- Introduction to Problem Statements, Purpose Statements, and Research Questions

Worksheets and Guides
Chapter 1 playlist.
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
Need help ask us.

Chapter 1 introduces the research problem and the evidence supporting the existence of the problem. It outlines an initial review of the literature on the study topic and articulates the purpose of the study. The definitions of any technical terms necessary for the reader to understand are essential. Chapter 1 also presents the research questions and theoretical foundation (Ph.D.) or conceptual framework (Applied Doctorate) and provides an overview of the research methods (qualitative or quantitative) being used in the study.
- Research Feasibility Checklist Use this checklist to make sure your study will be feasible, reasonable, justifiable, and necessary.
- Alignment Worksheet Use this worksheet to make sure your problem statement, purpose, and research questions are aligned. Alignment indicates the degree to which the purpose of the study follows logically from the problem statement; and the degree to which the research questions help address the study’s purpose. Alignment is important because it helps ensure that the research study is well-designed and based on logical arguments.
- SOBE Research Design and Chapter 1 Checklist If you are in the School of Business and Economics (SOBE), use this checklist one week before the Communication and Research Design Checkpoint. Work with your Chair to determine if you need to complete this.
Was this resource helpful?
- Next: Narrowing Your Topic >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006886

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

How To Write A Dissertation Introduction
A Simple Explainer With Examples + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing An Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
44 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
You explain what moment in life caused you to have a peaked interest in the thesis topic. Personal experiences? Or something that had an impact on your life, or others. Something would have caused your drive of topic. Dig deep inside, the answer is within you!
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
This is great!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How to write dissertation chapter 1, published by steve tippins on july 19, 2022 july 19, 2022.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 04:48 am
Congratulations, you’ve made it to the dissertation stage! You should be incredibly happy. However, beginning to write chapter one might be a little daunting. We’re going to cover a broad overview on chapter one here in this article so that you know the territory before you set out.
Purpose of Chapter One
The purpose of chapter one is to introduce the reader to what’s coming. Chapter one usually runs around 15 pages, and it gives the reader the highlights of what’s coming. Typically, you start with an introduction.
#1. Introduction
The introduction includes a few citations and says, “Hey, we’re going to talk about ___.” Fill in the blank with your topic (educational policy, or management handling of turnover, etc.). Also, don’t say “hey” like we did (that wouldn’t be very good academic writing).

#2. Background of the Problem
The next section is the background of the problem. I like to think of this as a very short literature review , showing the reader that there’s a foundation of scholarly research about this topic.
#3. Theoretical/Conceptual Framework
Follow that up by the theoretical or conceptual framework . Think of this as the seminal research upon which your study is based. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, for example, is an incredibly popular conceptual framework. Erickson’s theories are popular in education, and systems theory is being used in many disciplines now.
#4. Problem Statement
Next comes what many consider to be the guts or the foundation of the dissertation: your problem statement . Your problem statement is typically one line. Now it might be surrounded by a paragraph or two, but the actual problem statement is one sentence. It should begin, “The problem to be studied is…” and finish with something that directly aligns with your purpose and research questions. For example, “…we don’t know the impact of extra after school education on student grades in math,” or “…we are not aware of the perceptions of employees regarding management, changing retirement plans.”
Over 50% of doctoral candidates don’t finish their dissertations.
#5. Purpose Statement
Next comes your purpose statement . The purpose is directly related to the problem. If the problem is that the impact of management decisions on employee turnover is unknown, then our purpose would be to determine the impact of management decisions on employee turnover.
#6. Research Questions

Follow this by the research questions. Your research questions should be highly aligned with your problem and your purpose. For example, your research question could be: “what is the relationship between management decisions and employee turnover?” Or for another topic, “what are the perceptions of parents regarding teacher pay raises?”
Quick aside: You’re going to say things over and over and over again in your dissertation. Say them the exact same way. You get in trouble when you try to get interesting and use different terms, because doing so actually introduces new meanings. Be okay with sounding boring.
#7. Methodology
Next is a brief Methodology section. Am I going to use a quantitative approach? Am I going to use a qualitative approach? What sources am I going to use? Is this going to be secondary data? Am I going to interview parents? Quickly tell the reader that you’re going to have a whole chapter (chapter three) to really go further on this.
