning sciences. Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning comprises three learning principles: the dual channel principle, the limited capacity principle, and the active processing principle. Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning lays the theoretical foundation that underlies the practical applications to boost cognitive processes (2).
The dual channel principle proposes that learners process verbal and pictorial information via two separate channels (see figure below). Within each channel, learners can process limited amounts of information simultaneously due to limits in working memory, a phenomenon known as the limited capacity principle . In addition to these principles describing learning via the verbal and pictorial channels, the active processing principle proposes deeper learning occurs when learners are actively engaged in cognitive processing, such as attending to relevant information, creating mental schema to organize the material cognitively, and then relating to prior knowledge (3). These three principles work in tandem to describe the learning process that occurs when an audience of learners experiences a multimedia presentation.
Cognitive Load Theory, Adapted from Mayer (3) . Depicting how verbal and visual information is processed in dual channels through sensory, working, and long-term memory to create meaningful learning.
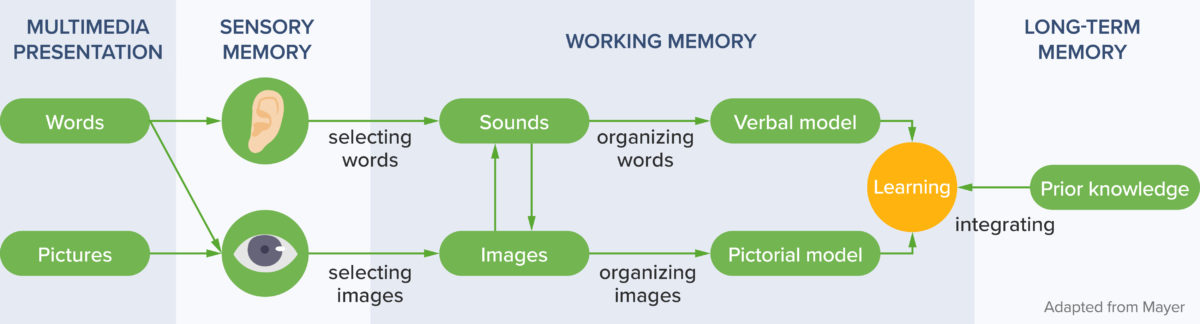
As learners listen to a lecture or watch a video, words and images are detected in the sensory memory and held for a very brief period of time. As the learners attend to relevant information, they are selecting words and images , which allows the selected information to move into the working memory where it may be held for a short period of time. However, working memory is limited to about 30 seconds and can only hold a few bits of information at a time. Organizing the words and images creates a coherent cognitive representation (schema) of these bits of information in the working memory. After the words and images are selected and then organized into schema, integrating these bits of information with prior knowledge from long term memory creates meaningful learning.
Cognitive Capacity . Three types of processing combine to determine cognitive capacity. To improve essential processing and generative processing, extraneous processing should be limited as much as possible .
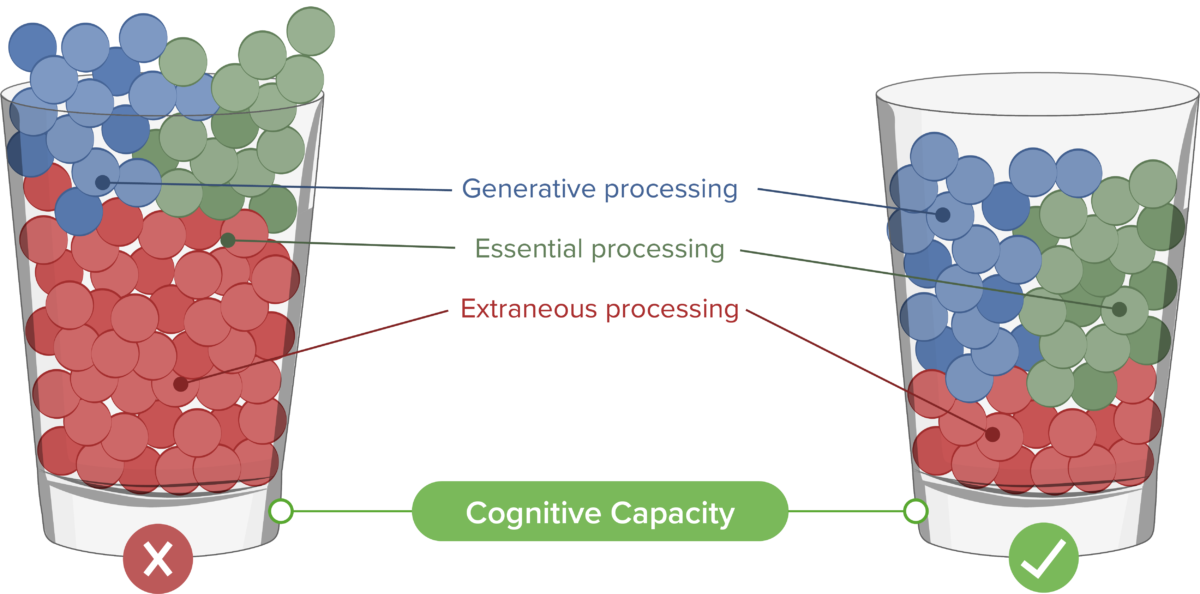
No matter how important the content may be, the capacity of learners to retain ideas from a single presentation is limited. The amount of information a learner can process as they select, organize, and integrate the ideas in a presentation relates to the cognitive load, which includes Essential, Extraneous, and Generative cognitive processing. Essential cognitive processing is required for the learner to create a cognitive representation of necessary and relevant information. This is the desired part of processing but should be managed to not overload the cognitive process. Extraneous processing refers to cognitive processing that does not contribute to learning and is often caused by poor design. Extraneous processing should be eliminated whenever possible to free up cognitive resources. Generative cognitive processing gives meaning to the material and creates deep learning. Learners must be motivated to engage and understand the information for this type of processing to occur.
Foundations in neuroscience
What we know about cognition and learning has been supported and informed by research in neuroscience (4). Neuroscience advances have also allowed us to gain deeper understanding into cognitive science principles, including those on multimedia learning. Researchers have been increasingly tracking learner eye movements to study learners’ attention and interest as a method of validating the impact of multimedia principles, and the results have supported the benefits of proper multimedia design on learner performance (5). Another avenue of research with great potential includes functional MRI (fMRI) readings or electroencephalography (EEG) (6). It has long been established that verbal and pictorial data is processed in different parts of the brain. More recently however, by examining changes in blood flow in different regions of the brain, researchers in Sweden were able to demonstrate that increased extraneous load could impact the effectiveness of learning, in line with the dual channel principle (7).
Evidence for effective presentations
Mayer’s multimedia principles.
Mayer’s Multimedia Principles.
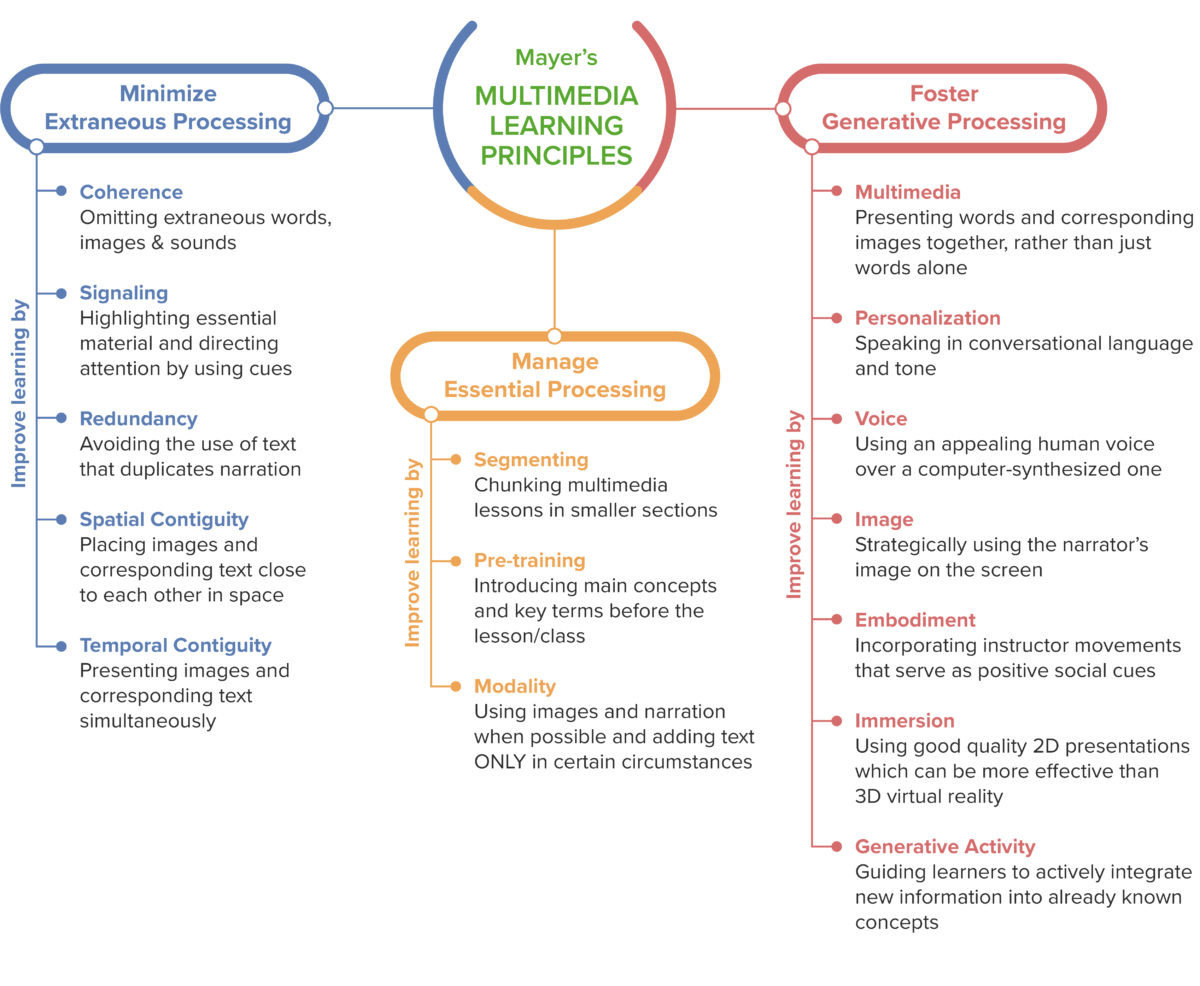
Mayer’s multimedia principles are a set of evidence-based guidelines for producing multimedia based on facilitating essential processing, reducing extraneous processing, and promoting generative processing (8). Mayer’s list of principles often includes fifteen principles, some of which have changed over time, and in a study conducted with medical students, the following nine principles were found to be particularly effective (3). The first three of these principles are used to reduce extraneous processing.
Principles for reducing extraneous processing:
- Coherence principle: eliminate extraneous material
- Signaling principle: highlight essential material
- Spatial contiguity principle: place printed words near corresponding graphics
To illustrate these principles, we will use a lesson about the kidneys. The instructor wants to make diagrams of the anatomy to use during discussion. The coherence principle says to only include the information necessary to the lesson. Graphics such as clip art, information that does not relate to anatomy, or unnecessary music reduces cognitive capacity. The signaling principle says to highlight essential material; this might include putting important content in bold or larger font. Or, if the kidney is shown in situ , the rest of the anatomy may be shown in grayscale or a much lighter color to de-emphasize it. The spatial contiguity principle says to place printed words, such as the labels, near the graphics.
Reduce extraneous processing . Do : keep labels next to diagrams, use only essential material, highlight essential material such as titles. Don’t: separate labels from diagrams, include extra facts, or have excessive text on a slide, especially with no indication of what is most important.
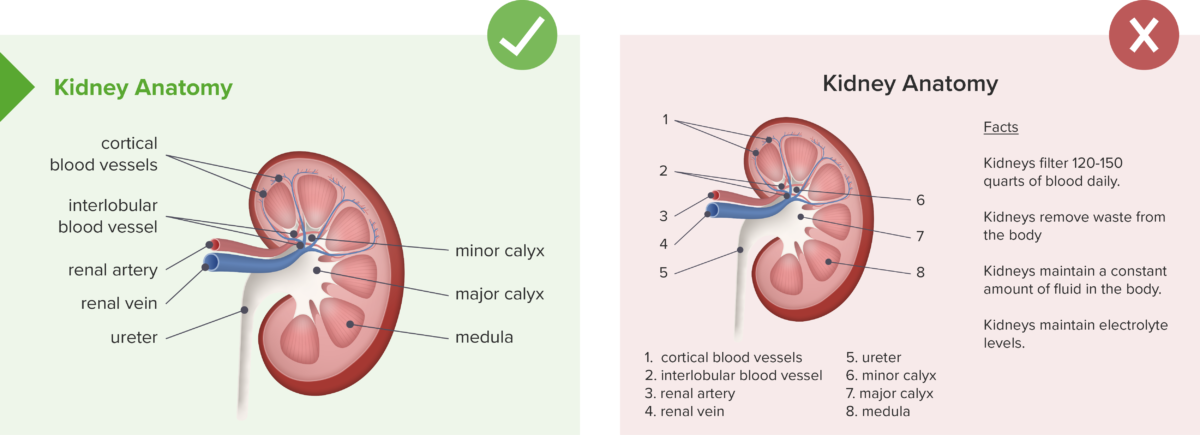
Principles for managing essential processing:
- Pre-training principle: provide pre-training in names and characteristics of key concepts
- Segmenting principle: break lessons into learner-controlled segments
- Modality principle: present words in spoken form
The next three principles are used to manage essential processing. If the kidney lesson moves into diseased states or diagnostics, the pre-training principle says that learners should be given information on any unfamiliar terminology before the lesson begins. To satisfy the segmenting principle , the learner should be able to control each piece of the lesson. For example, a “next” button may allow them to progress from pre-training to anatomy to diseased states and then diagnostics. The modality principle says that words should be spoken when possible. Voice-over can be used and text can be limited to essential material such as key definitions or lists.
Manage essential processing. Do: Present terms and key concepts first, break lessons into user-controlled segments, and present words in spoken form. Don’t: Give long blocks of text for students to read without priming students for key concepts.
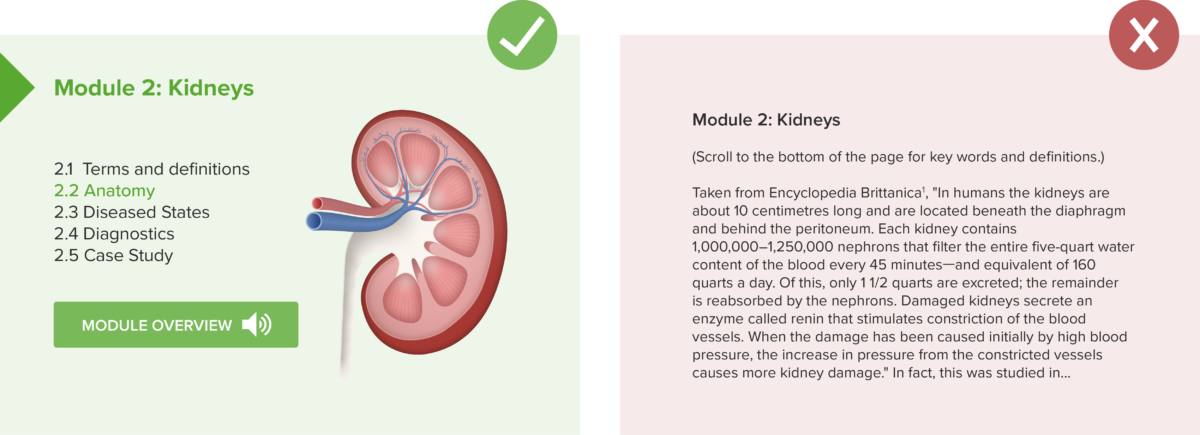
Principles for fostering generative processing:
- Multimedia principle: present words and pictures rather than words alone
- Personalization principle: present words in conversational or polite style
- Voice principle: use a human voice rather than a machine voice
Mayer’s work also includes principles to increase generative processing. The multimedia principle is a direct result of the dual channel principle and limited capacity principle. Words and pictures together stimulate both channels and allow the memory to process more information than words alone. To adhere to the personalization principle to promote deeper learning, a case study is better presented as a story than a page of diagnostics and patient demographics. Finally, the voice principle says that a human voice is more desirable, so it is better to use the instructor’s voice when doing voice-overs rather than auto-generated readers.