#8. Definition of Key Terms
Many chapter ones include a definition of key terms. If I’m talking about phenomenology, I’d better tell the reader what phenomenology is. If I’m talking about special ed teachers, I’m going to say what a special ed teacher is.
#9. Validity
You also may have a section in chapter one on validity. This is going to be somewhere in your dissertation, and it’s going to assure the reader that you’re following all the ethical steps and that results can be transferable.
#10. Conclusion and Segway to Chapter Two
Finally, you’re going to have a conclusion wrapping everything up, summarizing for the reader what they heard, and a segue into chapter two.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…

winning dissertation ideas & samples
- Dissertation Structure & Layout Explained + Examples
How do you write a dissertation chapter structure? Which chapter comes first and which one comes last? What do you write in your dissertation chapters and how do you write them? In this article, you will be getting the answers to all of these questions so keep reading.
Dissertation Chapters Outline
- Chapter One: Introduction
The dissertation chapter 1 outline basically comprises a hook, a background, the research aims/questions and the topic. In your dissertation chapter 1, the first thing you should write is the hook. The hook is what will determine whether the reader will be interested in further reading or get bored or confused with your dissertation. So, try to make your hook as interesting, controversial, or bold as possible.
After your hook, the next thing to do is write the background for your topic. This will let the reader relate to your topic as they can now understand what events led to it.
Next, state your research aims or questions. It is always best to break these into a list of numbered items.
Finally, introduce your topic and the other chapters. You may also choose to introduce your topic in the middle of the introduction or at the end of your dissertation chapter 1 example.
Note: Your reader must be able to fully understand the intent of your dissertation just by reading your introduction. What many students do not know is that the introduction, the methodology and the analysis chapters get the most points. So, you have to write them well.
- Chapter Two: Review of Literature
In this chapter, you will discuss your sources and show how their information is relevant to your topic. The dissertation chapter 2 outline consists of showing the relevance of other literature to your research work, why you chose them, how your dissertation differs from them, and your theoretical framework.
In your dissertation chapter 2, you should also critique this literature and point out the research gaps in them.
Now it is important to mention that you should only cite academic materials in your literature review and your entire dissertation. Citing sources from random blogs or websites may cost you some marks. Also, you do not have to limit your sources to written texts, you can use videos but do not forget to cite according to your school’s reference system.
- Chapter Three: Methodology
After writing your chapter two, the next chapter to write is your methodology chapter in your dissertation chapters structure. Here, you will explain your research design, the tools you use, and why you chose them. You will also mention if you encountered any challenges in the course of your research and what you did about them. Finally, you will write your ethical considerations. The ethical considerations usually entail proof that you did not force participants (if any) without their consent to fill questionnaires or partake in interviews. Also, you will mention if you employed the help of other researchers during your research.
Here, in your methodology chapter, you may need to use graphs, charts, tables, or any relevant image to give a visual representation of what you are explaining. Lastly, you will also tell if there is any new data or information you added to your research (that was not in your research proposal) and why you added them. Similarly, if you removed any data or information, you should state so in this chapter.
Now for some students, your methodology chapter may be as few as 1000 words while for some others, it may be as much as 3000 words. This depends on how much you have to write.
- Chapter Four: Analysis
In this chapter, you will present the data you have gotten during your research. You will carefully analyze each one of them from relevant to irrelevant. You will also point out any flaws or perfection in the data you have written. Your analysis chapter has to be well-written, detailed, and easy to understand as it is this chapter that most markers usually award the most points.
It is also in this chapter that you may use the most word count. You may also use the most word count in your results and discussion chapter. However, this is not always the case.
- Chapter Five: Results and Discussion
In this chapter, you present the results of your analysis and you discuss them. For some students, the results and discussion chapter may be merged with the analysis chapter to become one. In this chapter, you will discuss in detail the results you got from analyzing all the data you discovered. You will also point out research gaps, flaws, or perfection in your results. Make sure your interpretation of your analysis is broken down in a manner that your reader can understand.
- Chapter Six: Conclusion
Lastly, write the conclusion of your dissertation. Your conclusion is almost like writing your introduction. However, you will show what you have done rather than what you will do. That means you may use more past tense. Here, you will start from the beginning of what your dissertation aimed to do. Next, you will summarize the literature review, your methodology, and your analysis chapters. You will also make recommendations to future researchers that may use your research work for reference.