Foster generative processing. Do: Present words and pictures, present words in conversational style, and use a human voice. Don’t: Present text only, present words as a list of facts or overly technical language, or use a computer-generated voice.
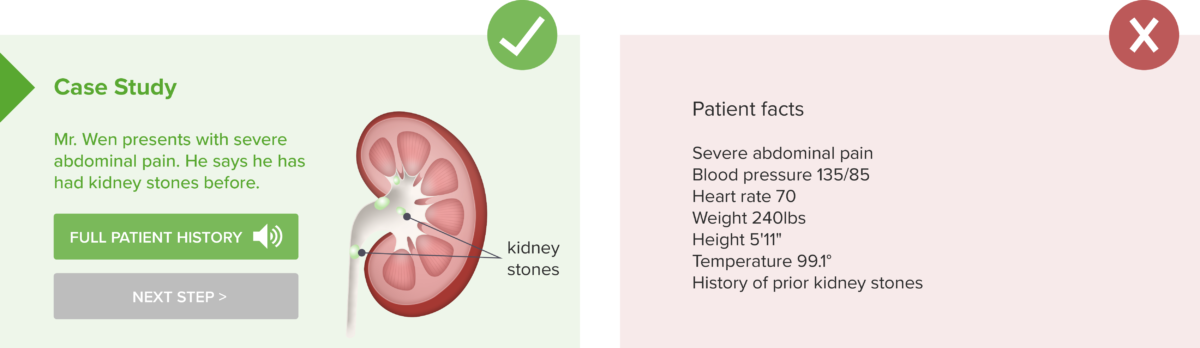
Additional multimedia principles:
- Temporal contiguity principle: present words and pictures simultaneously rather than successively
- Redundancy principle: for a fast paced lesson, people learn better from graphics and narration rather than graphics, narration, and text
- Image principle: people do not learn better if a static image of the instructor is added to the presentation
Additional principles include the temporal contiguity principle , which states that words and pictures should be shown simultaneously rather than successively. This also includes narration and images or animation. For example, if an animation demonstrates normal cell division, the narration should be given during the animation, not after. The redundancy principle states that people do not necessarily learn better if text is added to graphics and narration. The duplication of information creates extraneous processing as learners try to process print and spoken text. The image principle states that learners do not learn better if a static image of the instructor is added to a presentation. For example, if students are watching an animation with normal cell division, they do not learn better if an image of their instructor is placed next to the animation.
Additional principles for fostering generative processing:
- Embodiment principle: onscreen instructors should display high embodiment not low
- Immersion principle: 3D virtual reality is not necessarily better than 2D presentations
- Generative activity principle: use generative learning activities during learning
In the newest edition of Mayer’s Multimedia Learning (8), three additional principles have been added. The embodiment principle states that onscreen instructors should display high embodiment rather than low embodiment, meaning they should use natural gestures, look at the camera as if making eye contact, and if drawing, show the image being drawn. If demonstrating something like a surgical procedure, a first-person perspective should be used so the learner sees the perspective of the person performing. Low embodiment would include standing still, lack of eye contact, and using a third-person perspective. The immersion principle states that 3D immersive virtual reality is not necessarily more effective than 2D presentations, such as on a computer screen. This is thought to be caused by the cognitive load on the learning involved in using 3D immersive technology but more studies are needed. Lastly, the generative activity principle states that learners should use generative learning activities while learning such as summarizing, mapping, drawing, imagining, self-testing, self-explaining, teaching, and enacting. These activities help learners cognitively select and organize new material and then integrate with prior knowledge.
Other Design Principles
Mayer’s design principles are functional but do not address aesthetics per se . Anyone can master the basic graphic design principles as discussed by Reynolds (9) to captivate and engage an audience.
- Create graphics that are designed for the back of the room. Whatever the venue, the person in the back needs to be able to see and gather information from the graphics. Ensure font size is appropriate, image size and clarity is sufficient, and that font type and spacing allow words to be seen clearly from a distance. For online materials, this principle may mean designing for the person who will be viewing on the smallest screen (such as a phone) rather than assuming viewers will use a large monitor (10).
- Limit the types of fonts. Too many fonts or fonts that don’t coordinate well can make graphics seem jarring and unpleasant. Some programs will suggest font families that are appealing, and a safe guideline is to limit to two or three fonts maximum per graphic.
- Use contrasting colors. Colors that are too similar or using type on top of images that lack contrast can make type difficult to read. Color family suggestions can be found online or in software such as Powerpoint.
Graphic design principles. Do: Use coordinating fonts and color schemes with contrasting colors. Don’t: use multiple fonts, excessive colors, and/or non-contrasting colors that may be difficult to distinguish.
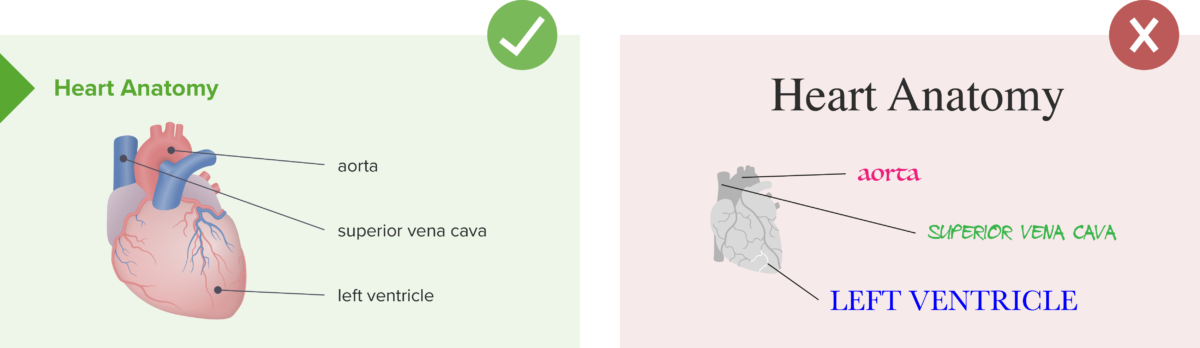
In addition to singular graphics or presentations, online course presentation makes a difference in how learners perceive and utilize a course. When designing online learning experiences, consider using guidelines such as Quality Matters to assess the functionality. Quality Matters rubrics look at key components that have been proven to facilitate learning by making navigation and presentation of course elements explicit. Key components include providing information on how to get started, including learning objectives, allowing learners to track their progress, and using learning activities and technology tools that support active learning. Navigation among course components should facilitate access to materials.
In addition to all of these principles, accessibility must be considered in all forms of presentation. In education, designing for accessibility can be guided by universal design principles . Some schools may even require all courses and materials to be fully accessible. Providing accessible options has been shown to benefit all learners, not just those with a documented need for accommodations (11). Some basic accommodations that should be offered in any class include offering media in multiple modes. For example, videos should have the option of captioning and/or access to a transcript, and photos and graphics should have captions that describe the image. Many learning management systems and software programs now have options to check for accessibility. Additionally, most schools can provide assistance in assessing and developing accessible materials.
Practical Applications for Presentations in Health Professions Education
Implementation in the classroom.
When planning how to present materials in the classroom, first consider the most effective form of presentation for the given information. It may be a Powerpoint, a video, a graphic, or a handout. Consider using a variety of media appropriate for the intended outcomes. Creating high quality materials may seem daunting, but quality content can be reused, shared, and has been shown to enhance student learning.
Powerpoint has been much maligned for overuse and abuse, but well-designed presentations can be remarkably effective (12). When designing in Powerpoint, limit the amount of text per slide. One rule to remember is the 5/5/5 rule: Use no more than 5 lines of text with 5 words each or 5 text-heavy slides in a row and try to avoid bullets (13). Graphics are preferable to text or tables when representing data, but graphs and labels should be kept as simple as possible using 2D graphics and simplified labels that are easy for viewers to see (14). When presenting, refrain from reading from the slides. Slides should highlight important concepts and provide visual aids, not present everything. In addition, keep Powerpoint and video presentations short; most listeners will lose attention in 6–10 minutes (15,16). Whenever possible, engage the audience by interspersing active learning elements. Between sections or topics, transition slides can be used to indicate pauses for activity or reflection or to cue students to changes in topic (14).
When planning a presentation, consider presenting some of the information online before class for students to review. This flipped classroom technique allows for more class to be spent using active learning and facilitates the presentation of multiple forms of media and accessible options.

Implementation online
Videos often become an integral part of the online learning experience. To facilitate learning, consider the following tips for your own video production (17,18):
- Align the video with learning objectives and course outcomes. Focus on pertinent instructional points to reduce extraneous processing and thereby reduce cognitive load.
- Limit the length of videos and use interactive elements to promote active learning. To help maintain student engagement and deepen learning, include interactive elements such as discussions, quizzes or embedded questions to maintain student attention.
- Limit extraneous information, graphics, and sounds that do not pertain to the learning goals (19). Busy backgrounds, music, or animations that don’t contribute to understanding concepts unnecessarily add to a learner’s cognitive load.
- When using existing videos, ensure the source is reliable and the video is high quality. Video production can take time, so using professional videos can be beneficial if they come from credible sources that target the learning objectives with up-to-date and accurate information.
Additionally, Schooley et al. (18) have proposed a 25-item quality checklist that can help educators create and curate high-quality videos. Many of the items in the checklist have been discussed here such as length, captioning, using relevant graphics, and self-assessment opportunities, but also included are other points an educator should consider, such as the offering learners the ability to download files and adjust playback speed as well as providing them with recommendations for further reading.
For a course in any modality, creating and curating content online can save time and facilitate student learning. As you consider what material to create and use for your courses, assess existing material using the guidelines above to determine if it could be made more beneficial to learners. Does it follow Mayer’s principles? Does it follow graphic design principles and universal design principles? Consider using a Quality Matters rubric to check the course design for best practices.
Recommendations
Educator’s perspective.
- Use Mayer’s multimedia design principles to revise existing presentations and review new creations for simple changes that can make a big difference (12).
- When delivering a presentation, start by discussing an unusual case, presenting an interesting story or an unexpected statistic, or explain how the topic impacts the listeners. This personalization will help gain their attention from the start (13).
- When designing your own materials and graphics, “less is more” is often a good guideline: limit the amount of information on slides, limit the types of fonts, and limit the excessive use of colors (9,12).
- Videos should be limited to 5–6 minutes when possible and avoid exceeding 10 minutes. Break up longer videos and intersperse interactive elements to keep students engaged (15–17).
- When using technology and online delivery, universal design and accessibility considerations can be complicated. See if your school has an expert that can review your materials to ensure all students will benefit.
Student perspective
- When creating presentations, reports, and charts, follow Mayer’s multimedia design principles to ensure your audience gets the most from your presentation.
- Avoid copy/pasting but rather try and present concepts in an original way in order to augment your understanding of the material.
- When looking at materials online, look for options such as captioning, transcripts, or audio buttons for accessing additional media output.
- If a presentation is lengthy, pause and insert your own activities to help yourself stay focused. Taking notes, pausing for reflection, and self-quizzing can help deepen your learning and keep your mind from wandering.
- If a variety of media aren’t offered, consider finding your own to supplement your learning. Credible sources with learning objectives that align with your course can augment your learning experience.
(Please select all that apply)
1. When creating a graphic about the current status of heart disease in the US, which of the following would align with best practices?
a. Gaining the audience’s attention with a picture of your dog.
b. Using 3 colors that coordinate well on a contrasting background.
c. A 2D graph with simple labels rather than a table of data.
d. An image on the left with labels listed separately on the right.
e. An image next to a paragraph of text that you will read for the audience.
2. Which of the following are true about educational videos?
a. They need to be created by professionals to be high-quality.
b. They should be less than 10 minutes.
c. There should be an option for closed captioning or a written transcript.
d. Longer videos may be used but should be broken up with active learning elements.
e. Videos don’t need to align to objectives as long as they’re well-made.
3. Which of the following would be examples of Mayer’s multimedia principles?
a. Using a human voice rather than a machine voice.
b. Using formal language instead of conversational language.
c. Playing soothing music in the background of a video.
d. Providing new words and definitions before the presentation begins.
e. Putting important words in bold for emphasis.
4. Which of these would follow best practices for online content?
a. Creating a module where all the material is on one page for easy access.
b. Adding buttons for next, back, and table of contents options for students to navigate.
c. Breaking material into 7-minute videos with practice questions between them.
d. Adding fun clip art and cool images to the pages even if it doesn’t directly relate to the content.
e. Having text only because images are distracting.
Answers: (1) b,c. (2) b,c,d. (3) a,d,e. (4) b,c.
Online Seminar
This online seminar and its accompanying article will focus on the topic of Effective Presentations, which have a set of key qualities: they are appealing, engaging, informative, and concise. Effective presentations gain attention and captivate the audience, but most importantly, they convey information and ideas memorably and efficiently. Using evidence-based principles in educational multimedia can ensure the development of high-quality learning experiences. Our host, Dr. Peter Horneffer will be sharing with us some key multimedia concepts that can help facilitate the development and implementation of effective multimedia into the educational process.
Watch the seminar recording:
Would you like to learn more? Explore the Pulse Seminar Library.
Share this page:

Meredith Ratliff is a doctoral student in Instructional Design and Technology at the University of Central Florida. Her research interests include evidence-based medical education, branching scenarios, and faculty development. She has received her B.S. and M.A.T. in Mathematics at the University of Florida and her MA in Instructional Design and Technology from UCF. She has been an Associate Faculty member in the mathematics department at Valencia College in Kissimmee, Florida for the past nine years. As part of the Learning Science team at Lecturio, she serves as an educational consultant helping to design and develop materials for medical educators.

Satria Nur Sya’ban is a doctor from Indonesia who graduated from Universitas Airlangga. While a student, he served as the president of CIMSA, a national medical student NGO, working on a diverse range of issues that included medical education and curriculum advocacy by medical students. Before graduating, he took two gap years to serve as a Regional Director, and subsequently as Vice-President, of the International Federation of Medical Students’ Associations (IFMSA)*, working on and developing various initiatives to better empower medical student organizations to make a change at the national level. At Lecturio, he serves as a Medical Education Consultant, supporting Lecturio in developing and maintaining partnerships with student organizations and universities in Asia, as well as providing counsel on how Lecturio can fit in existing teaching models and benefit students’ learning experience.
*IFMSA has been one of the leading global health organizations worldwide since 1951, representing over 1.3 million medical students as members spanning over 123 countries.

Adonis is a doctor from Lebanon who graduated from the University of Balamand. He was a research fellow at the Department of Emergency Medicine at the American University of Beirut Medical Center and has worked with the World Health Organization Regional Office of the Eastern Mediterranean. During his studies, Adonis served as the president of the Lebanese Medical Students’ International Committee (LeMSIC), a national medical student organization in Lebanon, and moved on to serve as the Regional Director of the Eastern Mediterranean Region of the IFMSA*. Among his roles as Regional Director, he focused on medical education advocacy, oversaw collaborations with external partners, and undertook several medical education projects and initiatives around the region. As a Medical Education Consultant at Lecturio, he advises the Lecturio team on how the platform can fit in existing teaching models and benefit students’ learning experience, develops and maintains partnerships with student organizations and universities in the MENA region, and conducts research on learning science and evidence-based strategies.

Sarah Haidar is an educator and educational specialist from Lebanon who has graduated with a BA in English Linguistics and a Secondary Teaching Diploma (T.D.) from Haigazian University in Beirut, Lebanon. She has received her M.Ed. in Teaching English as a Second Language (TESOL) from the Lebanese International University. She has been teaching ESL classrooms at the Deutsche Internationale Schule for four years. As part of the administrative team at the All American Institute of Medical Sciences (AAIMS), she is working on the design and implementation of a set of academic and administrative reforms that can help both faculty and students in their professional and academic endeavors. She has joined Lecturio to support the Learning Science team in the writing and communication based tasks that might be needed to announce and market their services and events that are targeted at medical educators. She is also supporting the Learning Science team with her perspective on educational and pedagogical topics that will inform the general audience of educators.