Writing a dissertation chapter outline does not have to be confusing or terrifying to you. Simply follow the steps and instructions in this article and you will find it easier to write.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on 8 June 2022 by Tegan George .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organisational structure of your thesis or dissertation . This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, frequently asked questions about outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- ‘Elevator pitch’ of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope, population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilising some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the ‘IS-AV’ (inanimate subject with an active verb) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The I construction
Another option is to use the ‘I’ construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and ‘I’ construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as ‘discuss’, ‘present’, ‘prove’, or ‘show’. Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
| Address | Describe | Imply | Refute |
| Argue | Determine | Indicate | Report |
| Claim | Emphasise | Mention | Reveal |
| Clarify | Examine | Point out | Speculate |
| Compare | Explain | Posit | Summarise |
| Concern | Formulate | Present | Target |
| Counter | Focus on | Propose | Treat |
| Define | Give | Provide insight into | Underpin |
| Demonstrate | Highlight | Recommend | Use |
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, June 08). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/outline-thesis-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
Dissertation Outline Writing Guide
Updated 26 Jul 2024
Since a dissertation represents one of the most challenging and time-consuming tasks, the dissertation outline becomes an integral element that helps identify structure and strategic research goals. The task also includes writing dissertation thesis, which is an obligatory stage in every student´s postgraduate studies. Before one starts with creation of scientific masterpiece, it is necessary to learn the difference between dissertation and thesis and develop an accurate plan for making inquiry clear and well-structured. In order to help you with essential steps that should be taken, we created dissertation proposal outline guide, including essay outline templates online and general rules.
An outline should represent a guide specifying what tasks must be fulfilled to achieve academic goals. It aims to determine what ideas and concepts are obligatory for addition to one's paper. In the sections below, you will find brief explanation of what is expected in excellent dissertation paper outline and how to organize it correctly. EduBirdie has " write my dissertation for me " services, your work will be the perfect one!
What is an Outline: Definition and Purpose
The dissertation structure aims to keep students focused on the proposed topic, so no time is wasted, and no extra ideas are introduced in progress. Planning thesis academically enables collecting required data and getting it organized scientifically in more logical and structured way. The paper draft serves as a guideline that helps to achieve goals and connect arguments to the main thesis. An outline helps to avoid confusion and repetition as lengthy paper is brought together.
Additionally, when a dissertation proposal outline is submitted to a college or university professor, most young scientists have to work with a sketch that reveals the topic and general ideas. Once composed correctly, it serves as a proposal for the overall assignment.
Different university professors in the United States may follow different dissertation structure outline, yet in most cases, the common structure consists of five sections, like in a general scientific paper: introduction, detailed literature review, methodology, analysis of presented data, and conclusion paragraph. Before we proceed with dissertation chapters, let us review several writing tips and things to check before starting! Are you stuck with your dissertation? Hire our dissertation writing service , and be done with stress headaches.
Useful Outline Writing Tips
- Start with a relevant topic and field of study you know and can support well with a sufficient number of scientific sources.
- Before choosing the main thesis, look through academic journals, manuals, and reviews on the subject in advance.
- Discuss every concern with the academic advisor, focusing on approach, methodology, and argumentative position. Show outline or sources for approval.
- Reading through scientific works on the topic, take notes for outline.
- Compose each section of the thesis offered, according to ideas presented without the introduction of extra bits.
- Working on dissertation proposal, with appendix and notes.
- Present all available information to the academic advisor so all unnecessary information is left out.
- The general rule is to avoid new ideas in conclusion and channel attention towards future objectives and calls to additional research.
- Compose a list of objectives beforehand as a personal checklist to "proofread the dissertation" this way.
- Proofread and polish your paper or ask professionals to provide thesis help .

Need more writing assistance?
Connect with our top writers and receive a dissertation sample crafted to your needs.
Sections of Dissertation in a Nutshell
It should be noted that there is no absolutely correct dissertation outline template that would fit every subject. While Social Sciences, for example, may include 4-5 parts, an assigned committee may introduce changes, so it is always better to check twice in advance. In our guide, we will focus on 5 chapter method with outline variations specified. Anyone can face struggles with writing such complex types of academic papers so you can hire an article review writer for confidential help.