Sara Keeth is a Ph.D. and certified PMP (Project Management Professional) who graduated from the University of Texas at Dallas. As an educator, she has worked as a Teaching Fellow at the University of Texas at Dallas, as a full-time professor at Richland College (now Dallas College’s Richland Campus), and has also taught at Austin College. Dr. Keeth has also worked as a consultant for Parker University’s Research Center and has a decade of experience as an operations manager for an advertising agency. As Senior Learning Science and Research Project Manager at Lecturio, she manages the Learning Science department’s activities, shares her education expertise and best practices for medical educators, and develops evidence-based content for both students and faculty.
- Newton PM. The Learning Styles Myth is Thriving in Higher Education. Front Psychol [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2022 Jun 3];6. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01908
- Mayer R, Mayer RE. The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning. Cambridge University Press; 2005. 688 p.
- Mayer RE. Applying the science of learning to medical education. Med Educ [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2022 Mar 23];44(6):543–9. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03624.x
- Ng B, Ong AKK. Neuroscience and digital learning environment in universities: What do current research tell us? J Scholarsh Teach Learn [Internet]. 2018 Oct 2 [cited 2022 Jun 4];18(3). Available from: https://scholarworks.iu.edu/journals/index.php/josotl/article/view/22651
- Alemdag E, Cagiltay K. A systematic review of eye tracking research on multimedia learning. Comput Educ [Internet]. 2018 Oct 1 [cited 2022 Jun 9];125:413–28. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360131518301660
- Dan A, Reiner M. Real Time EEG Based Measurements of Cognitive Load Indicated Mental States During Learning. 2017;9(2):14.
- Sörqvist P, Dahlström Ö, Karlsson T, Rönnberg J. Concentration: The Neural Underpinnings of How Cognitive Load Shields Against Distraction. Front Hum Neurosci [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2022 Jun 9];10. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00221
- Mayer RE. Multimedia Learning. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2021. 450 p.
- Reynolds G. Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery. New Riders; 2011. 462 p.
- Elias T. Universal instructional design principles for mobile learning. Int Rev Res Open Distrib Learn [Internet]. 2011 Feb 28 [cited 2022 Jun 15];12(2):143. Available from: http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/965
- Shimoni R, Barrington G, Wilde R, Henwood S. Addressing the needs of diverse distributed students. Int Rev Res Open Distrib Learn [Internet]. 2013 Jul 5 [cited 2022 Jun 10];14(3):134–57. Available from: https://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/1413
- Grech V. The application of the Mayer multimedia learning theory to medical PowerPoint slide show presentations. J Vis Commun Med [Internet]. 2018 Jan 2 [cited 2022 Jun 10];41(1):36–41. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/17453054.2017.1408400
- Vogel WH, Viale PH. Presenting With Confidence. J Adv Pract Oncol [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2022 Jun 10];9(5):545–8. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6505544/
- Lenz PH, McCallister JW, Luks AM, Le TT, Fessler HE. Practical Strategies for Effective Lectures. Ann Am Thorac Soc [Internet]. 2015 Apr [cited 2022 Jun 6];12(4):561–6. Available from: http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201501-024AR
- Guo P, Kim J, Rubin R. How video production affects student engagement: An empirical study of MOOC videos. 2014. 41 p.
- Carmichael M, Reid AK, Karpicke JD. Assessing the Impact of Educational Video on Student Engagement, Critical Thinking and Learning: :24. Available from: https://us.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/hevideolearning.pdf
- Dong C, Goh PS. Twelve tips for the effective use of videos in medical education. Med Teach [Internet]. 2015 Feb 1 [cited 2022 Jun 6];37(2):140–5. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2014.943709
- Schooley SP, Tackett S, Peraza LR, Shehadeh LA. Development and piloting of an instructional video quality checklist (IVQC). Med Teach [Internet]. 2022 Mar 4 [cited 2022 Jun 10];44(3):287–93. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2021.1985099
- Brame CJ. Effective educational videos [Internet]. Vanderbilt University. [cited 2022 Jun 10]. Available from: https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/effective-educational-videos/
- Data Privacy
- Terms and Conditions
- Legal Information
USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
Next Online Event
Never miss a pulse.
Get our insights direct to your inbox
- Wednesday, 17 April
- 9:00 PT | 12:00 ET | 18:00 CEST
- Wednesday Jan 24 at 09:00am ET
- Thursday Jan 25 at 12:00pm ET
Sign up for emails on new Lecturio Pulse content.
Never miss a pulse. We’ll email you when new content is published.
User Reviews
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

17 templates

american history
85 templates

49 templates

43 templates

el salvador
34 templates

art portfolio
100 templates
Medical Presentation templates
Create medical presentations with a professional design using our google slides and powerpoint backgrounds. talking about a case report or a breakthrough has never been easier., related collections.

4084 templates

858 templates

Breakthrough
620 templates

Medical Center
430 templates

Case Report
633 templates
- Calendar & Weather
- Infographics
- Marketing Plan
- Project Proposal
- Social Media
- Thesis Defense
- Black & White
- Craft & Notebook
- Floral & Plants
- Illustration
- Interactive & Animated
- Professional
- Career & Technical Education
- Emotional Intelligence
- Foreign Language
- High School Electives
- Language Arts
- Physical Education
- Practical Life
- Social Skills
- Social Studies
- Instagram Post
- Instagram Stories

It seems that you like this template!
Create your presentation create personalized presentation content, writing tone, number of slides.

Register for free and start downloading now
Aquatic and physical therapy center.
The way we present our company says a lot about it. This time we bring you a perfect template for aquatic therapy centers. Its background is white, which contrasts with the waves in blue and gray tones, simulating the movement of water. Edit the graphics, show your milestones and explain...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Being Hospitalized
We hope you never require hospitalization. That would mean that you have a healthy life and dodged any kind of injury! But many people require being hospitalized for a multitude of reasons. Their stay might be a reason to be stressed out, but explaining the procedures and information in general...

Basic Health Unit
Download the Basic Health Unit presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic resources....

Cream & Pastel Palette Healthcare Center Characters
Let us introduce you to a new way of presenting healthcare centers. Did you think that we were going to use blue? Tut-tut! This time, the palette revolves around cream (the color of the backgrounds) and other pastel tones. As you explain in detail (or in brief) your healthcare services,...
Hand Drawn Style Healthcare Center
If you need to present a healthcare center, the overall aesthetic you might be looking for is something peaceful and pretty. Something that makes your center look approachable and safe. In that case, we have the perfect template for you! These slides will make your presentation super calm and attractive:...

Breathing Issues
Download the Breathing Issues presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and seeking medical attention....

DNA Chain Backgrounds Medical Theme
Download the DNA Chain Backgrounds Medical Theme presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Healthcare goes beyond curing patients and combating illnesses. Raising awareness about diseases, informing people about prevention methods, discussing some good practices, or even talking about a balanced diet—there are many topics related to medicine that you could...

Clinical Case 06-2023
Slidesgo is back with a new free medical template, perfect for a presentation about a clinical case. The design is very appealing, so these slides are a nice tool to provide a lot of useful information for doctors and researchers.

Alcoholism Treatment Drugs Breakthrough
Drug addictions are a difficult condition to treat, but thanks to the investigations and studies conducted by health professionals, new breakthroughs are appearing to help people who suffer them. Speak about it with this visual design for breakthrough news and share the treatment you have discovered with the medical community!...

Healthcare Center Website
Does your healthcare center have a website? Nowadays it’s a very important part of healthcare, because lots of patients reach their doctors and specialists online, so having a well-designed website is a vital factor for the viability of your hospital. This template looks like an online page full of medical...

Taking Care of Heart Diseases
Download the "Taking Care of Heart Diseases" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and...

Clinical Case 01-2023
Present your clinical case to the medical community with this dynamic and engaging presentation by Slidesgo. Who said science can’t be creative and fun?

Indian Doctor’s Day
July 1st is a very important day in India. This day is dedicated to celebrate the importance of the people that work everyday in order to keep everyone safe and healthy: doctors! But why this date? July 1st is the birthday of India’s most famous physician, Bidhan Chandra Roy. Speak...
Animated Healthcare Center
Just like how at Slidesgo we work with the best professional designers to create great templates, you can use this one to show how your healthcare center has the best doctors to treat patients. The design is simple and elegant, and makes use of animated illustrations from Storyset, one of...

Doodle Style Medical Breakthrough
Communicating medical breakthroughs to a wide audience can be challenging - but the right presentation template makes it easier! With a medical breakthrough revolved presentation template for Google Slides & PowerPoint, showcasing your project to the world just became a breeze. This template uses creative doodles to illustrate complex medical...

Hospital Labs
How many blood tests have you undergone in your life? Probably too many to count. Where do those samples of blood go? To the lab! These labs are equipped with advanced technology and skilled professionals who work tirelessly to analyze samples and provide accurate results, but that's not the only...

Medical Collaboration Research
Download the "Medical Collaboration Research" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Gone are the days of dreary, unproductive meetings. Check out this sophisticated solution that offers you an innovative approach to planning and implementing meetings! Detailed yet simplified, this template ensures everyone is on the same page, contributing to a...

Postoperative Pain Clinical Case
Postoperative pain is a relatively common occurrence for those who have undergone a surgical procedure. While the pain can range from mild discomfort to severe throbbing, it is important to manage it effectively in order to promote a speedy recovery. This template, created for presenting clinical cases, gives you an...
- Page 1 of 177
Register for free and start editing online
27 Free Medical PowerPoint Templates with Modern Professional Design
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
By Al Boicheva
in Freebies
3 years ago
Viewed 89,786 times
Spread the word about this article:

Updated April 2022
PowerPoint is still the top choice for presentations and it seems that it’s not going anywhere any time soon. To keep with what we always do, today we’ve hunted down, selected, and gathered for you a collection of free medical PowerPoint templates. All examples are easy to edit so you can nail your audience’s attention right from the start.
Before we proceed with the thematic collection, you might also be interested in checking out the Best Free PowerPoint templates to download in 2022 . This selection features multipurpose templates for business and technology. Now back to the medical topic.
1. Free Healthcare Infographic Presentation

This multi-purpose template for PowerPoint and Keynote comes with more than 100 slides and dark and light versions. However, there is a free sample version that features 6 high-quality slides available to download and edit.
- Free Version: 6 slides
- 16×9 HD Ratio Display
- All Graphic Resizable and Editable
- Fully Editable (All Icons, Elements & Info-graphics as Vectors)
*Enter $0 for free download.
2. Free Medical Clinics Template

A free template for a medical clinic presentation. It features more than 20 editable slides with a modern business look.
*Free For Personal Use
3. Free Stylish Medical Presentation

Here we have 23 professional slides for PowerPoint, KeyNote and Google Slides with high-quality graphic design and beautiful teal gradients.
- PPTX file for Microsoft Powerpoint
4. Free Health Medical Presentation