- Introduction
As a rule, it encloses a general introduction and background description of the problem addressed. Next comes the problem statement that serves as a general thesis idea. The following part should present the study purpose and research questions that are significant for this specific work. The next section should focus on the significance of the chosen study, which usually includes topic relevance. Do not forget to provide clear definitions of terms used. It is also where personal assumptions and discovered limitations are mentioned. For conclusion of primary section, ensure to provide additional study details, if necessary.
- Literature Review
As the name suggests, dissertation chapter 2 describes, lists, investigates, and studies all implemented literature in depth. One has to provide a conceptual and/or theoretical framework to justify the use of provided materials. Depending on the topic variables, one should enclose a detailed review of the sources involved.
Note: Third chapter may differ, depending on topic and methods chosen or required!
- Qualitative Methodology
This is one of the trickiest sections because it has to show the research design, scientific relevance questions, provide a setting for analysis, and describe participants or objects of study. Next, a data collection paragraph is presented, which is followed by extensive analysis. This is where one must use citations when and if necessary. The final part should contain a brief overview of method justification.
- Quantitative Research Methods
In this case, it follows research design with problem description, problem questions, and hypotheses made. What makes it different are provided samples and population statistics related to methodology. Moreover, it has to include instrumentation used for accurate collection of data. It ends with their analysis.
- Combined Methodology Analysis
Choosing mixed approach, start with brief overview and strategy pattern. Continue by focusing on hypotheses and goals. Provide setting and sample(s) next. After collecting the data, it has to relate to the chosen work methods. Analysis has to include both opinion and references to scientific journals. With such an option, this section of the dissertation has to make the chosen methods obvious to the audience.
- Research Outcomes
The fourth chapter aims to explain the findings. It is recommended to organize them either by the research questions specified or the hypotheses given. Remember that the introduction must describe what has been found, while the conclusion is a summary that explains whether the research has been successful or not.
- Conclusion: Discussion and Future Research Suggestions
The final part has to provide a more detailed findings summary. It differs from previous chapter in depth of personal analysis involved. After one lists achieved goals, it is necessary to provide conclusion that includes analytical thought. To make things easier, continue with discussion of topic, describing paper's research, or contact us to write my discussion post for you. If appropriate and available, mention suggestions for additional investigation or what is necessary to add. Wrapping one's work together, remember to check twice not to forget anything. The last part of the dissertation plan is a good place to include opinions and justify the style used.
Dissertation Outline Template for Students
Here is a basic outline of dissertation sections that you can adjust to your paper topic and subject.
Chapter 1: Introduction
- Issue & Its Background
- Issue Statement
- Research Purpose & Questions
- Significance
- Glossary of Terms (optional)
- Limitations & Assumptions
- Concluding paragraph
Chapter 2: Literature Review
- Description of literature search
- Review of Literature
Chapter 3: Methodology (Qualitative/Quantitative/Mixed)
- Research Design
- Research Hypotheses & Question
- Setting/Sample & Population
- Participants/Instrumentation
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
- Concluding section
Chapter 4: Findings
Chapter 5: Discussion and Suggestions for Further Research
- Findings Summary
- Conclusions
- Suggestions for Further Investigation
- Final Conclusion Part
Read also: Research proposal writing help from real experts!
Custom Dissertation Helper Online
Dissertation belongs to one of most demanding academic tasks, which makes most American students seek for additional help. Even coming up with good plan may be insufficient. What we offer is expert writing help with custom guidance at every stage.
Our clients visit and come back again as it’s possible to choose writing experts based on credentials, study filed, and list of essays completed. Direct contact with assigned writer, allows controlling each little detail, add suggestions, and make paper truly custom. Our 100% plagiarism free papers include proofreading and adherence to professional terms usage. Hesitate no more and message us today! Buy dissertation online at EduBirdie, high quality guaranteed!
Try EduBirdie
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by Jamie Wallace
Jamie Wallace, editor and freelance writer, specializes in Philosophy, Literature, and Art. His interdisciplinary background and passion for critical analysis enable him to assist students in crafting compelling and well-researched papers.
Related Blog Posts
Dissertation defense: effective strategies for academic success.
One of the pivotal moments in any graduating student's educational path is defending a dissertation. This comprehensive process requires a deep und...
Business Dissertation Topics: 140+ Ideas for Your Research
Selecting the right topic for your business dissertation is a critical step in your academic journey. It not only shapes the direction of your rese...