Another variation of the previous template with 23 slides in patterned dark blue design. Features a useful set of ready-to-use vector icons.
5. Free Presentational Medical Posters

This free set has two PowerPoint templates for medical/scientific posters. All sections are editable to add your own images and information, depending on the project.
- 2 posters in PPT, Fonts, and images
*redirects to Google Drive
6. Free Business Medical Template

This free resource offers 13 editable slides for a medical presentation. The website requires registration for the free download.
- 13 Slides + editable resources and icons
7. Free Remendy Medical Presentation

Every feature found in these templates is fully editable and easy-to-use. The presentation offers 23 slides and icons for PowerPoint, KeyNote, and Google Slides. When you go to the website, you’ll be required to enter an email address.
8. Free Altra Medical Presentation

A second variation of the previous template. The presentation offers 23 slides and icons for PowerPoint, KeyNote, and Google Slides. When you go to the website, you’ll be required to enter an email address to receive a link for the download.
9. Free Multi-Purpose Medical Presentation

It is a Free Medical Powerpoint Template designed for healthcare, healthcare organizations, dentists, and doctors.
- Personal Use Only
10. Free Modern Design Medical Template

Medical Free PowerPoint Template includes 10 pre-made slides and a complete set of ready-to-use examples. The website requiresregistration for the free download.
- 10 Creative slides
- 16:9 widescreen layout
- Free Fonts and Icons
- Fully and Easily editable content
11. Free Conceptual Medical Presentation

A multi-purpose medical template. It’s ideal when you need to give a financial report to your investors. The website requires entering an email address for a direct free download.
12. Free Fracture Medical Presentation

Here we have a specialized template for fractured bones presentation, however, it’s adaptable for other purposes as well. The website requires entering an email address.
13. Free Chemistry Medical Presentation

A very fresh-looking simplistic template for presentations related to chemicals and pharmacy. The website requires entering an email address for a direct free download.
14. Free Medical Team Presentation Template

This template with lovely chemistry- patterns for a background is a great base for a medical team presentation. The website requires entering an email address for a direct free download.
15. Free Medical Business Template

A pre-made simplistic template with soft tones and 23 editable slides.
16. Free Red Cross Presentation Template

Here we have a conceptual presentational template with a red cross design.
17. Free Corporate Medical Presentation Template

23 slides of a beautifully designed medical presentation with a blue background.
18. Free Corporate Medical PowerPoint Template

Similar to the previous template in terms of sections and slides, this one has a more simplistic background. The PowerPoint presentation features 23 fully editable slides that you can adapt to your project.
19. Free Clinical Case Report Presentation Template

Submitting a clinical report requires rigor and a detailed scheme. These slides, however, are dedicated to the case presentation and feature sections for discussion on the subject, existing literature, and conclusion. The website requires an email address for the free download.
20. Free Hospital PowerPoint Presentation

This pair has similar slides for a multi-purpose medical presentation. The first one offers 23 slides with pale blue background and mostly text-based sections.
21. Free Orvos Medical PowerPoint Template

The next one is also with 23 slides, more contrast, and high-quality images. It’s more simple in terms of design and suits any purpose depending on your presentation.
22. Free Hospital Medical Presentation

A very stylish modern template with duotone colors and 22 slides ready to go and present your concept.
23. Free Medical Students Presentation

This PowerPoint template was made with medical students in mind. It’s free to download medical presentations with a license for personal use only.
*Redirects to GoogleDrive
24. Free Salud Medical Template

Our last two choices come with two similar concepts with 23 slides and image placeholders.
25. Free Sigma Medical Template

Again with 23 editable slides, this template offers a beautiful thematic frame and infographics.
Final Words
Those were the 27 hand-picked free medical presentation templates to aid you in your professional projects. As usual, before using, make sure to read the licensing rules first. Some of the templates are available for personal use only. Others – for personal and commercial use. Either way, you can use these templates the way they are or completely transform them to match your personal style.
While on the topic of free PowerPoint templates, here are other free resource collections you could check out:
- 70+ Free Medical Illustrations For Your Design Projects and Presentations
- 35 Free Google Slides Infographic Templates to Grab Now
- 60 Free Medical Background Resources with Modern Design
The Ultimate Medical Presentation Template

This medical presentation template comes with 77 slides compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides, great for educational and business purposes.
- 48 slides to present you as a medical and business professional , your team, values, business plan, accomplishments, and ideas.
- 23 Infographic slides with editable graphs and charts to present your ideas, research, and compare statistics.
- 6 virus-themed slides for statistics, protection, safety, and symptoms.
- Editable in PowerPoint, Google Slides, Keynote, Adobe CC

Add some character to your visuals
Cartoon Characters, Design Bundles, Illustrations, Backgrounds and more...
Like us on Facebook
Subscribe to our newsletter
Be the first to know what’s new in the world of graphic design and illustrations.
- [email protected]
Browse High Quality Vector Graphics
E.g.: businessman, lion, girl…
Related Articles
30 free marketing presentation templates with modern design, 30 free cute powerpoint templates: collection for a sweet presentation, 46 colorful adobe character animator backgrounds (free and premium), where to find free vector images for commercial use, 800+ free silhouette graphics to download now, 500+ free and paid powerpoint infographic templates:, enjoyed this article.
Don’t forget to share!
- Comments (0)

Al Boicheva
Al is an illustrator at GraphicMama with out-of-the-box thinking and a passion for anything creative. In her free time, you will see her drooling over tattoo art, Manga, and horror movies.

Thousands of vector graphics for your projects.
Hey! You made it all the way to the bottom!
Here are some other articles we think you may like:

Free Vectors
Free world map vector collection: over 55 different designs.
by Iveta Pavlova
50+ Free Social Media Icon Sets For your Designs [Vector-Based]
by Lyudmil Enchev

40 Trendy Free Fonts for Commercial Use in 2021
by Al Boicheva
Looking for Design Bundles or Cartoon Characters?
A source of high-quality vector graphics offering a huge variety of premade character designs, graphic design bundles, Adobe Character Animator puppets, and more.
- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services

- Business Slides
- Guide & How to's
Make an impact with an engaging medical presentation
If you want to explain medical concepts or demonstrate a new medical invention, you’d better use medical presentations in PowerPoint. It allows you to make your slides modern & visually appealing with a few creative design moves. Suppose you need to illustrate a healthcare document or make a presentation on a medical topic. In that case, PowerPoint is good for organizing all points to mention, supporting your speech with images, and attracting people with great animation.
You can find plenty of medical presentation examples on the web to inspire or borrow some elements, e.g., icons, colors, themes, etc. If you lack time and skills, you can always address professional services and order medical or business presentation slides . It helps to devote more time to speech and full sleep.
Today, let us help you find out when to use, how to start, and what to add to create modern-looking healthcare PowerPoint visuals.

When to Use Medical PPT Presentation?
Initially, presentations are used to inform, educate or persuade different external and internal audiences. Medicine includes hard and simple explanations, so you can create a healthcare presentation for both children and scientists.
Using the power of words and correct animation, you can deliver the most complex concepts and explain to pupils how blood cells move. So, medical slide presentations are used for:
- Medical conferences;
- Medical cases;
- Medical training;
- Medical networking;
- Medical investment pitch;
- Medical services presentation;
- Medical TED talk;
- Medical university/college/school lecture;
- Medical invention demonstration.
We bet you can make up more situations where medical presentations fit, and we’ve collected the most common causes. Anytime you talk about healthcare problems or news, you need a medical presentation.
How to Start a Presentation on Healthcare?
Medicine topics refer to the section of hard ones, so PowerPoint presentations must be used wisely and correctly to make speech easier to understand. If you have to explain complex concepts, the presentation can be your life-saver if you approach it in a meaningful way.
Step 1: Rely on visuals
The first step is to look for visuals that can accompany your text. PowerPoint was created for animation, but many people incorrectly use slides for paragraphs of scientific information. Meanwhile, we grasp visual information 60,000 times faster than written one.
So, whenever you present technical information, your audience would want relevant visuals to support their understanding. Do not name types of bone fractures or blood cells, show them!
Step 2: Crop and enlarge your images
The next step is the extension of the first one. We recommend using one picture per slide and enlarging it if it contains tiny elements. For example, you want to show a cataract, so increase the image in size for all people to see clearly. Do not be afraid to sacrifice text for the big high-quality picture.
Step 3: Use charts to visualize numbers
Please, forget about bullet points and endless lists on slides. Pity your audience.
- Decide how many numbers or statistics you have to add as separate slides.
- Do not mix pictures with charts or graphs.
- Make them simple but clear.
- Use contrasting backgrounds and comment on every figure.
See, bullet points are only good in articles to make some space and differentiation in a long text.
Step 4: Make your graphics look more professional
Google for medical presentation video tutorials or address custom presentation services to improve PowerPoint presentation . If you need to present in front of professionals, they will most likely have expectations. Thus, use high-resolution images, position every element accordingly, match sizes of arrows/lines within one slide, and just remove all alien elements that clog the animation.