List of 130+ Dissertation Topics in Education for in-depth Research
As you reach the final stage of your academic journey in education, you'll be required to submit a dissertation. The journey of choosing dissertati...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most

PhD Dissertation Outline: Creating a Roadmap to Success

A good PhD dissertation outline is as important to your dissertation as a map is to get you to your destination. Imagine for instance you’re trying to drive to a specific place to attend a party you’ve been looking forward to. You know the address, but you don’t have a map or a driving app. You get there eventually, but it takes a lot longer that it should have and stresses you so much that you’re in a bad mood when you get there. The party ends up being a bust.
This is similar to trying to write an academic paper, especially a PhD dissertation, without using an outline.
Why you need a PhD dissertation outline
When you do your PhD, outlines become the driving app for your academic paper, giving you direction so you know what’s in front of you. This is especially important for a PhD dissertation because of its physical length and the amount of time you will need to live with it. Successful PhD dissertation writing requires a laser focus, and an outline makes a great navigator.
There are many advantages of creating a PhD dissertation outline 1,2 :
- Organize your project – Using an PhD dissertation outline will help you organize your thoughts and your work. If you have an idea or find a bit of information to include in a different section, simply write a note in the appropriate place to remind yourself.
- Stay on task – Like the driving app, a PhD dissertation structure keeps you on the proper road and minimizes distractions. When writing without keeping in mind your PhD dissertation structure, it’s easy to find yourself in the weeds.
- Increase productivity – A PhD dissertation outline keeps you aware of what you have to do, allows you to set goals, and be more productive.
- Save time – This is a major advantage in PhD dissertation writing. The faster you can successfully complete your dissertation process, the more money you’ll save, and the sooner you can get on with the rest of your life.
- Reduce anxiety – The effective use of a good PhD dissertation outline will give you control over this massive project. You’ll be more confident that you can successfully complete your PhD dissertation.
How to write a PhD dissertation outline
So, now that you’re convinced that you need a PhD dissertation outline, where do you start? A few general steps will get you on the right road 3 :
- Select an appropriate topic: This one might seem obvious, but it is often a very difficult decision to make. The topic will guide the approach and research methodology. Although the research question will probably be tweaked along the way, not choosing a relevant topic at the start will result in chaos later on.
- Review other dissertations on your topic: This will give you an idea about what your PhD dissertation structure will look like.
- Draft a research problem: The research problem is the core of your dissertation and will guide your methodology and thus strongly influence your PhD dissertation structure.
- Get input from your advisor/supervisor: Seek advice from your supervisor on some PhD thesis outline examples and take advantage of any assistance they provide to help you choose wisely. This will help keep you on the right road
PhD dissertation structure
Doctoral dissertations typically have five standard chapters, although your university might have a specific required structure. Here is a brief description of the typical five-chapter PhD dissertation format 3 .
Chapter 1: Introduction – This section provides an overview of the dissertation including its topic, purpose, and relevance. Typically, the general subject area is discussed and narrowed down to the research topic. Then, the research questions are posed, and the methodology is presented. Chapter 2: Literature Review – A comprehensive survey and synthesis of existing studies on the research topic, the literature review demonstrates the research gap and sets the context for the research question. Depending on the topic, theory may also be explored. Existing methodologies used to address this topic are also discussed. Chapter 3: Methodology – In this section, the methodology and materials used to collect and analyze the research data are presented in enough detail to demonstrate the validity of the method and allow the research to be duplicated by others. Chapter 4: Results – The research findings are reported in this section and presented in relation to the research question. Relevant visuals such as tables and figures are typically included here to communicate the findings effectively. C hapter 5: Discussion – In a five-chapter format, this is the final chapter in a PhD dissertation format. In this chapter, the findings are discussed and interpreted in light of the research question. Bits from all the chapters are synthesized to completely address the research question.
An additional chapter is sometimes added that includes conclusions, recommendations, and suggestions for future research.
Tips for creating your PhD dissertation outline 3,4
Finally, here are some quick and useful tips for your PhD thesis outline journey.
- Use the structure to complete the outline – Carefully think about each chapter and write down questions and information you will need.
- Create your outline early – Keep it up to date through your early research and advisor meetings.
- Be flexible – Changes will need to be made to your outline as you progress.
- Be detailed – You never know when a small piece of information you jotted down in your outline will save you time and anxiety.