8 Simple Tips to Improve Your Healthcare PowerPoint Presentation
Even though the following tips are simple and easy to implement, they will have a significant impact on your medical slides.
Think ‘Non-Linear’
If you have to explain some definitions, do not present them in a boring linear way. It can easily disengage the audience from the slide. Instead, create an animated explanation with arrows: make the main word big in the middle of the slide and ‘draw’ around it. Why use only words if you work with PowerPoint?
Use simple animated visuals to explain concepts
For example, you have to explain how molecules move in the electric field. A sheet of hard-to-understand text does not attract the audience at all. To engage people better, draw how charged molecules move forward and back. Besides, add an oral explanation for people to visualize better. Thus, the information sticks to the audience’s brains and keeps them involved till the presentation ends.

This slide does not just give a list of 3D printing examples but shows its real usage, which helps the audience visualize the information.
Label your images right
Images are an integral part of any medical presentation, but some presenters misuse them and create eye hops. It means the number of places the eyes have to land on a slide to gather information. When you create a presentation, THINK ABOUT THE AUDIENCE. Try to imagine how their eyes walk through the slide and make this path as convenient as possible.
For example, when you label throat parts, do not create a 1-5 list next to the picture. It may get people tired to walk from the list back to the image and again to the list. It is better to avoid numbers and label parts with names immediately.

Here is a great example of a visually attractive and informative slide. The author has exactly thought about the people because he helped them perceive the information step by step.
Use tables for comparison
Bullet points are good, but slide space is limited, so you’d better use it wisely. Even if you apply custom animation using bullet points, you still present in a linear way. Accordingly, we advise you to use the table to compare two items with a column that defines the characteristics you oppose. It helps the audience of different levels to follow your thoughts. If people do not understand, they distract faster. So, do not let them do it.
Pay attention to information clarity
Make sure the images you place on the slide match with headlines or other marks. Sometimes, people are afraid of many slides and try to put images and text into one. And they disregard the fact that the audience in the back seats sees nothing.
For example, this slide is good and informative, but the text might not be visible for the last lines.
Use charts to present numbers
For example, you want to list etiological factors for a specific disease. Instead of simply saying percentages, show them! People perceive and remember visual information better, so use charts to show the share of each factor. PowerPoint is created for animations, so always look for ways to avoid many words.
Lead with appropriate visuals
We highly do not recommend using photos of wounds, skin/organ diseases, or other body health problems. It may avert some people because these pictures aren’t indeed attractive. Instead, use drawn pictures, e.g., do not show SSI classification on real skin but use cross-section (like the one used in medicine books).
Avoid Using Photos as Slide Backgrounds
Strangely, many medical presenters still use photos for background for some unknown to us purposes. On the contrary, we suppose it is extremely hard for the audience to differentiate the main image or words from the background clog. Background photos do not bring you much value, but people perceive things better on a pure basis. So, please, stop using this habit. The simpler, the better!
Eye-catching animation has never spoiled anyone’s medical presentation. By adding suitable colors and pictures for a neat look, you demonstrate your expertise and support your speech. You will no more get lost if someone interrupts you. Complex topics are better explained with attractive visuals because all people perceive information better if accompanied by images. Therefore, you should use this preference to fit the audience of any size, age, and gender. Master medical presentations in PowerPoint and enjoy people’s attention!
#ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active::before { background-color: #ededed; } Table of contents
- Presenting techniques
- 50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]
- Present financial information visually in PowerPoint to drive results
- Keynote VS PowerPoint
- Types of presentations
The importance of visual storytelling in presentations (+ effective tips to consider)
- Design Tips
Why presentation of data is important?

8 rules of effective presentation
Introduction to Medical Terminology
Medical terminology is language that is used to describe anatomical structures, processes, conditions, medical procedures, and treatments. At first glance, medical terms may appear intimidating, but once you understand the standard structure of medical words and the definitions of some common word elements, the meaning of thousands of medical terms is easily unlocked.
Most medical terms adhere to a fixed structure of a prefix, a root, and a suffix. These word components are assembled like building blocks to create a vast vocabulary.
The physicians of Greece are considered the founders of rational medicine, and medical terms are primarily derived from Greek and Latin. 1 Over the centuries, the language of medicine has evolved into multiple national medical languages. Today, medical English is the primary language for international communication. It is used in most influential medical journals and has become the language of choice at international conferences. 2
Basic Term Structure
Medical terms are composed of these standard word parts :
- Prefix: When included, the prefix appears at the beginning of a medical term and usually indicates a location, direction, type, quality, or quantity.
- Root: The root gives a term its essential meaning. Nearly all medical terms contain at least one root. When a prefix is absent, the term begins with a root.
- Suffix: The suffix appears at the end of a term and may indicate a specialty, test, procedure, function, disorder, or status. Otherwise, it may simply define whether the word is a noun, verb, or adjective.
- Combining vowel: A combining vowel (usually the letter “o”) may be added between word parts to aid in pronunciation.
Breaking a word down into its component parts should help readers ascertain the meaning of an unfamiliar term. For example, hypothermia has the prefix hypo- (meaning below normal), the root therm (heat or warmth), and the suffix -ia (condition).