- Keep in close contact with your PhD dissertation advisor/supervisor – Make sure to share your outline. You may just save yourself a lot of time and misery if major changes need to be made.
- Stay calm – Changes will come from different committee members. Remember, they are just trying to strengthen your work.
- Statistics Solutions. The benefit of outlining. https://www.statisticssolutions.com/the-benefits-of-outlining/ [Accessed 14 July 2022].
- PapersOwl. How To Create An Outline For A Dissertation? https://papersowl.com/blog/outline-for-dissertation [Accessed 14 July 2022].
- Research.com. What Is A University Dissertation: Structure, Challenges & Writing Tips. https://research.com/research/what-is-a-university-dissertation [Accessed 14 July 2022].
- Docformats.com. Dissertation Outline Templates. https://www.docformats.com/dissertation-outline-templates/ [Accessed 14 July 2022].
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write a Research Paper Outline: Simple Steps for Researchers
- Good Publication Practices: 6 Essential Steps for Publication Success
- How to Choose and Use Keywords in Research Papers
- Supplementary Materials in Research: 5 Tips for Authors
Paperpal Partners with the American Accounting Association for a Smooth Author Submission Journey
How to write a research paper summary, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., 9 steps to publish a research paper, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for..., how to make your thesis supervision work for..., how to write a conclusion for research papers..., ethical research practices for research with human subjects, 5 reasons for rejection after peer review.
PRTH 987 Dissertation Writing in Practical Theology I
- Course Description
For information regarding prerequisites for this course, please refer to the Academic Course Catalog .
Course Guide
View this course’s outcomes, policies, schedule, and more.*
Requires a student login to access.
*The information contained in our Course Guides is provided as a sample. Specific course curriculum and requirements for each course are provided by individual instructors each semester. Students should not use Course Guides to find and complete assignments, class prerequisites, or order books.
PRTH 987 is the transitional course that assesses competency from PhD in Practical Theology course work and prepares the PhD candidate for dissertation writing. This is accomplished through the successful completion of a comprehensive field exam, prospectus development and approval, and pairing the candidate with an appropriate dissertation supervisor. All these tasks are necessary before dissertation writing can formally commence.
Course Assignment
Textbooks readings and lecture presentations.
No details available.
Course Requirements Checklist
After reading the Course Syllabus and Student Expectations , the student will complete the related checklist found in the Course Overview.
Quiz: Preprospectus Proposal Consultation
The student will submit to the instructor teaching PRTH 987 a “Preprospectus Proposal” developed in the Tier II courses for the instructor’s evaluation and feedback, especially as it relates to the three overriding principles of dissertations in the PhD in Practical Theology program; namely, that they must be appropriately biblical, theological, and practical. The student will then meet with the instructor to discuss the details of the proposal before the first draft of the prospectus is composed. This initial consultation will provide opportunity for redirection and refinement as appropriate, along with advice on how the particular topic might best be developed into a library-based, biblically, and practically oriented PhD dissertation. The student will complete a quiz verifying that they have completed the requirement. (CLO: A, B).
Comprehensive Exam 4: Journal Article Proposal Assignment
The fourth and final comprehensive exam requires the composition of an article related to the student’s intended dissertation topic. The article functions as a “field essay” and (1) establishes that the student has “read themselves into the field” sufficient to demonstrate mastery of the issues and literature appropriate to the PhD level of research, and (2) establishes that the student has a viable proposed research topic in the field. In preparation for the exam, the student must write a brief proposal (2-page maximum) to be submitted to the professor for approval. (CLO: A).
Comprehensive Exam 4: Journal Article Assignment
Once the Comprehensive Exam 4: Journal Article Proposal Assignment has been approved by the instructor of PRTH 987, the student must prepare and submit a publishable article on an approved topic relevant to the student’s dissertation that explores a gap in the literature. This exam must demonstrate that the student has a mastery of the field, a grasp of the literature, and an ability to integrate information and themes developed in their PhD in Practical Theology coursework. (CLO: A).
Dissertation Prospectus: First Draft Assignment
The PhD in Practical Theology prospectus will be submitted in two stages: first draft and final draft. In the first draft submission, the student will submit a prospectus containing 4 key components: (1) a dissertation abstract; (2) a description of the dissertation’s research methodology and design of the dissertation’s argument; (3) a chapter-by-chapter outline; (4) a working bibliography. (CLO: B, C).