A root is the foundational element of any medical term. Roots often indicate a body part or system.
Common word roots:
| Head | |
|---|---|
| brain | |
| ear | , |
| eardrum | , |
| eye | , |
| face | |
| nose | |
| skull | |
| tongue | |
| tooth | , |
| Heart and Circulatory System | |
|---|---|
| aorta | |
| arteries | |
| blood | , |
| blood vessels | |
| heart | |
| veins | , |
| Bones and Muscles | |
|---|---|
| arm | |
| back | |
| bone | |
| foot | , |
| muscle | |
| rib | |
| shoulder | |
| wrist | |
| Digestive System | |
|---|---|
| appendix | |
| colon | |
| esophagus | |
| intestine (usually small) | |
| kidney | , |
| liver | |
| stomach | |
| Other Common Roots | |
|---|---|
| cancer | |
| drug | |
| electric | |
| heat | |
| knowledge | |
| life | |
| pressure | |
| returned sound | |
Compound Words
A medical word may include multiple roots. This frequently occurs when referencing more than one body part or system. For example, cardio-pulmo-nary means pertaining to the heart and lungs; gastro-entero-logy means the study of the stomach and intestines.
Combining Forms
A combining vowel is used when a root is followed by another word part that begins with a consonant. A combining vowel (usually the letter "o") is added after the root (e.g., neur- o -logy) to aid pronunciation. The root and vowel together (e.g., neur-o) are called the combining form. For simplicity, combining vowel options are omitted from the word part tables.
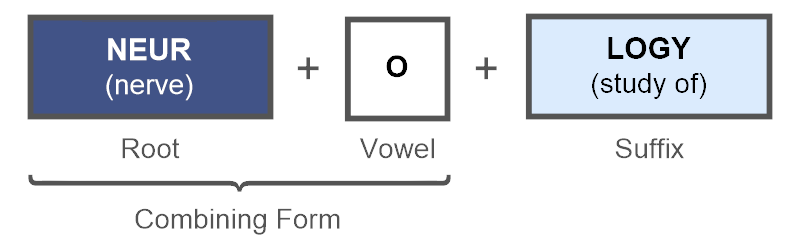
A prefix modifies the meaning of the word root. It may indicate a location, type, quality, body category, or quantity. Prefixes are optional and do not appear in all medical terms.
Common prefixes:
| Size | |
|---|---|
| large | , |
| small | |
| Number | |
|---|---|
| half | |
| half (one side) | |
| one | , |
| two | three | four | | | |
| equal | |
| many | |
| Level | |
|---|---|
| above normal | |
| below normal | |
| normal/good | |
| Time or Speed | |
|---|---|
| before | , , |
| after | |
| back/backward | |
| again | |
| fast | |
| slow | |
| new | |
| time, long time | |
| Location or Relationship | |
|---|---|
| away from | |
| above | |
| around | |
| across | |
| between | |
| out of, outside | , |
| self | |
| through, completely | |
| together | |
| toward | |
| within, inside | |
| Function or Quality | |
|---|---|
| against | , |
| bad | |
| cause | |
| self | |
| without | , |
| abnormal, bad | |
Medical terms always end with a suffix. 3 The suffix usually indicates a specialty, test, procedure, function, condition/disorder, or status. For example, “itis” means inflammation and “ectomy” means removal.
Alternatively, the suffix may simply make the word a noun or adjective. For example, the endings -a, -e, -um, and -us are commonly used to create a singular noun (e.g., crani-um).
Although the suffix appears at the end of the term, it often comes first in the definition. For example, appendicitis means inflammation (-itis) of the appendix. 4 Accordingly, it is sometimes helpful to read unfamiliar medical terms from right to left.
Occasionally, medical terms are composed of only a prefix and a suffix. For example, apnea includes the prefix a- (without) and suffix -pnea (breathing).
Common suffixes (letters in parentheses are not always present):
| Basic Noun and Adjective Suffixes | |
|---|---|
| (noun form) | , , , |
| causing | |
| condition | , , , |
| specialty | , , |
| specialist | , |
| structure | , |
| small, little | |
| study of | |
| pertaining to | , , , , , , , |
| Tests and Procedures | |
|---|---|
| removal of | |
| image/record | |
| recording instrument | |
| cut in | |
| visual examination | |
| opening | |
| Pathology or Function | |
|---|---|
| blood (condition of) | |
| breathing | |
| inflammation | |
| condition or disease | |
| deficiency | |
| disease | |
| excessive flow | |
| mass, tumor | |
Plural Forms
Adding an “s” or “es” to the end of a word is often the straightforward method to make a word plural in English and many modern Romance languages. In medical terminology, however, things are a little more complicated. The plural form of each word is based on the last two letters of the singular suffix.
There are several exceptions. For example, “virus” is a Latin term without a plural form. “Viruses” is the accepted plural form. Elsewhere, the suffix “s” or “es” occasionally prevails in common usage. For example, the plural form of “hematoma” is “hematomas” rather than “hematomata.”
Common singular endings and corresponding plural endings:
| Plural Forms | |
|---|---|
| Singular | |
| a | |
| en | |
| ex, ix, yx | |
| is | |
| ma | |
| (a/i/y)nx | |
| um | |
| us | |
Additional resources:
- OpenMD Medical Dictionary and word parts glossary , which provides definitions for 750 medical roots, prefixes, and suffixes.
- Understanding Medical Words by MedlinePlus provides a concise introduction to medical terminology and several quizzes.
- TheFreeDictionary's Medical Dictionary by Farlex is a comprehensive dictionary of medical terms (including word parts) from American Heritage, Collins Encyclopedia, and other major publishers.
Related Guides:
- The History of Medical Terminology Review of the Greek and Latin origins of modern medical terminology.
- Banay GL. An Introduction to Medical Terminology I. Greek and Latin Derivations. Bulletin of the Medical Library Association. 1948;36(1):1–27.
- Wulff HR. The Language of Medicine. J R Soc Med. 2004;97(4):187–8.
- Ehrlich A, Schroeder CL. Introduction to Medical Terminology. 3rd ed. Delmar, Cengage Learning; 2014:5.
- Nath, JL, Lindsley KP. A Short Course in Medical Terminology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2018:38.
- Cohen BJ. Medical Terminology: An Illustrated Guide. 6th ed. Baltimore: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. Tables 2–4.
Published: January 9, 2020
Last updated: November 1, 2022
Medical Presentation Templates
Elevate medical communication with Venngage's presentation templates, designed to effectively convey intricate concepts through informative content and clear visuals. Craft impactful medical presentations that cater to healthcare professionals, researchers, and educators, ensuring precise and engaging communication of complex medical information.
Other presentation templates
- Pitch decks
- User persona
- Brand guidelines
- Professional
- Group project
- Valentine's day
- Book report
- Mother's day
- Father's day
- Visual chart
- Architecture
- Social media
- Advertising
Popular template categories
- Infographics
- White papers
- Letterheads
- Newsletters
- Business cards
- Human resources
- Certificates
- Invitations
- Table of contents
- Magazine covers
- Price lists
- Album covers
- Book covers
- See All Templates

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Access this presentation on ESC 365 from ESC Congress 2024 on Drug therapy by Doctor Y. Kang (United States of America,US) on ESC 365. ... Harvard Medical School Teaching Hospital, Boston (United States of America) ... Terms & Conditions. Update my Cookie Settings. Contact us. Follow us ...
The oral presentation is a critically important skill for medical providers in communicating patient care wither other providers. It differs from a patient write-up in that it is shorter and more focused, providing what the listeners need to know rather than providing a comprehensive history that the write-up provides.
a strategy for decoding medical terminology and unfamiliar words in the English language. Word Parts . If all three word parts are present in medical terminology, they will be in the order of prefix root word suffix. Look at the following example to understand the function of each word part: anti-bacteri-al
Slide 6. Here's an example of how each is used. The first word is cardiology. The word root is cardi (pronounced CARD-ee) which means heart. So our term cardiology means study of the heart. The second word example is tachycardia (pronounced tacky-CARD-ee-uh). The prefix is tachy (pronounced tacky), which means fast.
This definition of medical jargon appears to be a dictionary definition. Please rewrite it to present the subject from an encyclopedic point of view. (May 2023) In medicine, a presentation is the appearance in a patient of illness or disease—or signs or symptoms thereof—before a medical professional.
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions is an Open Educational Resource (OER) that focuses on breaking down, pronouncing, and learning the meaning of medical terms within the context of anatomy and physiology. ... There is a clear presentation of images and charts which enhances the learning experience. Each chapter integrates ...
In short: getting the presentation design right is just as important as delivering it well. Here's how to create an effective and engaging medical presentation — without wasting hours on PowerPoint! Simple is better. Be wise with your color choice. Don't overcrowd slides with text.
0 shares Share0 Share +10 Tweet0 Pin0 Share0 About Medical PresentationsMedical presentations are fundamentally different from other presentation types. In fact, they are one of the toughest type of presentations to design.Medical slides have research facts, data charts, diagrams and illustrations that demand a totally different approach to design. You need a slide creation method […]
Medical Dictionary. Search medical terms and abbreviations with the most up-to-date and comprehensive medical dictionary from the reference experts at Merriam-Webster. Master today's medical vocabulary. Become an informed health-care consumer!
Here are some tips for presenting the top three types of medical presentations: lectures, research presentations, and case reports. By. Derek Murray. Building presentations. With your long to-do list as a medical professional, giving presentations is probably not a high priority. Yet, medical presentations are inevitable.
Medical presentations are a helpful tool for medical professionals, research clinics, and organizations to help inform and educate their communities on a wide variety of urgent topics. ... Unless you're presenting to third year residents, your audience probably won't be able to digest complicated medical terminology. It's important to ...
The ability to design and deliver an effective presentation is an important skill for all learners to develop. The Undergraduate Medical Education Section of the Group on Educational Affairs developed this toolkit as a resource for medical students and health professions trainees as you learn to create and give effective presentations in the classroom, in the clinical setting, and at academic ...
Learn about effective presentations, their qualities, benefits, and the key multimedia principles that can help medical educators develop effective multimedia for their classrooms. ... and long-term memory to create meaningful learning. ... The application of the Mayer multimedia learning theory to medical PowerPoint slide show presentations. J ...
Download the DNA Chain Backgrounds Medical Theme presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Healthcare goes beyond curing patients and combating illnesses. Raising awareness about diseases, informing people about prevention methods, discussing some good practices, or even talking about a balanced diet—there are many topics related to ...
Medical terminology is the language of healthcare. It's the means for healthcare professionals to confer on the intricacies of the human body, both in states of health and states of injury or disease. As such, medical terminology comprises the lexicon of labels for all known anatomical features, physiological processes, and medical ...
Basic Medical Terminology Powerpoint - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The document provides an overview of medical terminology and its components. It explains that medical terms often originate from Greek or Latin and are constructed from prefixes, roots, and suffixes.
1. Free Healthcare Infographic Presentation. This multi-purpose template for PowerPoint and Keynote comes with more than 100 slides and dark and light versions. However, there is a free sample version that features 6 high-quality slides available to download and edit. Free Version: 6 slides.
To make a medical presentation, first consider two things: 1) what medical information or message you want your audience to receive and 2) what you want them to do. Next, choose the best medical template for the job. Finally, prepare for your presentation by practicing your talking points.
Step 2: Crop and enlarge your images. The next step is the extension of the first one. We recommend using one picture per slide and enlarging it if it contains tiny elements. For example, you want to show a cataract, so increase the image in size for all people to see clearly.
Introduction to Medical Terminology. Medical terminology is language that is used to describe anatomical structures, processes, conditions, medical procedures, and treatments. At first glance, medical terms may appear intimidating, but once you understand the standard structure of medical words and the definitions of some common word elements ...
Enhance medical communication with Venngage's specialized presentation templates, merging informative content with clear visuals seamlessly. Create impactful medical presentations that effectively convey complex concepts, catering to healthcare professionals, researchers, and educators seeking to communicate with precision and impact.