Dissertation Prospectus: Final Draft Assignment
The final draft of the dissertation prospectus will contain the same 4 components as the Dissertation Prospectus First Draft Assignment and will gather up, address, and remediate any issues raised by the instructor. (CLO: B, C).
Quiz: Dissertation Supervisor Pairing Assignment
The student will complete the Dissertation Supervisor Pairing Quiz to verify that they are ready to be paired with a dissertation supervisor. (CLO: G).
Argument Analysis and Research Methodology Assignment
Considering the elements of a good argument in Turabian’s A Manual for Writers, Chapter 5, “Planning Your Argument,” the student will assess their dissertation’s proposed argument relative to (1) its central claim; (2) warrants on which the claim relies; (3) evidence supporting the claim the student intends to present in the dissertation; and (4) the student’s response to potential objections to the argument. Then, the student will describe their research methodology relative to 4 key concerns: (1) it employs library-based (rather than human subject) research; (2) it employs an evidence-based, logically-defensible research heurism; (3) it is biblical and theological with engagement with primary sources as appropriate; and (4) it is practical. The paper must be double-spaced and between 7-10 pages in length, exclusive of title page, contents page, and bibliography, and follow current Turabian format guidelines, utilizing footnote citations. The paper must consist of two distinct sections: argument analysis and revised research methodology. (CLO: D).
Quiz: Primary Source Research
Because this is a PhD in Practical Theology, engagement with the biblical text (primary source) sufficient to undergird both the theological and practical components of the student’s research is both required and expected. The student will complete a quiz verifying that they have engaged in appropriate primary source research related to their dissertation’s topic and focus. (CLO: E, F).
Quiz: Turabian Review
Because Kate Turabian’s A Manual for Writers is the style standard for the student’s dissertation, the student will complete a quiz verifying that they have reviewed the style guide sufficiently to be able to produce a clean dissertation. (CLO: E, F).
Quiz: Dissertation Supervisor Initial Consultation Assignment
Once the student has been notified of dissertation supervisor pairing, the student will reach out to the dissertation supervisor and request an initial consultation. This consultation meeting will typically be 20 to 30 minutes in length and will be conducted virtually through Microsoft Teams or the current video conferencing platform the university is using at the time. (CLO: G).

Have questions about this course or a program?
Speak to one of our admissions specialists.
Inner Navigation
- Assignments
Have questions?

Are you ready to change your future?
Apply FREE This Week*
Request Information
*Some restrictions may occur for this promotion to apply. This promotion also excludes active faculty and staff, military, non-degree-seeking, DGIA, Continuing Education, WSB, and certificate students.
Request Information About a Program
Request info about liberty university online, what program are you interested in, choose a program level.
Choose a program level
Bachelor’s
Master’s
Certificate
Select a Field of Study
Select a field of study
Select a Program
Select a program
Next: Contact Info
Legal first name.
Enter legal first name
Legal Last Name
Enter legal last name
Enter an email address
Enter a phone number
Full Address
Enter an address
Apt., P.O. Box, or can’t find your address? Enter it manually instead .
Select a Country
Street Address
Enter Street Address
Enter State
ZIP/Postal Code
Enter Zip Code
Back to automated address search
Start my application now for FREE
HOW TO WRITE CHAPTER 1 OF A DISSERTATION OR THESIS
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
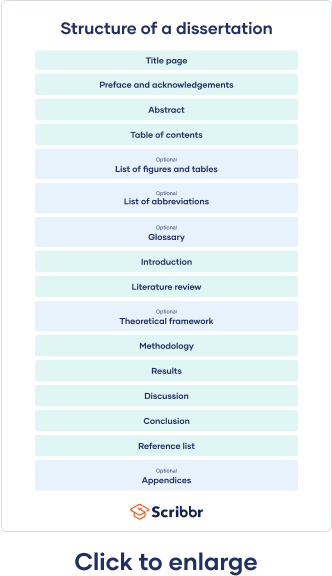
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?

IMAGES
COMMENTS
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION This chapter introduces and provides an overview of the research that is to be undertaken. Parts of Chapter 1 summarize your Chapters 2 and 3, and because of that, Chapter 1 normally should be written after Chapters 2 and 3. Dissertation committee chairs often want students to provide a 5-10 page overview of their proposed
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION. 1. The purpose of this qualitative grounded theory study was to identify what motivates. women to stay in or return to science, technology, engineering, and math professions. (STEM), leading to a motivation model. As illustrated in the literature review, research has. abbreviations. introduce introduce you can use Once ...
Chapter 1 Objectives • Provide a cursory glance at the constitution of an entire dissertation. • Offer a comprehensive outline of all key elements for each section of the dissertation—that is, a precursor of what is to come, with each element being more fully developed and explained further along in the book.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
Listed as 1. . . . 2. . . . 3. . . . . . . n. Definition of Terms . The terms in this section should be terms directly related to the research that will be used by you throughout the study. Procedures . A brief description of the procedures and methodology used to accomplish the study . Significance of the Study . Its importance to practice, to ...
Measure one. Describe your survey in detail, including the number of items in each. section, the response scale, any available validity and reliability information, as well one or two. sample items. Measure two. Provide the same information for each measure you will use in your study, including extant student achievement data from SOLs.
Chapter 1: Introduction. In Chapter 1, a compelling case should be made regarding the problem under investigation, the purpose of the study, and research questions to be investigated. Where applicable, the theoretical or conceptual framework upon which the dissertation is based should also be introduced.
Chapter 1: Introduction. Right, now that the "admin" sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you'll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter - as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
Dissertation OverviewThe traditional dissertation is organized into 5 chapters and includes the following elements and pages:Title page (aka cover page) Signature ...
Chapter 1 Objectives. Provide a cursory glance at the constitution of an entire dissertation. Offer a comprehensive outline of all key elements for each section of the dissertation—that is, a precursor of what is to come, with each element being more fully developed and explained further along in the book.
Dissertation Chapter 1 - 5 Sections Rubric - Version 1 May 1, 2019 APA formatting errors. Verb tense is an important consideration for Chapters 1 through 3. For the proposal, the researcher uses future tense (e.g. "The purpose of this study is to…"), whereas in the dissertation, the chapters are revised to reflect past tense (e.g. "The
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 introduces the research problem and the evidence supporting the existence of the problem. It outlines an initial review of the literature on the study topic and articulates the purpose of the study. The definitions of any technical terms necessary for the reader to understand are essential.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Read and Evaluate Chapter 1 Exemplars. Topic 3: Background and Introduction. In this activity, you will read "exemplar" Chapter 1s from sample Ed.D. dissertations and detail the attributes that cause these to be especially strong or especially weak exemplars. Provided is the outline for Chapter One and a brief overview of the components of ...
Chapter one usually runs around 15 pages, and it gives the reader the highlights of what's coming. Typically, you start with an introduction. #1. Introduction. The introduction includes a few citations and says, "Hey, we're going to talk about ___.". Fill in the blank with your topic (educational policy, or management handling of ...
The dissertation chapter 1 outline basically comprises a hook, a background, the research aims/questions and the topic. In your dissertation chapter 1, the first thing you should write is the hook. The hook is what will determine whether the reader will be interested in further reading or get bored or confused with your dissertation. So, try to ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
Dissertation Outline Template for Students Here is a basic outline of dissertation sections that you can adjust to your paper topic and subject. Chapter 1: Introduction Intro Issue & Its Background Issue Statement Research Purpose & Questions Significance Glossary of Terms (optional) Limitations & Assumptions Concluding paragraph Chapter 2 ...
There are many advantages of creating a PhD dissertation outline 1,2: ... Here is a brief description of the typical five-chapter PhD dissertation format 3. Chapter 1: Introduction - This section provides an overview of the dissertation including its topic, purpose, and relevance. Typically, the general subject area is discussed and narrowed ...
Outline Guide for Dissertation Quantitative Study Qualitative Study Chapter 1: Introduction • Phenomenon of interest • Problem statement • Purpose of the study • Significance of the study including connection to caring science • Research questions/hypotheses where appropriate • Theoretical or conceptual framework
Considering the elements of a good argument in Turabian's A Manual for Writers, Chapter 5, "Planning Your Argument," the student will assess their dissertation's proposed argument relative ...
Conclusion. 1. Understand the elements and objectives of chapter 1 In a dissertation or thesis, the introduction always appears as chapter 1 right after the table of contents. To write an effective chapter 1, you first need to grasp the key elements that build up the introductory chapter and the main purposes of an introduction.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...